Lung diseases are among the most prevalent medical conditions worldwide, with about 1 in 7 adults having different lung problems. With three main types of lung disease, many people have hereditary problems, problems due to genetic mutation, or overall poor health conditions. Three types can be classified – airway diseases, lung tissue diseases, and lung circulation diseases.
Common cold, asthma, lung cancer, the collapse of part or all the lung, and bronchitis are among the most common lung illnesses. Lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system, as their principal function is to extract oxygen from the air and push it into the bloodstream and organs that need it to work optimally. Imperiled rhythm can cause many problems, some even fatal.
Chronic respiratory diseases are in everyday incline worldwide due to the harmful environment. Around 6,000 rare disorders exist today, causing health issues to numerous people. Unfortunately, not every disease gets proper research. However, experts are working on finding more about the symptoms and treatment necessary for some of the rarest respiratory and lung diseases every day.
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis (PAP)
- Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome (BHD)
- Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM)
- Mesothelioma
- Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome (CCHS)
- Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis (PAM)
- Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS)
- Diffuse Idiopathic Pulmonary Neuroendocrine Cell Hyperplasia (DIPNECH)
Causes: Age, Continuous work in wood/metal dust, and more
Symptoms: Dry cough, chest pain, leg swelling, shortness of breath
Treatment: Not established yet; Oxygen therapy, medicine, pulmonary rehabilitation

photo source: Mayo Clinic
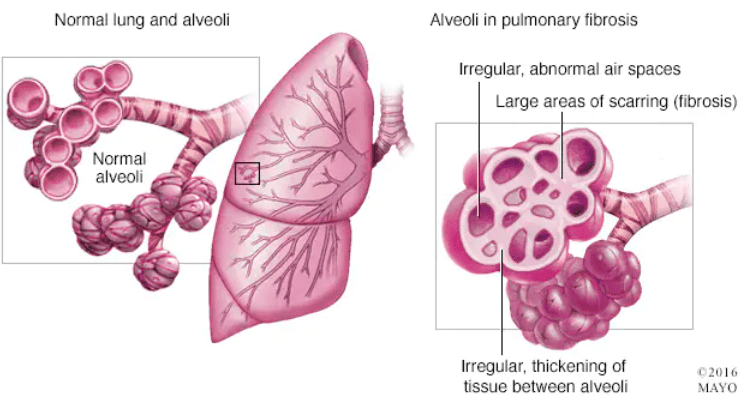
Pulmonary Fibrosis, also known as Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis, is a severe lung disease that leads to scar tissue growing inside the lungs and making the breathing process difficult. Medicine and oxygen therapy can help alleviate the symptoms.
The causes vary – from age (almost everyone diagnosed is over 50 years old) to regular breath intake of wood or metal dust, genetics, and smoking. This illness is predominant in males, and biopsies can determine whether you have it, as IPF can be terminal with time.
Did you know?
This illness is not very known, despite 1 per 10,000 people having it worldwide. The idiopathic disease is a disorder that is hard to diagnose.
Causes: Buildup of surfactant protein, and more
Symptoms: Dry cough, shortness of breath, fatigue, fever, weight loss
Treatment: Whole-lung lavage (WLL)

