When thinking about economics, certain names often come to mind, like Adam Smith or John Maynard Keynes. However, the field is much broader than these famous figures. Numerous economists have made significant contributions but remain relatively unknown. These lesser-known yet highly influential thinkers have shaped modern economic thought in ways that often go unnoticed. Their work continues to impact policies and theories today.
Joan Robinson
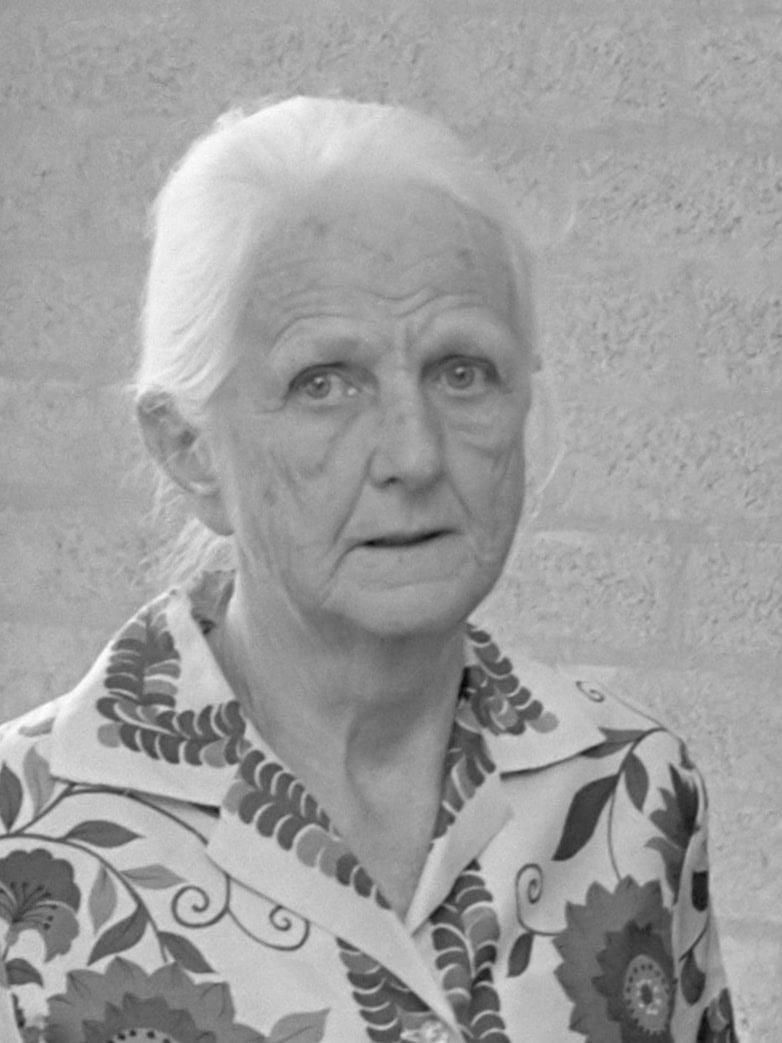

Joan Robinson was a pioneering British economist. She made significant contributions to economic theory, especially in the field of imperfect competition. Her work challenged traditional views and opened up new areas of study. Robinson was also a key figure in the development of post-Keynesian economics. Her sharp intellect and innovative ideas left a lasting impact on economic thought.
Hyman Minsky

Hyman Minsky was an economist whose theories gained attention during financial crises. He developed the Financial Instability Hypothesis, which explained how financial markets can lead to economic instability. Minsky’s work highlighted the risks of speculative bubbles and debt accumulation. His ideas became particularly relevant during the 2008 financial crisis. Minsky’s insights continue to shape economic discussions on financial stability.
Ragnar Frisch

Ragnar Frisch was a Norwegian economist and one of the founders of econometrics. He introduced mathematical and statistical methods into economics. Frisch’s work helped transform economics into a more precise science. He also co-won the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1969. His contributions laid the foundation for modern economic analysis and forecasting.
