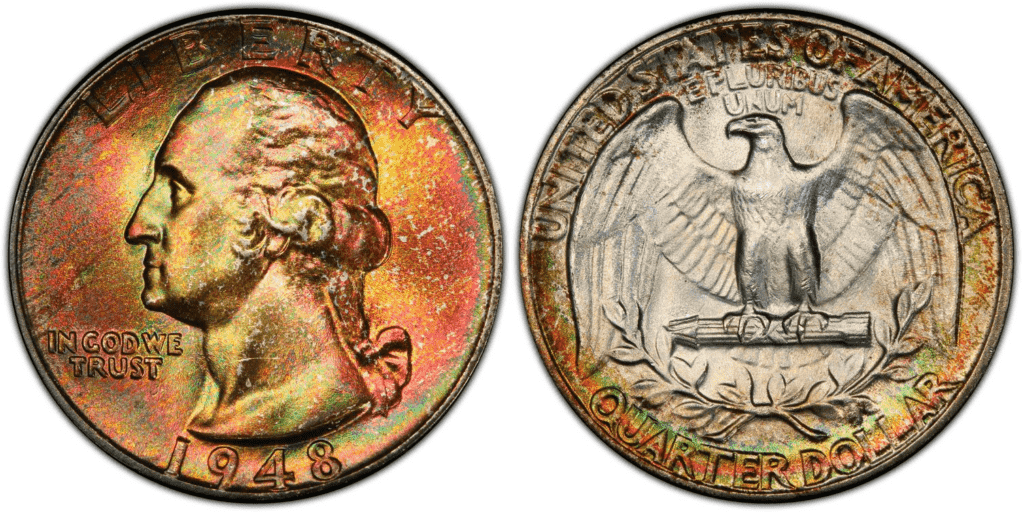What Is the 1948 Washington Quarter Made Of?
The 1948 Washington quarter is already more than 70 years old. This means that this coin is valuable in the eyes of many collectors. Thus, if you have one or are interested in getting one, this article will help you gain more insights.
The 1948 quarter coin is made of 90% silver and 10% copper. Its fineness is 0.9, and its actual silver weight (ASW) is 0.1808oz. The 1948 25-cent has a reeded edge. With a weight of 6.30 grams, it is slightly heavier than the quarter coins today. Its diameter is 24.3 millimeters, and it has a 180-degree orientation.
A lot has changed since the Washington quarter was first struck in 1932. During that time, it has a higher silver content. However, the US Mint changed its composition to copper and nickel in 1965. It is a move to encourage the public to use the coin instead of hoarding it. Not only that, but silver is getting more and more expensive, and thus, it needs to be transitioned to base metals.
The Washington quarter replaced the Standing Liberty quarter. However, did you know the original plan was to put Washington on the half-dollar and replace the Walking Liberty design? Not only that, but the plan was also to have Washington on a coin for just a year. Nevertheless, all plans were changed; thus, we now have the Washington quarter.
In regards to the design, it was the sculptor John Flanagan who prepared the Washington quarter’s look. Interestingly, many people would like to have the design of Laura Gardin Fraser. The bicentennial committee, the people in charge of facilitating the smooth mintage of the Washington quarter, liked Fraser’s design.
Even the Commission of Fine Arts and its chairman liked the work of Fraser. However, the Treasury Secretary at that time, Andrew Mellon, chose the design of Flanagan.

So, when it comes to design, the obverse features the left-facing image of George Washington, the first president of the United States. By the way, a fun fact as well, 1932, the year the Washington quarter was first issued, was the same year that Washington would have celebrated his 200th birthday.
Alright, going back to the design, on the obverse of the coin, you’ll find the following inscriptions:
- Liberty
- In God We Trust
- 1948
The reverse design has more engraved elements. The main feature is the bald eagle with its wings spread out. It holds in its talon a bundle of arrows. Then, below the arrows is an olive branch. The eagle represents the strength of the United States, the arrows symbolize the readiness of the US to go to war, and the olive branch signifies peace.
The inscriptions on the reverse side of the coin include the following:
- United States of America
- E Pluribus Unum
- Quarter dollar
1948 Washington Quarter Varieties
In 1948, the US Mint produced almost 68 million Washington quarters through its Philadelphia, San Francisco, and Denver Mint Centers. The Philadelphia Mint produced the most number of Washington quarters.
For the 1948 Washington quarter, there were three varieties produced. These are the 1948-D, 1948-P, and 1948-S Washington Quarter.
Aside from the standard-issued varieties, there are also those error coins that sporadically appear.