photo source: Cleveland Clinic
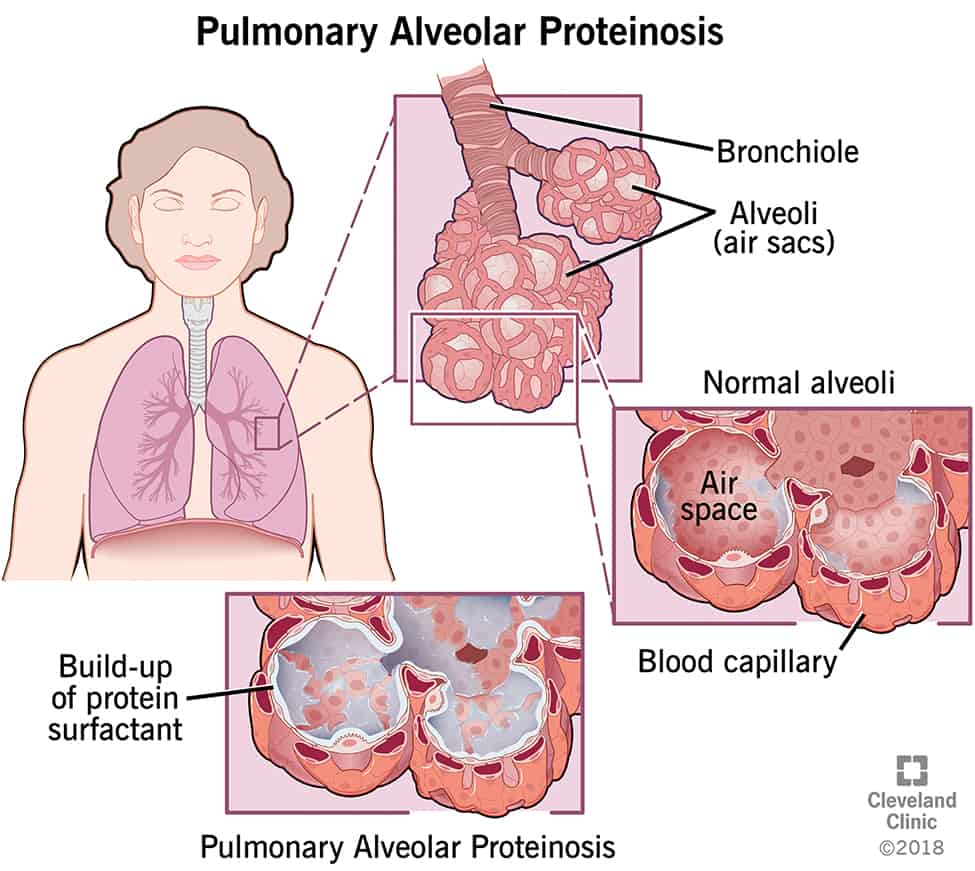
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis is a rare lung illness usually caused by the accumulation of protein surfactant layering the lungs. The lack of the GM-SCF antibody responsible for removing the extra protein results in breathing problems, the first sign of the disease.
PAP is usually diagnosed before the age of 40, mostly in males, on a chest x-ray for other symptoms, as the cause can develop during young adulthood. Treatment includes Whole-lung lavage or physical removal of protein from the affected lungs due to being proven most effective.
Did you know?
It affects about one person in 100,000 worldwide. Patients can live long-term with this disease with proper treatment and early diagnosis. But there were reports of fatality because of respiratory failure or lack of oxygen in the blood.
Causes: Hereditary
Symptoms: Benign skin lesions, skin papules (raised areas of skin), collapsed lungs
Treatment: Laser ablation, lung and kidney surgery