Jan Tinbergen
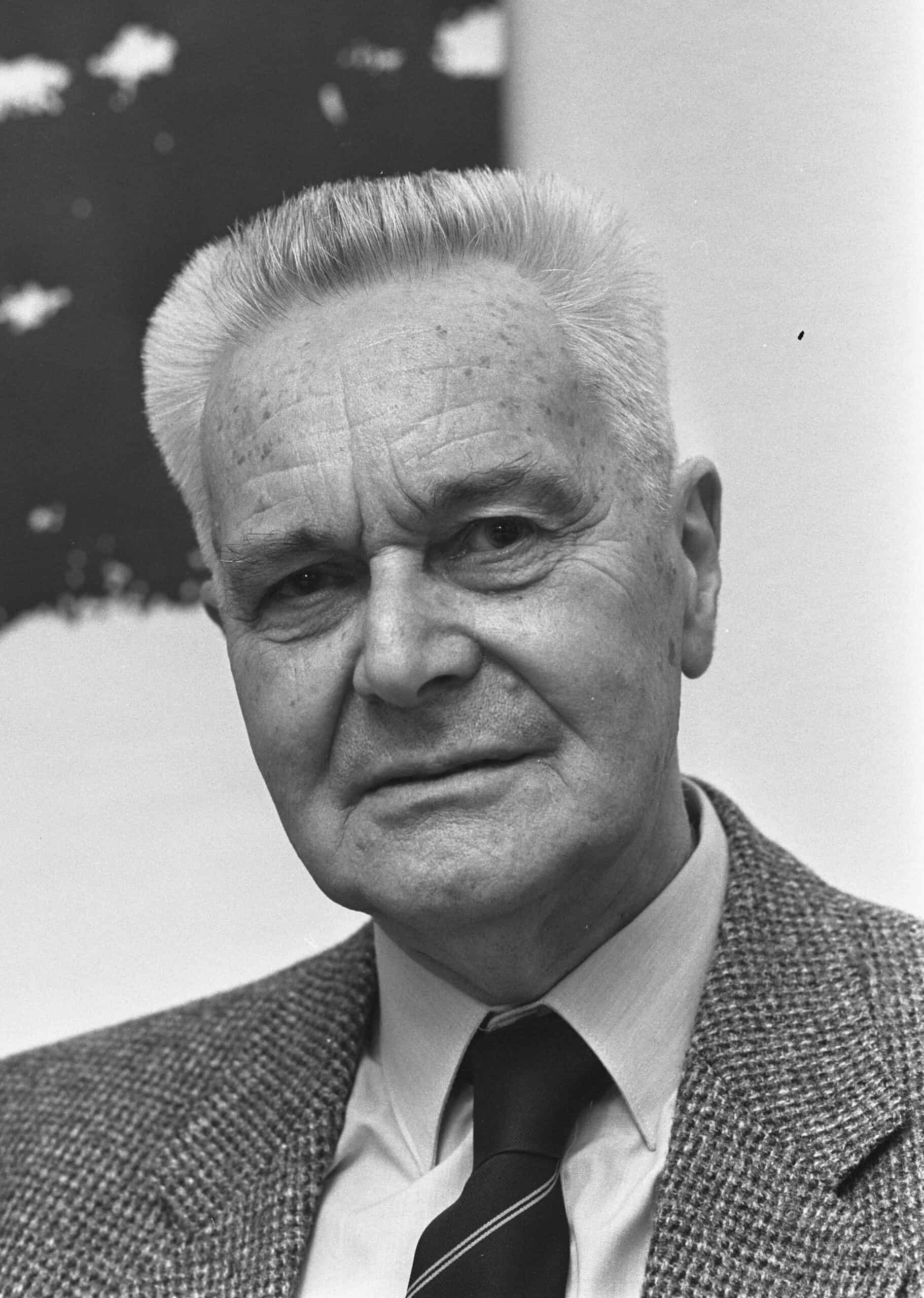

Jan Tinbergen was a Dutch economist who played a key role in developing econometric models. He created the first macroeconomic model to analyze and predict economic trends. Tinbergen’s work in economic planning and policy-making was groundbreaking. He also shared the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences with Ragnar Frisch. His models continue to influence economic policy decisions worldwide.
