The 1953 nickel is a five-cent coin issued by the US Mint in 1953. As a 70-year-old coin, it carries a lot of sentimental and numismatic value.
If you are planning to buy or sell a 1953 nickel or want to learn about this specific coin’s historical significance, value, composition, and design, then you should read the rest of this article.
What Is the 1953 Jefferson Nickel Made Of?
The 1953 Jefferson nickel comprises 75 percent copper and 25 percent nickel. The core of the 5-cent coin is made of copper while it is clad with nickel.
Here are some specifications that you need to know:
- Value – five cents ($0.05)
- Diameter – 21.21 mm
- Mass – 5 g
- Plain edge
- Designer – Felix Schlag
- Years of minting – from 1938 to present
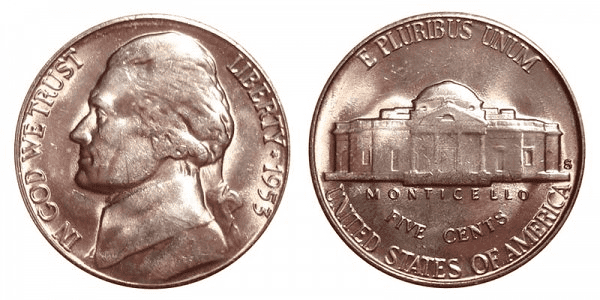
The 1953 Jefferson nickel wasn’t always made of copper and nickel. During World War II, there was a shortage of nickel. Thus, the US Mint temporarily changed the nickel composition from 1942 to 1945 to copper, silver, and manganese.
After 25 years of minting the Buffalo nickel, the US Mint changed its design. The new design would feature the founding father, Thomas Jefferson, and his Monticello mansion. Felix Schlag’s design was chosen after winning the open competition held by the US Mint. However, the US Mint asked Schlag to change the reverse design.
1953 Jefferson Nickel Varieties
The US Mint produced more than 125 million Jefferson nickels in 1953, more than in 1952, and even in 1954. The Denver, Philadelphia, and San Francisco Mint helped produce nickels that year.
There are four varieties of the 1953 Jefferson nickel. The varieties differ based on their mint mark and whether they are proof coins. Here’s a quick look at these nickel varieties, along with their mintage figure:
| Variety | Mint Location | Mintage |
| 1953 D Jefferson Nickel | Denver | 59,878,600 |
| 1953 P Jefferson Nickel | Philadelphia | 46,644,000 |
| 1953 P Proof Jefferson Nickel | Philadelphia | 128,800 |
| 1953 S Jefferson Nickel | San Francisco | 19,210,900 |
| Total | 125,862,300 |
Let’s now have a deeper look at the 1953 nickel varieties:
1953 D Jefferson Nickel
Year of minting: 1953
Mint Mark: D
Place of minting: Denver
Quantity produced: 59,878,600
Face Value: $0.05 (five cents)
Price: $0.10 and $0.50 (circulated condition)
Mass: 5.00 grams
Diameter: 21.20 mm
Edge: Plain
Designer: Felix Schlag
Composition: 75% Copper, 25% Nickel
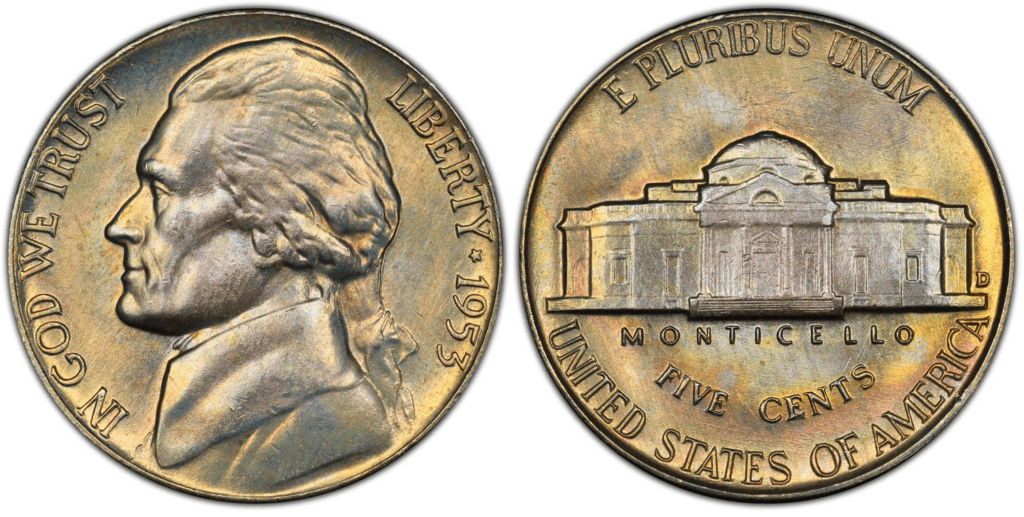

The Denver Mint produced the most number of 1953 nickels. The price of 1953 D nickel is around $0.10 and $0.50 for the circulated ones.
