The universe is full of mysteries waiting to be uncovered, and recent advancements in technology and research have led to some of the most fascinating space discoveries ever made. From the detection of gravitational waves to the first image of a black hole, these groundbreaking findings have expanded our understanding of the cosmos. This article explores the top 9 most fascinating space discoveries, highlighting the incredible insights they provide about our galaxy, the potential for extraterrestrial life, and the fundamental workings of the universe. Whether you’re a space enthusiast or simply curious about the wonders of the universe, these discoveries offer a captivating glimpse into the vast and mysterious expanse beyond our planet.
Gaia Mapping the Milky Way
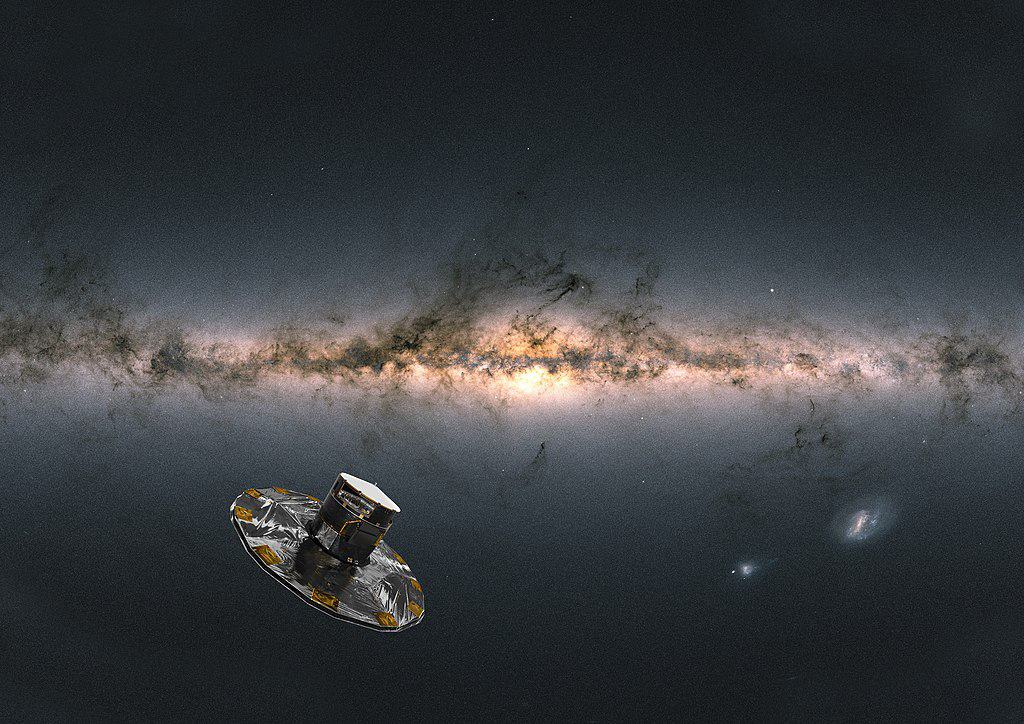