Knut Wicksell
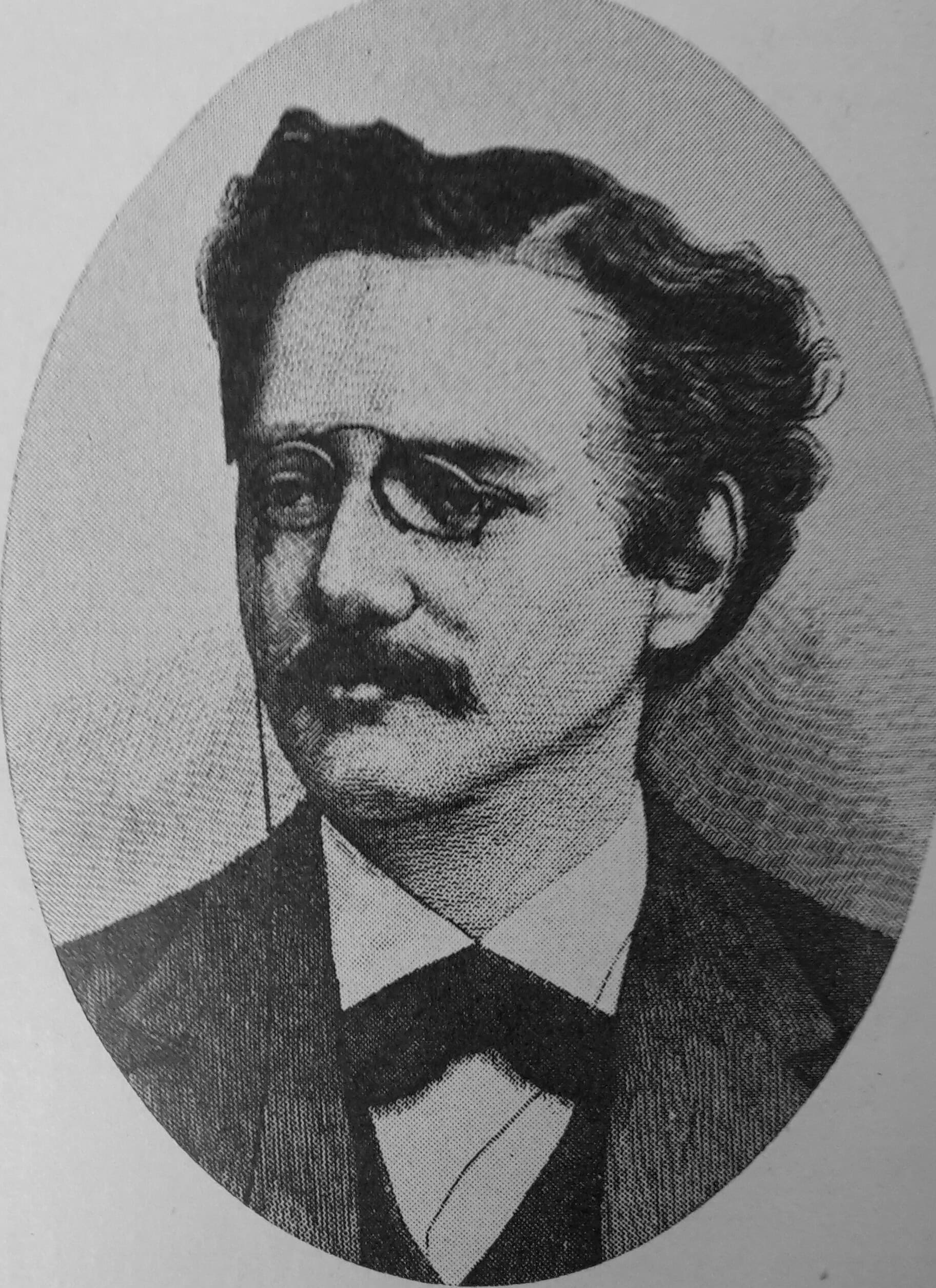

Knut Wicksell was a Swedish economist who made lasting contributions to monetary theory. He introduced the concept of the natural rate of interest. Wicksell’s work provided a framework for understanding inflation and interest rates. His ideas influenced later economists, including John Maynard Keynes. Wicksell’s theories remain fundamental to modern monetary policy.