Here’s a quick breakdown of the mintage figures for the 1948 Washington quarter:
| Mint Center | Type | Mintage |
| Denver | Regular strike | 16,766,800 |
| Philadelphia | Regular strike | 35,196,000 |
| San Francisco | Regular strike | 15,960,000 |
| Total | 67,922,800 |
The United States was just a few years away from World War II in 1948. Thus, you will see that coin production at this time is still recovering. As the years passed, the Mint Centers were able to increase production steadily.
Take a look at the 1948 Washington quarter varieties below:
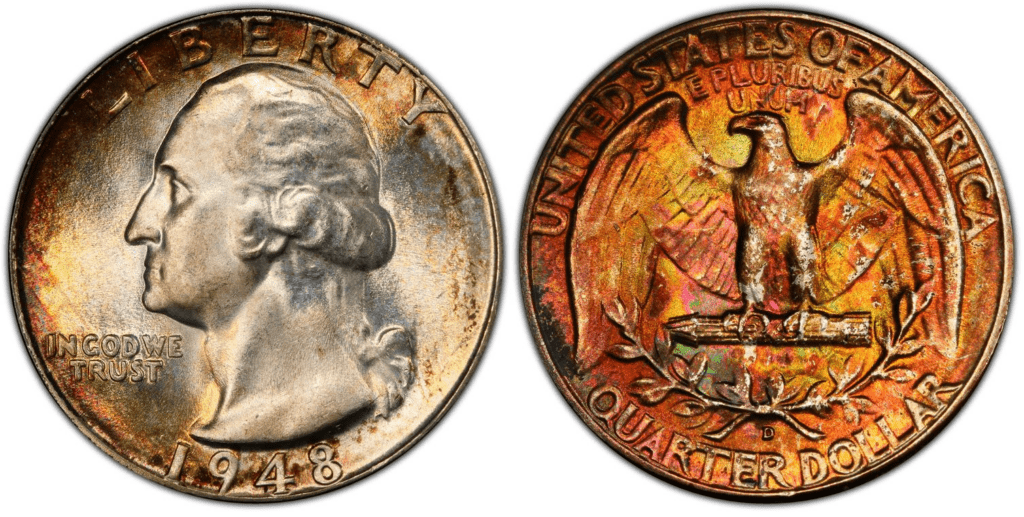
1948 D Washington Quarter
Edge: Reeded
Mint Mark: D
Place of minting: Denver
Year of minting: 1948
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: $7 to $20 (or more)
Quantity produced: 16,766,800
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 90% silver and 10% copper
Mass: 6.30 grams
Diameter: 24.3 millimeters
Thickness: 1.75 millimeters

photo source: PCGS
The 1948 D Washington quarter was struck in the Denver Mint. All 1948 quarters struck in Denver bear the D mint mark. The Denver Mint produced the second-highest number of 1948 D quarters with a mintage of 16,766,800. The production of Washington quarter by the Denver Mint peaked in 1948 because from 1949 until 1951, the production decreased.
Among the 1948 quarter coins, it is the 1948-D, which is considered to be the rarest in Gem condition. Price may range from $7 to $20.
1948 P Washington Quarter
Edge: Reeded
Mint Mark: No mint mark
Place of minting: Philadelphia
Year of minting: 1948
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: $7 to $20 (or more)
Quantity produced: 35,196,000
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 90% silver and 10% copper
Mass: 6.30 grams
Diameter: 24.3 millimeters
Thickness: 1.75 millimeters

photo source: PCGS
The 1948-P quarter coin was made in the Philadelphia Mint. At the end of 1948, 35,196,000 P Washington quarter coins were produced, making it the most abundant variety of 1948 25-cent coins. However, the Philadelphia mint had a significantly lower mintage the following year.
1948-P quarters can easily be found in circulated conditions up to MS66 grade. Therefore, pricing may start at around $7.