1953 P Jefferson Nickel
Year of minting: 1953
Mint Mark: none
Place of minting: Philadelphia
Quantity produced: 46,644,000
Face Value: $0.05 (five cents)
Price: $0.10 and $0.50 (circulated condition)
Mass: 5.00 grams
Diameter: 21.20 mm
Edge: Plain
Designer: Felix Schlag
Composition: 75% Copper, 25% Nickel

The Philadelphia Mint produced more than 46.6 million nickels in 1953. Although the circulated 1953-P coin could only be less than $1 in value, it could be more valuable when in good condition.
What’s worth noting about the Philadelphia Mint is that the quality control was poor in 1953. That’s why you’ll find a lot of 1953 nickels that are poorly struck with slightly poor luster. So, if you find a 1953 nickel with higher grades, you might be looking at a very valuable coin.
1953 Proof Jefferson Nickel
Year of minting: 1953
Mint Mark: none
Place of minting: Philadelphia
Quantity produced: 128,800
Face Value: $0.05 (five cents)
Price: $11 or more (uncirculated condition)
Mass: 5.00 grams
Diameter: 21.20 mm
Edge: Plain
Designer: Felix Schlag
Composition: 75% Copper, 25% Nickel
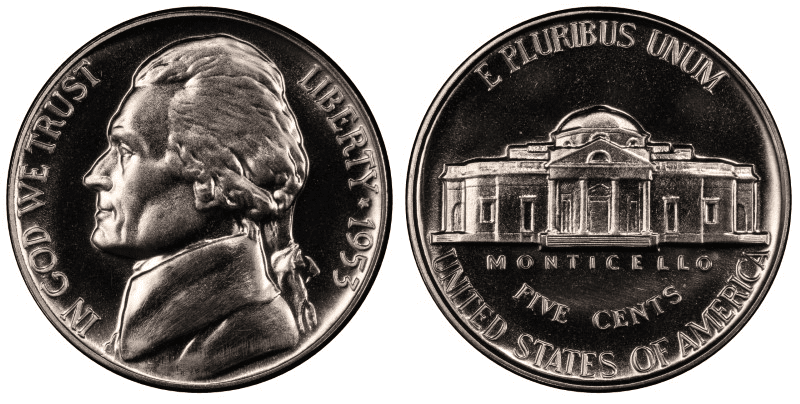
The sale of proof coins soared starting in 1953. That’s why you can see that about 50% more proof coins were produced in 1953 compared to the previous years. Because of the sudden increase in proof sales, the US Mint seemed to rush things and didn’t produce high-quality proof nickel coins in 1953. This means that proof coins with a grade of at least PR 67 are highly valuable.