Michal Kalecki

Michal Kalecki was a Polish economist whose work paralleled that of Keynes. He developed theories on income distribution, business cycles, and full employment. Kalecki’s insights into the role of government spending were pioneering. His work laid the groundwork for many modern economic policies. Despite his contributions, Kalecki is less well-known outside academic circles.
Léon Walras
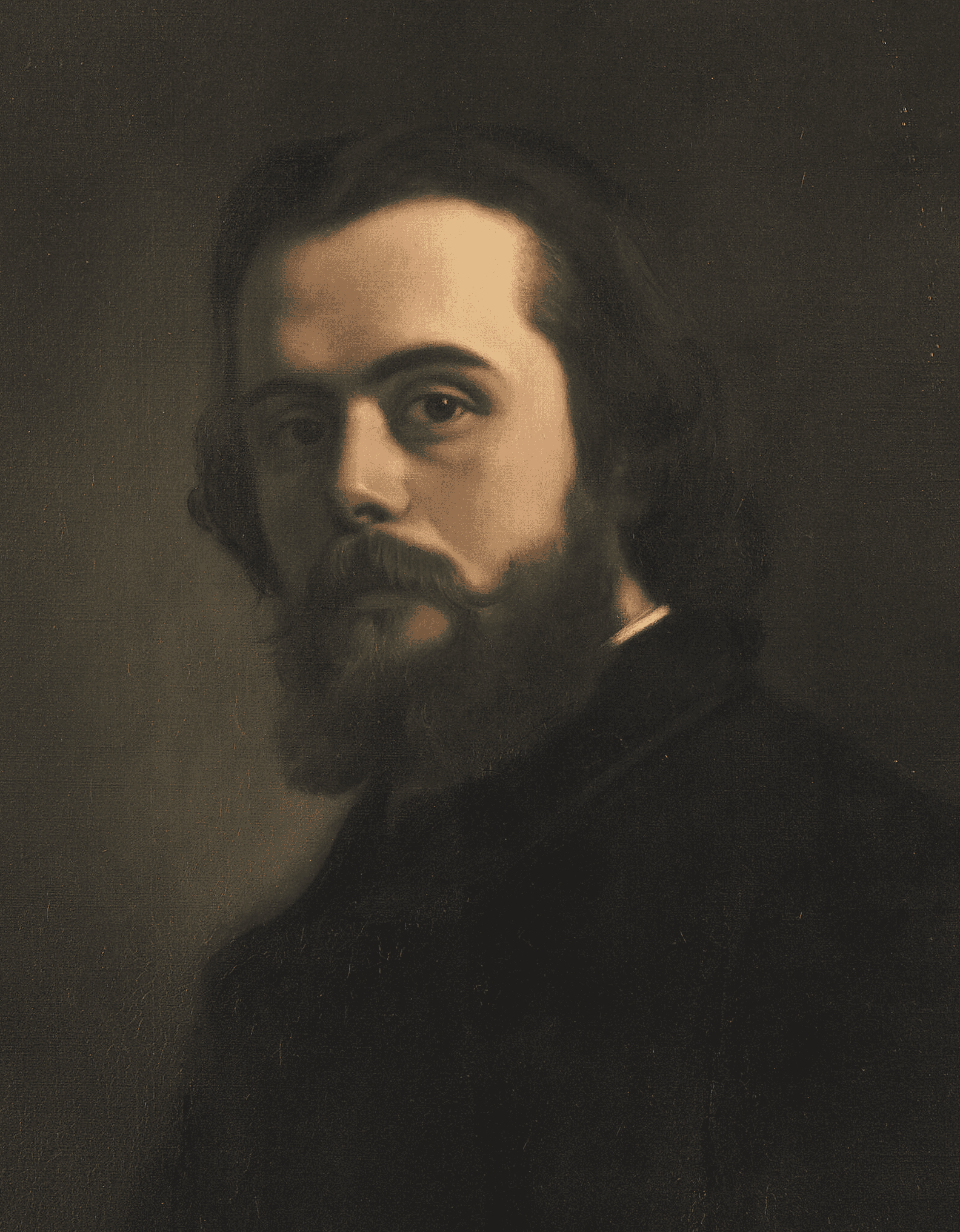

Léon Walras was a French economist who developed the theory of general equilibrium. He introduced the concept of a perfectly competitive economy where supply and demand are in balance. Walras’s work provided a mathematical framework for analyzing markets. His ideas laid the groundwork for modern microeconomic theory. Despite his significant contributions, Walras is often overlooked in discussions of economic history.