photo source: Semantic Scholar
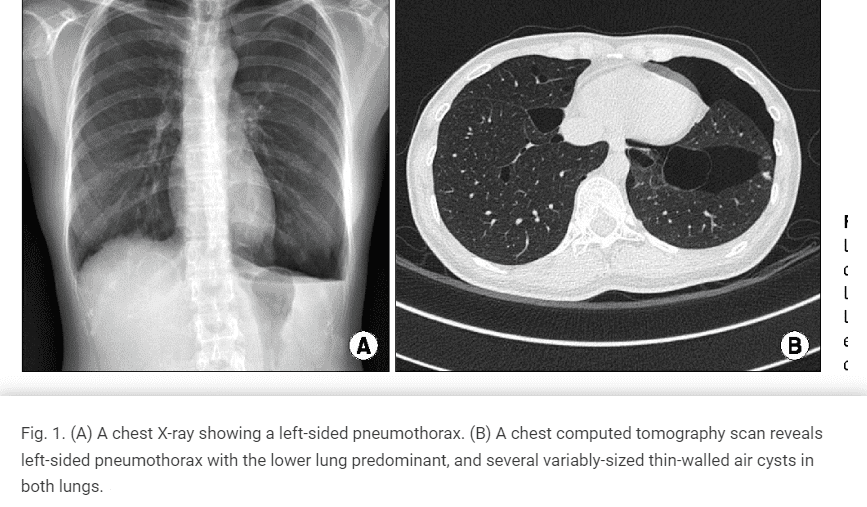
Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome is a rare inherited disorder that happens when the air gets inside the chest cavity, putting pressure on the lungs from outside, causing collapsed lungs. Diagnosis is frequent in families with a history of kidney cancer and lung cysts.
Different skin tissue in color, size, bumps, sores, and ulcers can be symptomatic of this illness. Detailed patient history, and biopsy, among other things, are necessary to diagnose it properly. This illness is not life-threatening since the treatments are usually beneficial.
Did you know?
BHD is a rare disease with around 600 families reported worldwide or about 2 cases per million people, but many researchers believe it is underdiagnosed. The syndrome got its name after the three Canadian doctors that first used the term in 1977 – Arthur R. Birt, Georgina R. Hogg, and William J. Dubé.
Causes: Hereditary
Symptoms: Shortness of breath, chest pain, wheezing, cough, fatigue
Treatment: No direct cure; Medication; Lung transplant

photo source: Wikipedia
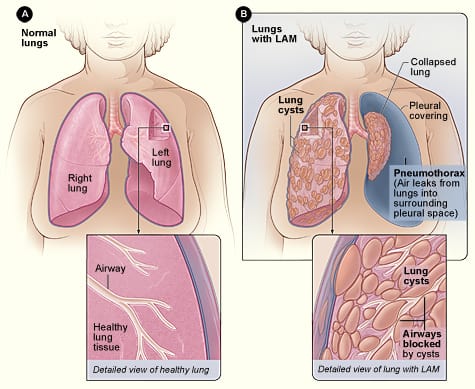
Lymphangioleiomyomatosis (LAM) is a rare lung illness usually occurring in women during their twenties and thirties, caused by abnormal growth of muscle cells in the lungs. It can happen in the kidneys and lymphatic system as well.
Symptoms of LAM can develop slowly over time, but the most dangerous are stabbing chest pain and hard time breathing. Chest x-rays are usually not sufficient to diagnose it, so doctors perform CT scans and blood tests to determine the right cause.
Did you know?
An estimate suggests approximately 30,000 to 50,000 patients struggle with LAM worldwide, or for every million women, three to five have LAM. However, patients can live a long life with efficient treatment.
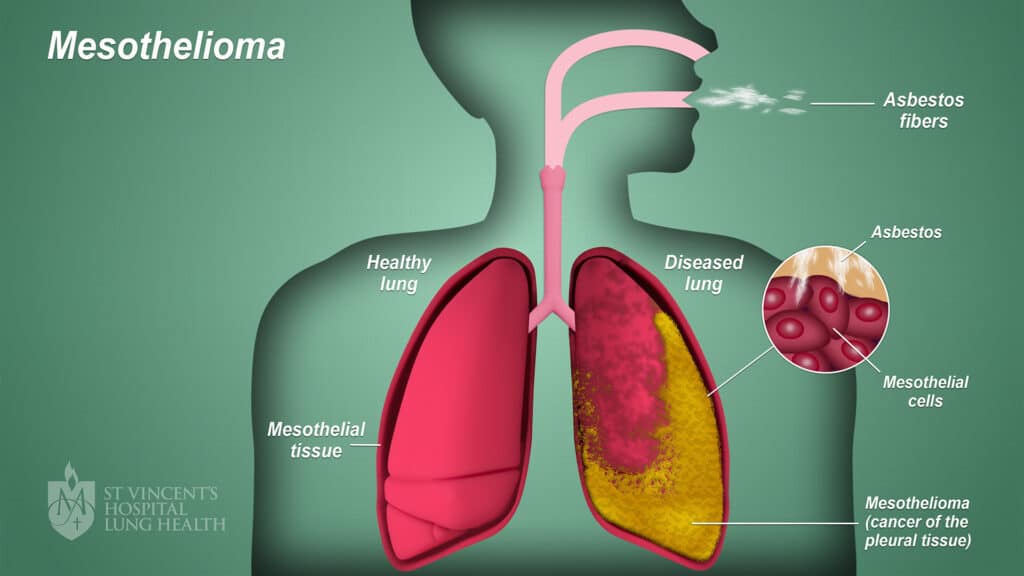
Causes: Exposure to asbestos
Symptoms: Chest pain, shortness of breath, a buildup of fluid called pleural effusion
Treatment: No direct cure; Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy

photo source: Lung Health
Mesothelioma is among the rarest lung cancer subtypes, accounting for less than 0.3% of worldwide cancer diagnoses. It develops in the mesothelium, a thin tissue lining the lungs and abdomen, caused by continued exposure to asbestos.
Doctors need to take several tests (blood tests, chest x-ray, CT scan) for a proper diagnosis because the symptoms are common in different diseases. After diagnosis, patients need to have a mix of treatments such as surgery, immunotherapy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
Did you know?
The average life expectancy with this cancer is 12 to 21 months after diagnosis. But the patient can survive longer depending on the cancer stage, mesothelioma cell type, and location of the tumor.
Causes: Genetic mutation, Severe brain or spinal trauma (injury)
Symptoms: Shallow breathing, abnormal pupils, impaired bowel function
Treatment: Not established yet; Respirator usage, iron lung, tracheostomy

photo source: Washington Post
Congenital central hypoventilation syndrome is a very rare disorder of the automatic nervous system that affects normal breathing, especially during sleeping. Caused by a genetic mutation, CCHS can cause problems in the digestive tract, eye abnormalities, and more.
Patients with this disorder sometimes need a surgical opening through the neck to breathe, but so-called iron lung ventilation has shown stellar results along with oxygen therapy. The disease is common to be diagnosed soon after birth, with around 1,000 total cases as of 2008.
Did you know?
Patients, especially infants, would need the help of different machines to breathe during sleep and sometimes while awake. Sadly, not many people survive their infant years with this disease in extreme cases, especially if they receive no treatment from the start.
Causes: Genetic mutation
Symptoms: Fatigue, dry cough, shortness of breath
Treatment: Not established yet; Supplemental oxygen, lung transplantation