1953 S Jefferson Nickel
Year of minting: 1953
Mint Mark: S
Place of minting: San Francisco
Quantity produced: 19,210,900
Face Value: $0.05 (five cents)
Price: $0.10 to $0.50 (circulated condition)
Mass: 5.00 grams
Diameter: 21.20 mm
Edge: Plain
Designer: Felix Schlag
Composition: 75% Copper, 25% Nickel
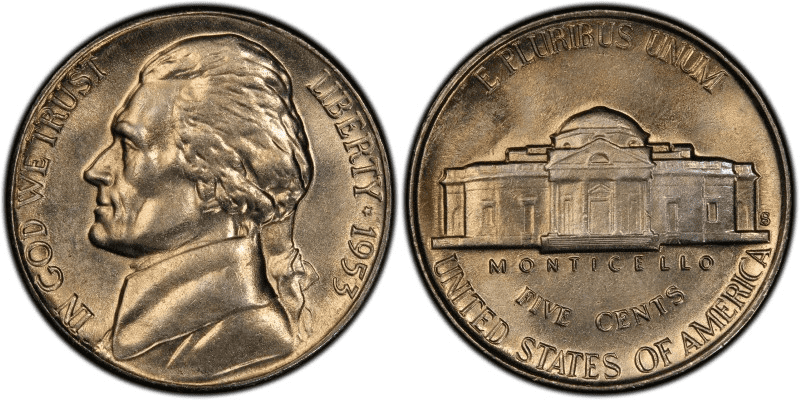

In 1953, the San Francisco Mint produced more than 19 million nickels. Interestingly, this year, the San Francisco Mint stopped repolishing worn dies, a usual practice of the Mint in previous years. Repolishing worn dies could lead to poor strikes. Thus, in 1953, San Francisco Mint produced more beautiful nickels.
List Of 1953 Jefferson Nickel Errors
The 1953 Jefferson nickel is not immune to errors.
Mechanical and human errors could cause coins to have errors in them. Here are some of the examples of 1953 Jefferson Nickel Errors:
Lamination error
Lamination errors happen when some impurities get into the mix of the correct composition of the coin. Since the impurities don’t properly adhere with copper and nickel, the coin’s surface starts to split or peel away once the planchet cools down.
Repunched mintmark (RPM)
The mintmark of the 1953 nickel was separately struck to the coin. Thus, it’s possible that you only see this error on the mintmark with no sign of errors to the rest of the coin. RPMs can cause the mintmark to look blurry or doubled.
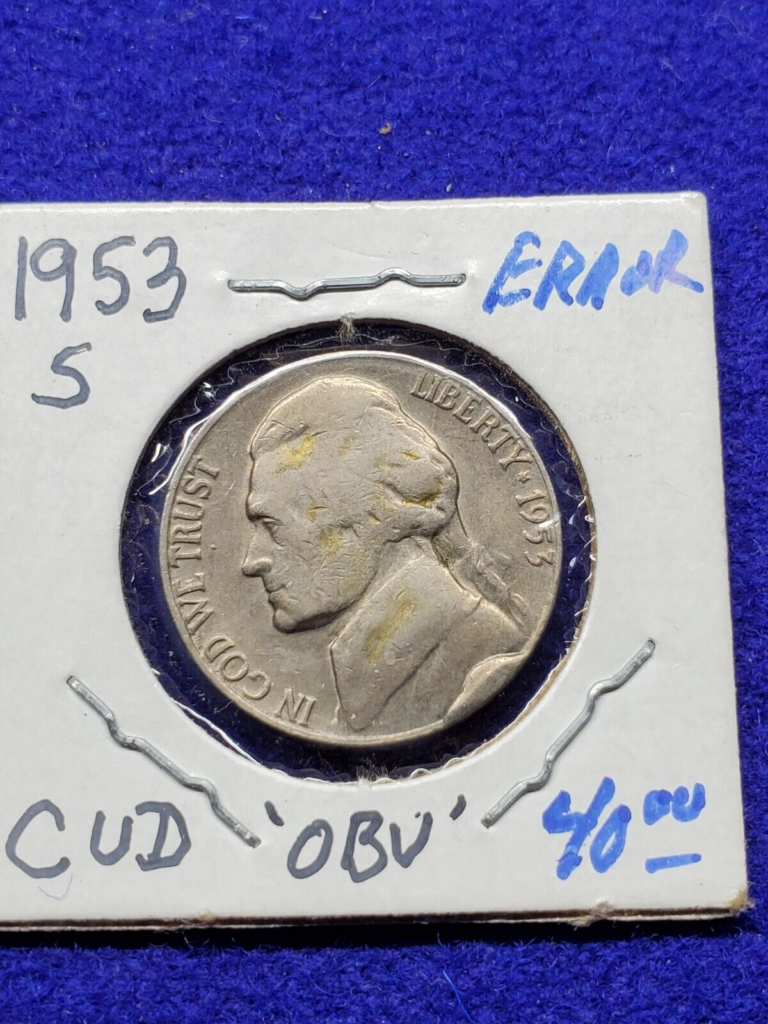
Cud error
The cud error can unintentionally add a “bump” or raised portion on the coin’s surface. This is caused by the die having a defective dent or gouge.