Elinor Ostrom
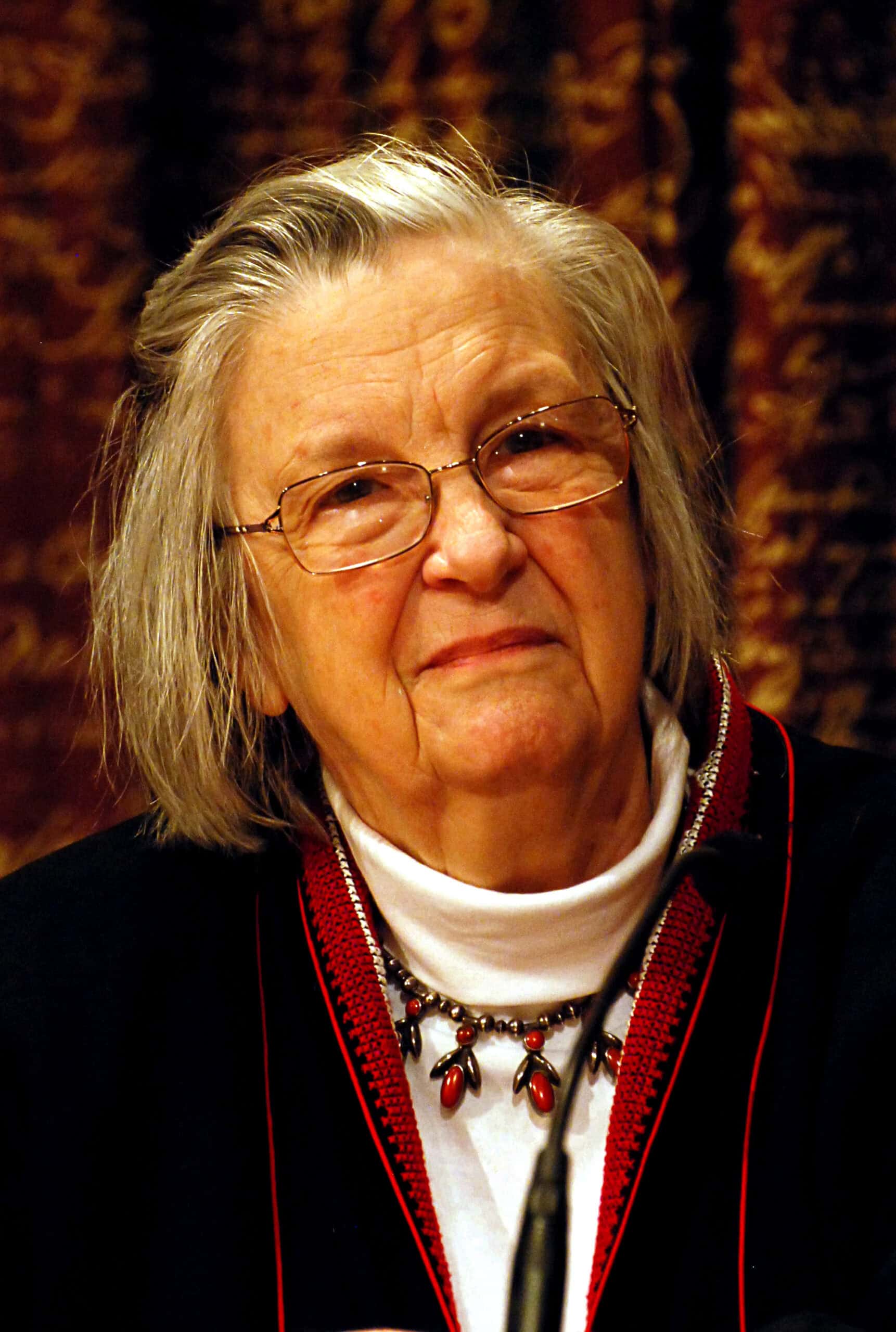

Elinor Ostrom was the first woman to win the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences. She challenged the traditional view of managing common resources. Her work demonstrated that communities could successfully govern shared resources without central authority. Ostrom’s research focused on real-world examples, highlighting the importance of collective action. Her findings have influenced policies on environmental and resource management globally.