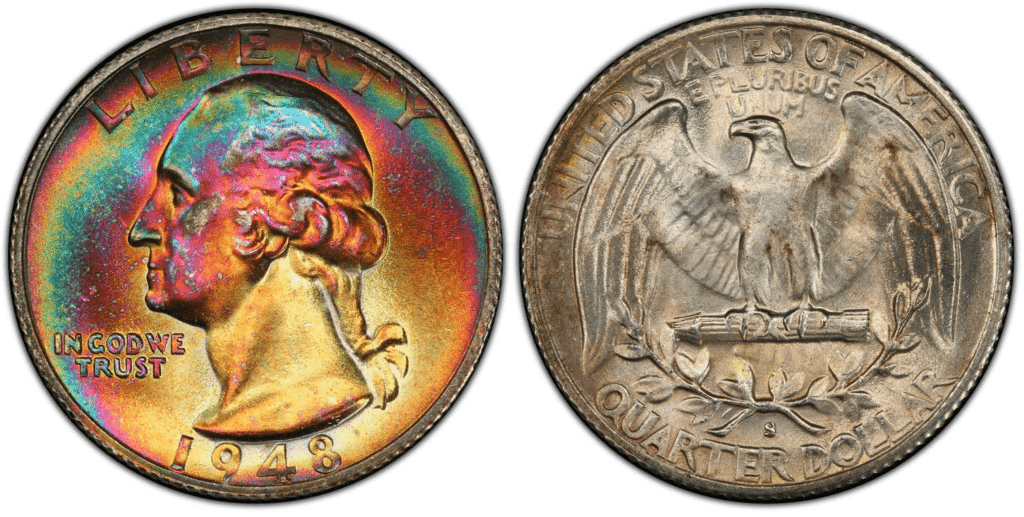
1948 S Washington Quarter
Edge: Reeded
Mint Mark: S
Place of minting: San Francisco
Year of minting: 1948
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: $6 to $16 (or more)
Quantity produced: 15,960,000
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 90% silver and 10% copper
Mass: 6.30 grams
Diameter: 24.3 millimeters
Thickness: 1.75 millimeters

photo source: PCGS
The 1948 S Washington quarter was struck in the San Francisco Mint. All 1948 quarters struck in San Francisco bear the S mint mark. The San Francisco Mint produced 15,960,000. The following year, 1949, the San Francisco Mint didn’t produce any quarter coins.
Price may range from $6 to $16. 1948-S is pretty common up to MS66 grade.
List of 1948 Washington Quarter Errors
There were millions of Washington quarters produced in 1948. So, it won’t come as a surprise to find some 1948 quarter error coins.
In comparison, the quarter coins produced in the Denver Mint were considered more beautiful than those made in Philadelphia and San Francisco. Although, in San Francisco, some coins were struck as if they looked like proof coins. This happened due to the use of newly polished dies.
In Philadelphia, the quality control was poor. Thus, you’ll find more 1948–P quarters less detailed and attractive.
Like any other coins, the 1948 coin errors would include off-center strikes, broadstrikes, clipped or folded planchets, doubled-die strikes, strike-throughs, and others.
Perhaps, the most notable error for the 1948 Washington quarter would be the S over S error. This usually happens when the mint mark is struck on the coin twice. Unfortunately, this leaves the S mint mark to look doubled.
However, another S over S error also seems to be rare. It looks like this:

If you look closely, the last letter S on the word “STATES” seems to have another inverted letter S. If you have a coin like this, it can be sold for more than a thousand dollars.
How Much Is The 1948 Washington Quarter Worth Today?
The 1948 Washington quarter has a face value of 25 cents. Since this coin is made with silver, its melt value can be higher. At the time of this writing, the melt value is $4.3349. The melt value can increase or decrease depending on the market value of silver. On average, 1948 quarter coins are sold for $3.90.
Of course, the value of the 1948 Washington quarter lies on its numismatic value, meaning, if it is rare and has a good grade, then it should be worth more than its face and melt value.
To give you an idea of how this coin can be valuable, here’s a 1948 Washington Quarter values chart:
| Coin | Condition | Grade | Mintage | Value |
| 1948 D Washington Quarter | Circulated/mint | Not graded | 16,766,800 | $3.90 to $6.17 |
| 1948 D Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-66 | 16,766,800 | $42 to $70 |
| 1948 D Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-67 | 16,766,800 | $240 to $360 |
| 1948 D Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-68 | 16,766,800 | $2,280 to $3,480 |
| 1948 P Washington Quarter | Circulated/mint | Not graded | 35,196,000 | $3.90 to $4.97
|
| 1948 P Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-66 | 35,196,000 | $30 to $456 |
| 1948 P Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-67 | 35,196,000 | $114 to $174 |
| 1948 P Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-68 | 35,196,000 | $2,818 to $4,600 |
| 1948 S Washington Quarter | Circulated/mint | Not graded | 15,960,000 | $3.90 to $5.37 |
| 1948 S Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-66 | 15,960,000 | $30 to $86 |
| 1948 S Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-67 | 15,960,000 | $149 to $408 |
| 1948 S Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-68 | 15,960,000 | $13,200 to $23,500 |
The 1948 quarter coin can indeed be valuable. To know its value, take a look at the following auction records for each variety:
- $43,200 – a 1948 25C (Regular Strike) with a grade of MS68 sold in March 2021 by Stack’s Bowers
- $23,500 – a 1948-S 25C (Regular Strike) coin with a grade of MS68 CAC sold in January 2013 by Heritage Auctions
- $8,050 – a 1948-D 25C (Regular Strike) with a grade of MS67 sold in April 2012 by Heritage Auctions
As you can see, the 1948 quarter coin can be astronomically more valuable than its face value and melt value.