Here’s an example of a 1953 nickel with cud error:

Strike through error
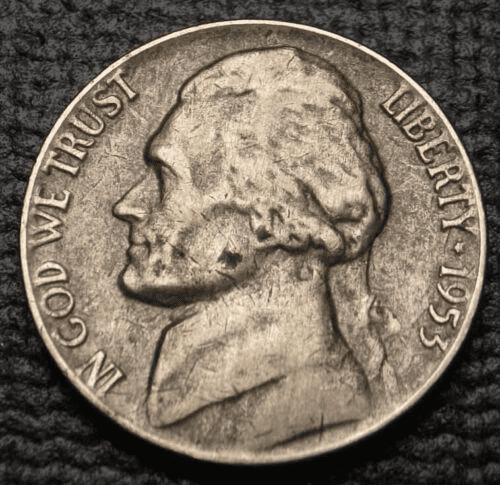
The strike-through error happens when a piece of a foreign object, like wire, debris, metal clippings, and grease, gets stuck between the die and planchet. During the striking process, the die would strike through the foreign object.
The strike-through error can cause indentation or deformation on the coin’s surface. Some strike-through errors can increase the value of the 1953 nickel.
Here’s an example of a 1953 nickel with a strike-through error:

D over inverted D mintmark
There are other rare error coins during the 1953 minting of nickel. One example is this coin with a repunched mint mark. Interestingly, the D mintmark was repunched on an inverted D.
Here’s how it looks:
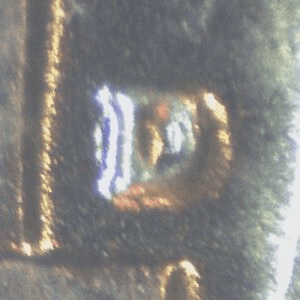
How Much Is The 1953 Jefferson Nickel Worth Today?
The 1953 Jefferson nickel has a face value of 5 cents. It’s not made of precious metals. So, you can expect its usual value to be around 5 cents. Even the melt value is only $0.0674. Most circulated 1953 nickels would also be just under $1 in value.
Nevertheless, this shouldn’t discourage you. Remember, the 1953 Jefferson nickel is an old coin. This means that it bears a lot of numismatic value.
To give you an idea, check out this table that lists the auction records for each of the 1953 Jefferson variety:
| Coin | Condition | Grade | Sold date | Sold by | Value |
| 1953 S Jefferson Nickel | Gem Uncirculated – Full Steps | MS 65 | January 14, 2019 | Heritage Auctions | $24,000 |
| 1953 D Jefferson Nickel | Superb Gem Uncirculated – Full Steps | MS 67 | January 6, 2016 | Heritage Auctions | $15,275 |
| 1953 Proof Jefferson Nickel | Superb Gem Uncirculated – Deep Cameo | PR 68 | April 24, 2013 | Heritage Auctions | $15,275 |
| 1953 P Jefferson Nickel | Gem Uncirculated – Full Steps | MS 65 | August 14, 2004 | Bowers & Merena | $8,050 |
How Does The Grading System Work?