The Gaia spacecraft, launched by the European Space Agency (ESA) in 2013, is revolutionizing our understanding of the Milky Way. Gaia’s mission is to create the most precise 3D map of our galaxy, charting over a billion stars. By measuring the positions, distances, and motions of these stars, Gaia provides invaluable data on the structure and evolution of the Milky Way. This unprecedented stellar census allows astronomers to trace the galaxy’s formation history, uncover new celestial objects, and test theories of stellar dynamics and dark matter distribution. Gaia’s detailed mapping continues to unveil the complexity and beauty of our galactic home.
Explosion of Exoplanet Exploration
NASA Hubble Space Telescope / Flickr
The discovery of exoplanets—planets orbiting stars outside our solar system—has exploded over the past two decades, transforming our understanding of the universe. Since the first confirmed detection of an exoplanet in 1992, thousands have been discovered, revealing a stunning diversity of worlds. This surge in discovery is largely thanks to missions like NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope and the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), which have identified planets ranging from hot Jupiters to Earth-like rocky worlds in habitable zones. The ongoing exploration of exoplanets opens up the tantalizing possibility of finding life beyond Earth and understanding the formation and evolution of planetary systems.
Phosphine on Venus
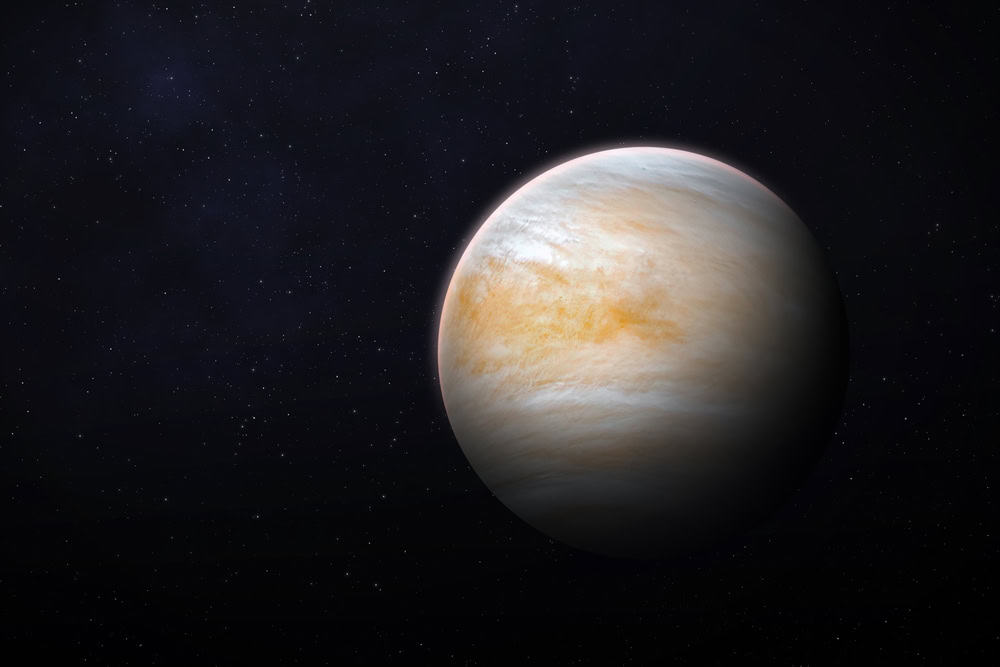

In 2020, scientists announced the detection of phosphine in the atmosphere of Venus, a discovery that sparked significant excitement and debate. Phosphine is a gas typically associated with biological processes on Earth, and its presence on Venus raises the intriguing possibility of microbial life in the planet’s harsh, acidic clouds. While the origin of the phosphine remains uncertain, its detection highlights Venus as a target for further astrobiological studies. This finding has renewed interest in Venus exploration, prompting discussions about future missions to investigate its atmosphere and surface conditions more thoroughly.
Water Jets on Enceladus
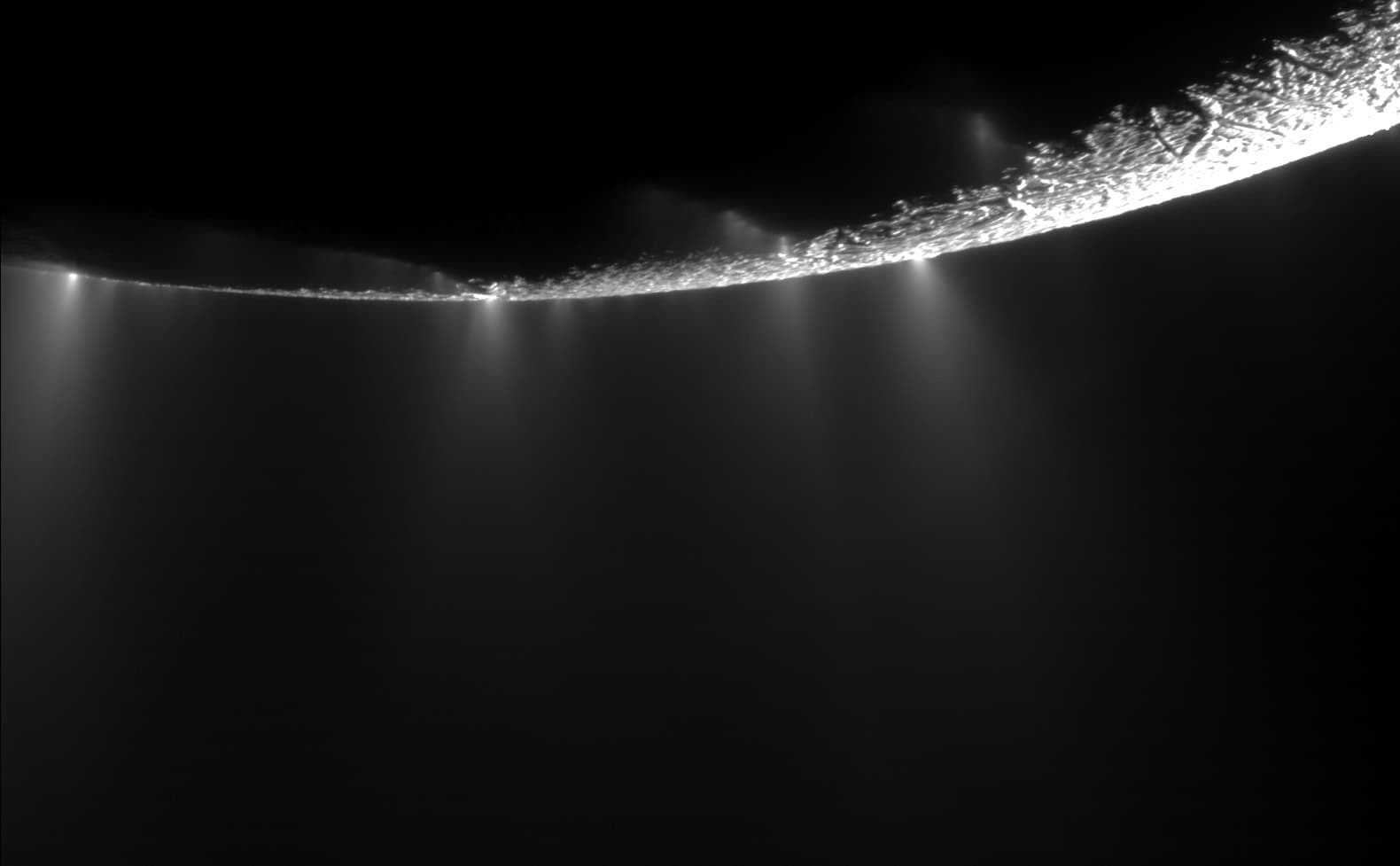