How Does The Grading System Work?
The Sheldon Scale is used by numismatists to provide a numerical value to coins. The Sheldon Scale goes from poor (P-1) to perfect mint state (P-1) (MS-70). Coins were originally evaluated using words to reflect their condition (Good, Fair, Excellent, Etc.). Unfortunately, coin collectors and dealers had different ideas about what each of these terms represent.
Professional numismatists joined together in the 1970s and established CoinGrading standards. These numismatists now assign grades at key places on the seventy-point scale, using the most regularly utilized numeric points in conjunction with the original adjective grade. The following are the most common coin grades:
-
-
- (P-1) Poor – Indistinguishable and probably damaged; if used, must have a date and mintmark; otherwise, rather battered.
- (FR-2) Fair – Nearly smooth, but without the damage that a coin graded Poor often possesses. The coin must have enough detail to be identified.
- (G-4) Fair – Inscriptions have merged into the rims in some areas, and important elements have been mostly erased.
- (VG-8) Very Good- A little weathered, but all of the primary design elements are visible, albeit faintly. There is little if any, central detail left.
- (F-12) Good – The item is very worn, yet the wear is even, and the overall design details stand out clearly. Rims are almost completely isolated from the field.
- (VF-20) Very Fine – Moderately weathered, with some finer features still visible. The motto or all letters of LIBERTY are readable. Both sides of the coin have entire rims that are separated from the field.
- (EF-40) Extremely Fine – Gently used; all gadgets are visible, and the most important ones are bold. The finer details are bold and clear, however, light wear may be seen.
- (AU-50) Uncirculated – Slight evidence of wear on the coin’s design’s high points; may have contact marks; eye appeal should be adequate.
- (AU-58) Uncirculated Choice – Slight traces of wear, no severe contact marks, almost full mint shine, and great eye appeal.
- (MS-60) Mint State Basal – Strictly uncirculated; no indication of wear on the coin’s highest points, but an unsightly coin with reduced luster, visible contact marks, hairlines, and other flaws.
- (MS-63) Mint State Acceptable – Uncirculated, but with contact scratches and nicks, little reduced shine, but otherwise appealing appearance. The strike is weak to average.
- (MS-65) Mint State Choice – Uncirculated with great mint shine, very little contact blemishes, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is unusually severe.
- (MS-68) Mint State Premium Quality – Uncirculated with superb luster, no obvious contact marks to the naked eye, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is quick and appealing.
- (MS-69) Almost Perfect Mint State – Uncirculated with perfect brilliance, a sharp and appealing strike, and extremely good eye appeal. A near-perfect coin with minor imperfections in the planchet, strike, and contact markings (seen only under 8x magnification).
- (MS-70) Mint State Perfect – Under 8x magnification, there are no tiny imperfections discernible; the strike is crisp, and the coin is perfectly centered on a beautiful planchet. Rarely seen on a coin, this coin is bright and whole, with original luster and exceptional eye appeal.
-
Where To Buy Or Sell 1948 Washington Quarter?
The 1948 Washington quarter should be available on the Internet. The most popular websites you can go to would include the following:
- Amazon
- eBay
- Etsy
- JM Bullion
- USA Coin Book
- Gray Sheets
What’s great about these websites is that they allow you to buy and sell coins.
If you’re not techy and want to buy 1948 25-cent coins in the old fashion way, you can most certainly visit coin shops, pawnshops, and antique stores. Join auctions as well. Some of the most expensive and rarest coins are found in auction houses.
FAQs
What is a 1948 quarter made out of?
The 1948 quarter coin is made of 90% silver and 10% copper.
How much is a 1948 no mint quarter worth?
The 1948 no-mint quarter is worth around $3.90. If you’re basing its worth on the face value, it should be $0.25. The melt value can be higher, which is around $4. However, uncirculated graded 1948 coins can be sold for hundreds and even thousands of dollars. For example, a 1948 Washington quarter was sold for $43,200 in March 2021.
Where is the mint mark on a 1948 quarter?
Not all coins have mint marks. You can find it on the coin’s reverse side if it has one. Look for it below the olive branch and on top of the letter “R” in the word quarter. The mint mark can be either D or S.