The 1953 nickel is graded based on its condition, color, luster, strike, and level of preservation. Grading includes using the Sheldon Scale, which involves a 70-point grading system.
Professional numismatists joined together in the 1970s and established CoinGrading standards. These numismatists now assign grades at key places on the seventy-point scale, using the most regularly utilized numeric points in conjunction with the original adjective grade. The following are the most common coin grades:
- (P-1) Poor – Indistinguishable and probably damaged; if used, must have a date and mintmark; otherwise, rather battered.
- (FR-2) Fair – Nearly smooth, but without the damage that a coin graded Poor often possesses. The coin must have enough detail to be identified.
- (G-4) Fair – Inscriptions have merged into the rims in some areas, and important elements have been mostly erased.
- (VG-8) Very Good- A little weathered, but all primary design elements are visible, albeit faintly. There is little, if any, central detail left.
- (F-12) Good – The item is very worn, yet the wear is even, and the overall design details stand out clearly. Rims are almost completely isolated from the field.
- (VF-20) Very Fine – Moderately weathered, with some finer features still visible. The motto or all letters of LIBERTY are readable. Both sides of the coin have entire rims separated from the field.
- (EF-40) Extremely Fine – Gently used; all gadgets are visible, and the most important ones are bold. The finer details are bold and clear; however, light wear may be seen.
- (AU-50) Uncirculated – Slight evidence of wear on the coin’s design’s high points; it may have contact marks; eye appeal should be adequate.
- (AU-58) Uncirculated Choice – Slight traces of wear, no severe contact marks, almost full mint shine, and great eye appeal.
- (MS-60) Mint State Basal – Strictly uncirculated; no indication of wear on the coin’s highest points, but an unsightly coin with reduced luster, visible contact marks, hairlines, and other flaws.
- (MS-63) Mint State Acceptable – Uncirculated, but with contact scratches and nicks, little reduced shine, but otherwise appealing appearance. The strike is weak to average.
- (MS-65) Mint State Choice – Uncirculated with great mint shine, little contact blemishes, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is unusually severe.
- (MS-68) Mint State Premium Quality – Uncirculated with superb luster, no obvious contact marks to the naked eye, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is quick and appealing.
- (MS-69) Almost Perfect Mint State – Uncirculated with perfect brilliance, a sharp and appealing strike, and extremely good eye appeal. A near-perfect coin with minor imperfections in the planchet, strike, and contact markings (seen only under 8x magnification).
- (MS-70) Mint State Perfect – Under 8x magnification, no tiny imperfections are discernible; the strike is crisp, and the coin is perfectly centered on a beautiful planchet. Rarely seen on a coin, this coin is bright and whole, with original luster and exceptional eye appeal.
For the nickel, one particular category should also be noted. This is the Full Steps category. A coin with a Full Steps designation means that the steps on the base of the Monticello are detailed, and five or six steps can easily be distinguished.
Where To Buy Or Sell 1953 Jefferson Nickel?
The 1953 Jefferson nickel is available in coin shops and auction houses. In some instances, you might find them in antique stores or pawnshops. The advantage of buying or selling a 1953 Jefferson nickel in person is that you can physically see and inspect coins.
However, if you wish to get immediate results, you should try the Internet. There are numerous websites today that help people to buy and sell coins, which include the 1953 nickel. A simple Google search should give you a lot of options.
FAQs
Is a 1953 nickel made out of silver?
The 1953 nickel is not made of silver. Rather, it is made of 75% copper and 25% nickel.
Where is the mint mark on a 1953 nickel?
Turn to the reverse side of the coin and look for the mint mark near the edge of the coin, just next to the right side of the Monticello.
What makes a 1953 nickel valuable?
The 1953 nickel becomes valuable when it is still in good condition. Graded 1953 nickels can instantly establish their high value. Plus, 1953 nickels with rare errors can also dramatically increase value.