John Bates Clark
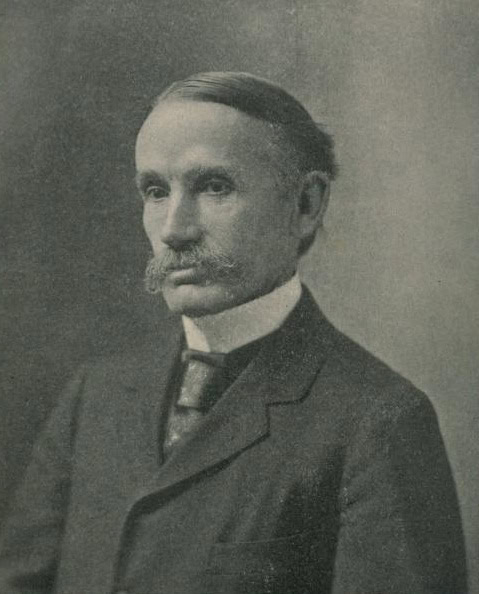
John Bates Clark was an American economist who developed the marginal productivity theory of distribution. He argued that wages and rents are determined by the productivity of labor and capital. Clark’s work laid the foundation for modern theories of income distribution. His ideas influenced later economic thought, particularly in neoclassical economics. Despite his contributions, Clark’s name is not as widely recognized today.
Tjalling Koopmans
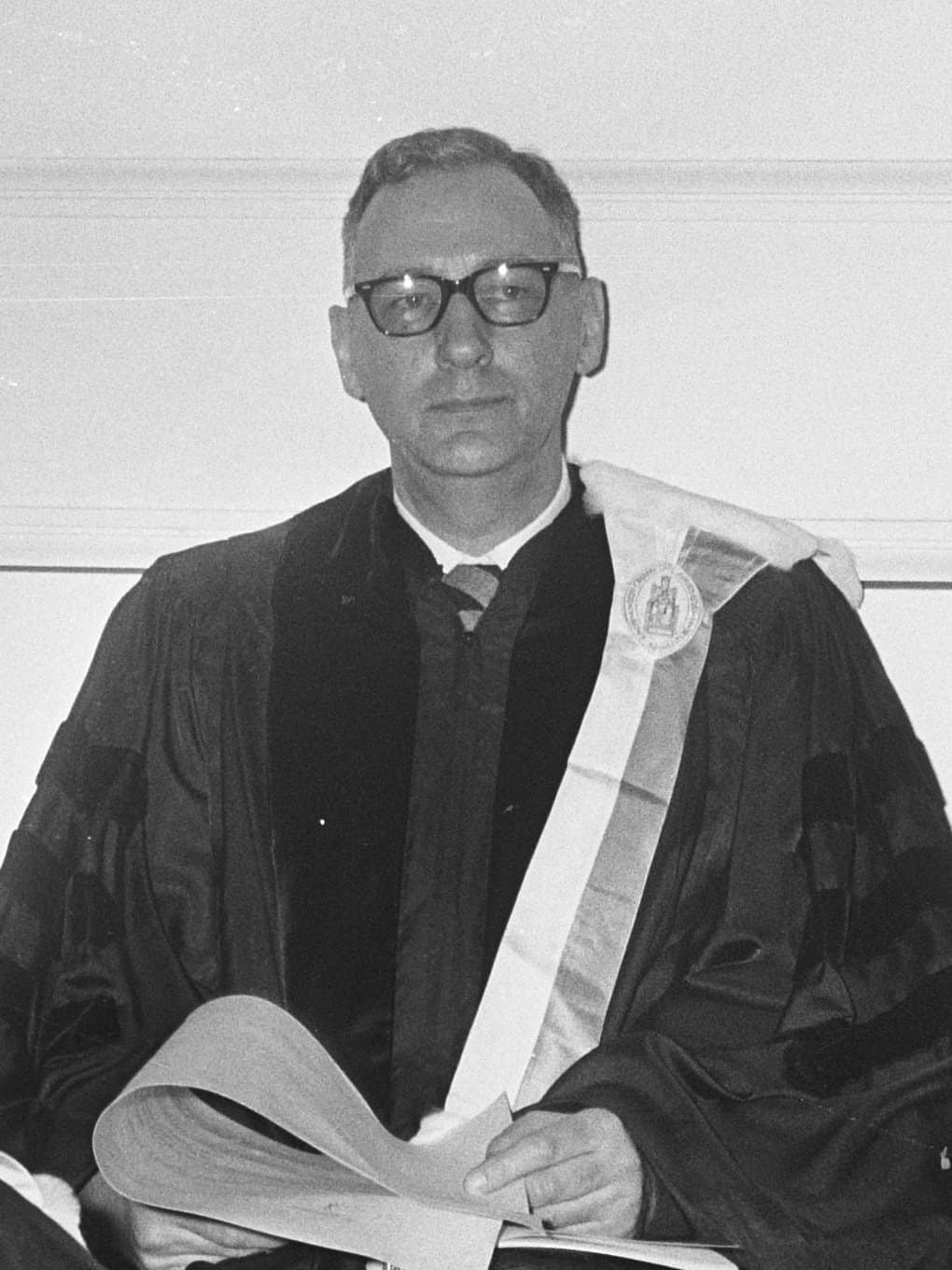

Tjalling Koopmans was a Dutch-American economist known for his work in econometrics and mathematical economics. He developed