One of the most exciting discoveries in the search for extraterrestrial life is the detection of water jets on Enceladus, one of Saturn’s moons. The Cassini spacecraft, which orbited Saturn from 2004 to 2017, discovered plumes of water vapor and ice particles erupting from Enceladus’s south pole. These jets originate from a subsurface ocean beneath the moon’s icy crust, potentially creating an environment suitable for life. The presence of organic molecules within the plumes further enhances Enceladus’s potential as a habitable environment. This discovery has made Enceladus a prime target for future missions aiming to search for signs of life.
Methane on Mars

The detection of methane on Mars has been one of the most intriguing findings in the quest to understand the Red Planet’s potential for life. Methane is a gas that can be produced by biological processes, and its presence in Mars’s atmosphere suggests that either microbial life or geochemical processes are active beneath its surface. Observations by the Curiosity rover and other missions have confirmed seasonal fluctuations in methane levels, hinting at complex and dynamic processes. While the exact source of Martian methane remains a mystery, its detection significantly impacts our understanding of Mars’s habitability and geologic activity.
Gravitational Waves

The first direct detection of gravitational waves in 2015 by the LIGO (Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory) marked a groundbreaking achievement in astrophysics. Predicted by Albert Einstein a century earlier, gravitational waves are ripples in spacetime caused by violent cosmic events, such as the collision of black holes or neutron stars. This discovery opened a new window for observing the universe, allowing scientists to study phenomena that are invisible to traditional telescopes. Gravitational wave astronomy has since provided insights into the nature of black holes, neutron stars, and the fundamental properties of gravity, revolutionizing our understanding of the cosmos.
First Image of a Black Hole
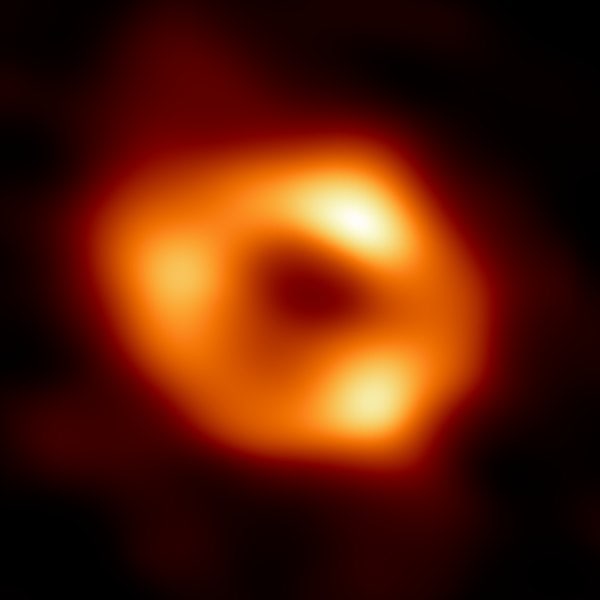