photo source: Nature
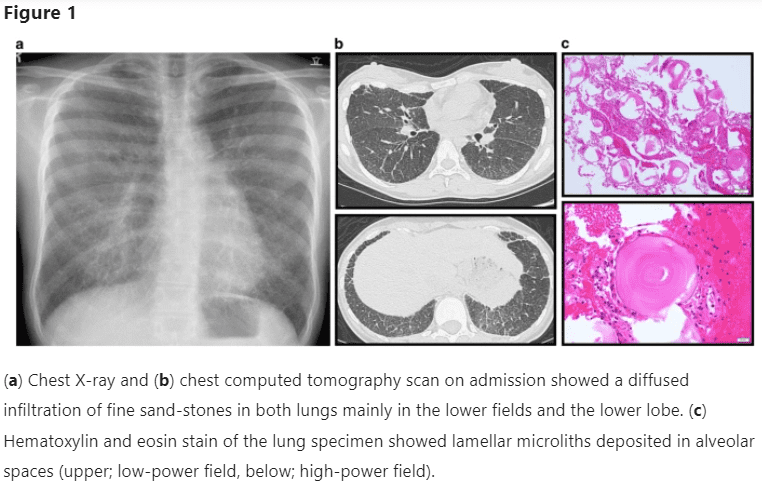
Pulmonary Alveolar Microlithiasis is an illness caused by the buildup of protein calcium phosphate in the form of small stones in the alveoli. PAM is an extremely rare disorder with around 1,000 affected individuals worldwide.
People can also have traces of this protein in their kidneys, testes, gallbladder, and the heart aorta, where more challenging difficulties could occur.
Did you know?
PAM occurs on almost every continent, with most cases in Asia, common in Turkey, Italy, Japan, and the USA. This illness is slightly predominant among women.
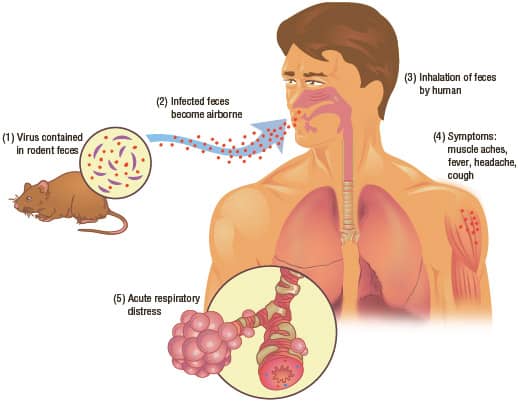
Causes: Rodents in usually rural areas, airborne transmission
Symptoms: Fatigue, fever, cough, shortness of breath, chest pain
Treatment: No direct cure, but an early diagnosis can help; Oxygen therapy, Medications

photo source: Science Vector Art
Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome (HPS) is an extremely rare illness transmitted to humans from infected urine or saliva of rodents. The virus causes blood vessels to become weak in the lungs, making breathing challenging once blood enters them.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), 728 cases of HPS were identified in the United States in the previous years, starting with 1993. It can be life-threatening to people as HPS has a mortality rate of 38%, not fatal to rodents.
Did you know?
The disease had an outbreak in 1993 in the area known as The Four Corners – Arizona, Colorado, New Mexico, and Utah. The cause of this was the extreme drought, followed by heavy snow and rainfall that brought in much more rodents than before.
Causes: Unknown
Symptoms: Chronis cough, wheezing, shortness of breath, hyperinflation
Treatment: Not established yet; Glucocorticoids (anti-inflammation medicines)

photo source: Cardiopulmonary Imaging
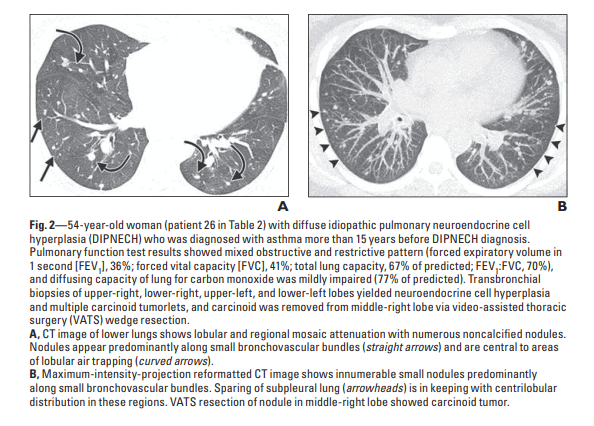
DIPNECH is the rarest lung disease that hasn’t had its case study yet. The diagnosis isn’t apparent from pulmonary function tests and blood work, making the illness underdiagnosed.
The causes are not known just yet, but the overgrowth of pulmonary neuroendocrine cells contributes to the manifestation of the disease. Various other health conditions have similar symptoms, and the illness is predominant in middle-aged, nonsmoking women.
Did you know?
DIPNECH was first explained in a case study published by Aguayo in 1992, with six cases that doctors inspected, all with similar symptoms. Experts think that DIPNECH is a precursor of pulmonary carcinoid tumors.