In 2019, the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) collaboration released the first-ever image of a black hole, located in the center of the galaxy M87. This groundbreaking achievement was made possible by a global network of radio telescopes working together to create an Earth-sized virtual telescope. The image revealed the black hole’s shadow against the backdrop of glowing gas, confirming theoretical predictions about the appearance of these enigmatic objects. This historic image provided direct visual evidence of a black hole’s event horizon and offered new insights into the behavior of matter and energy in extreme gravitational fields.
Dark Matter in the Bullet Cluster
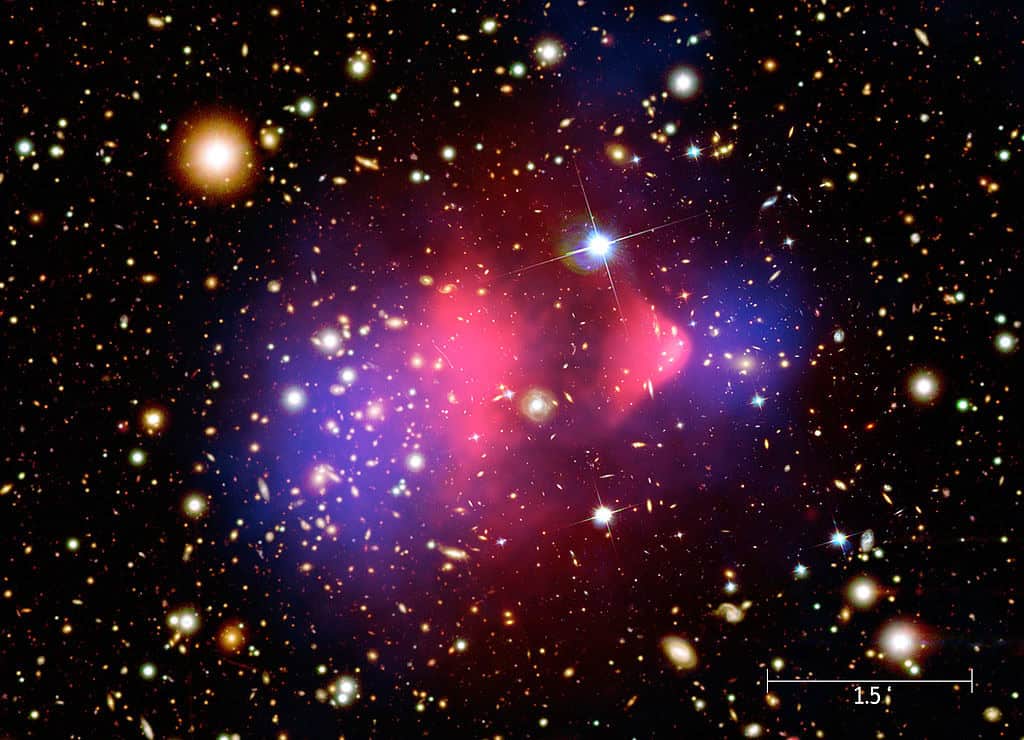
The Bullet Cluster (1E 0657-56) provides one of the most compelling pieces of evidence for the existence of dark matter. This galaxy cluster collision has created a separation between the visible matter, observed through X-ray emissions, and the dark matter, inferred from gravitational lensing effects. The displacement between the hot gas (ordinary matter) and the dark matter demonstrates that dark matter does not interact with electromagnetic forces but only through gravity. The Bullet Cluster serves as a natural laboratory for studying dark matter’s properties and supports the theory that dark matter is a fundamental component of the universe.
New Horizons Flyby of Pluto
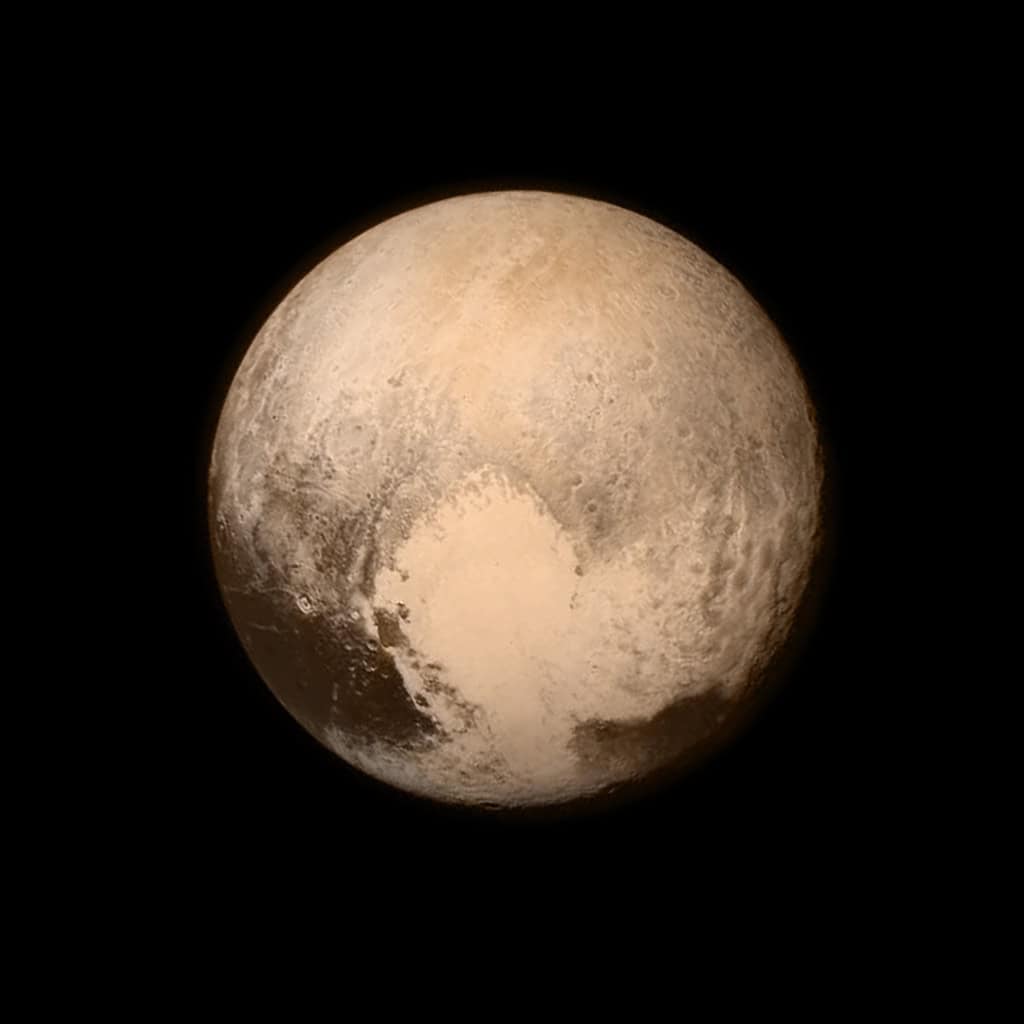

In 2015, NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft conducted the first-ever flyby of Pluto, revealing a complex and diverse world far beyond expectations. The high-resolution images and data captured by New Horizons showed Pluto’s varied terrain, including icy mountains, vast plains, and a stunningly smooth heart-shaped region called Sputnik Planitia. The mission also discovered that Pluto has a blue sky, layers of atmospheric haze, and possible subsurface oceans. These findings have transformed our understanding of Pluto and the Kuiper Belt, highlighting the dynamic nature of these distant objects in our solar system.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More from Rarest.org
17 Most Bizarre Flowers Found Around the World

The world of flora is filled with extraordinary and peculiar flowers that captivate our imagination with their unusual shapes, vibrant colors, and unique adaptations. From blossoms that mimic the appearance of animals to those that emit unexpected scents, these bizarre flowers showcase nature’s creativity and diversity. Read more.
8 Rare Harry Potter Collectibles

Collecting Harry Potter memorabilia is a passion for many fans. The most sought-after items are those that hold unique value and historical significance. Read more.
20 Most Expensive Silver Coins in History

Collecting rare silver coins is a fascinating hobby that blends history, artistry, and investment. Some of the most coveted coins have reached staggering prices due to their rarity, historical significance, and intricate designs. Read more.