models that optimized the allocation of resources in an economy. Koopmans also contributed to the theory of optimal growth. He shared the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1975 for his work on the theory of optimal allocation of resources. Koopmans’s models are still used in economic planning and policy analysis.
François Quesnay
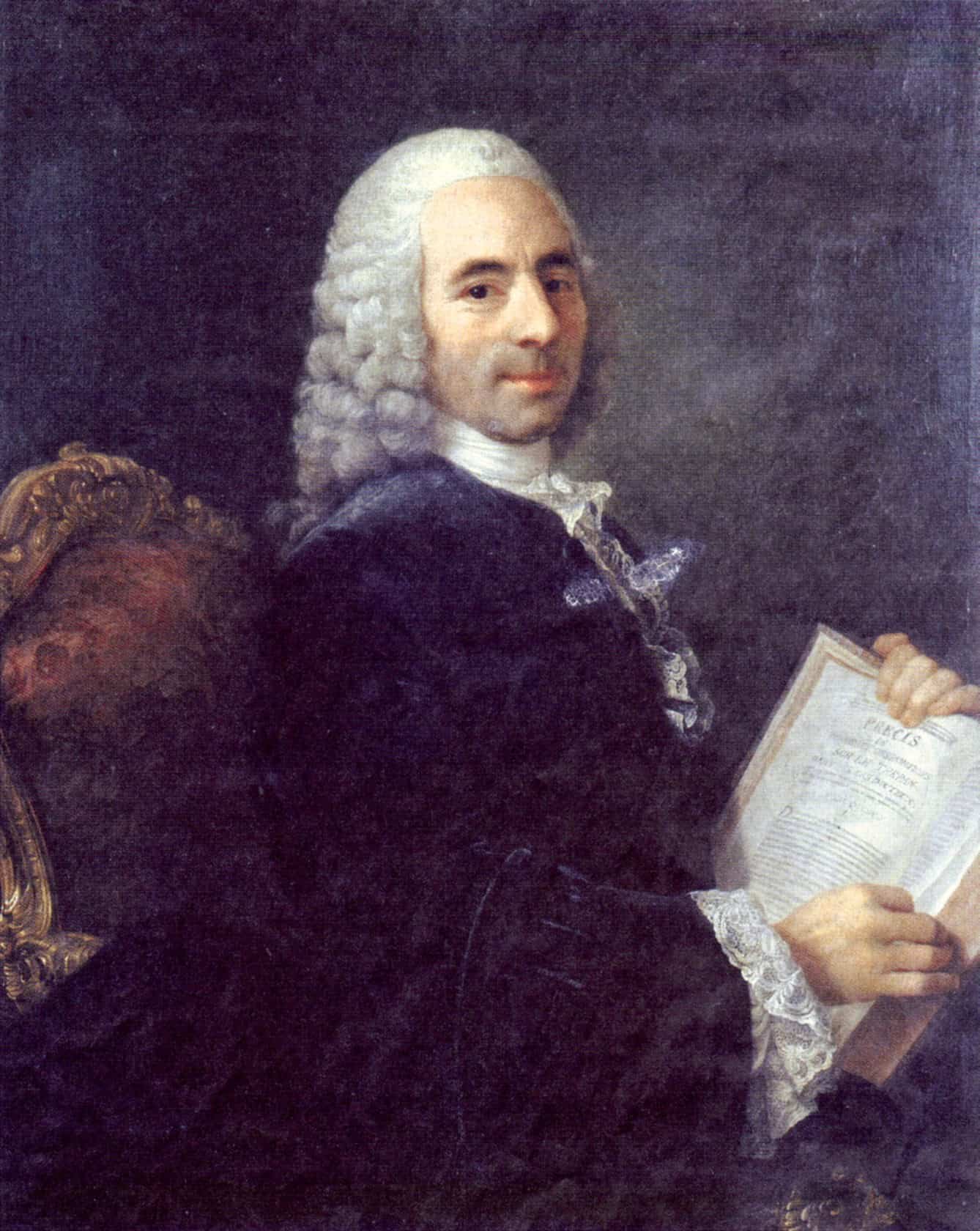

François Quesnay was a French economist and the leader of the Physiocrats, the first school of economic thought. He developed the Tableau Économique, which depicted the flow of goods and money in an economy. Quesnay’s work emphasized the importance of agriculture as the source of wealth. His ideas influenced later economic theories, including classical economics. Quesnay is often referred to as the father of economic liberalism.
Simon Kuznets
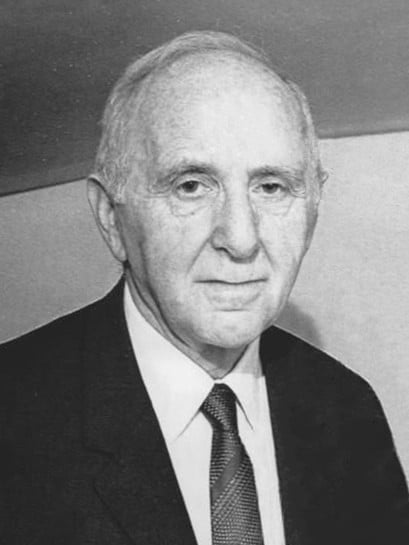

Simon Kuznets was a Russian-American economist who developed the concept of Gross National Product (GNP). He pioneered the study of economic growth and income inequality. Kuznets’s work helped establish national income accounting as a vital tool for economic analysis. He won the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1971 for his research on economic growth. Kuznets’s ideas continue to influence economic policy and development strategies.
Irving Fisher
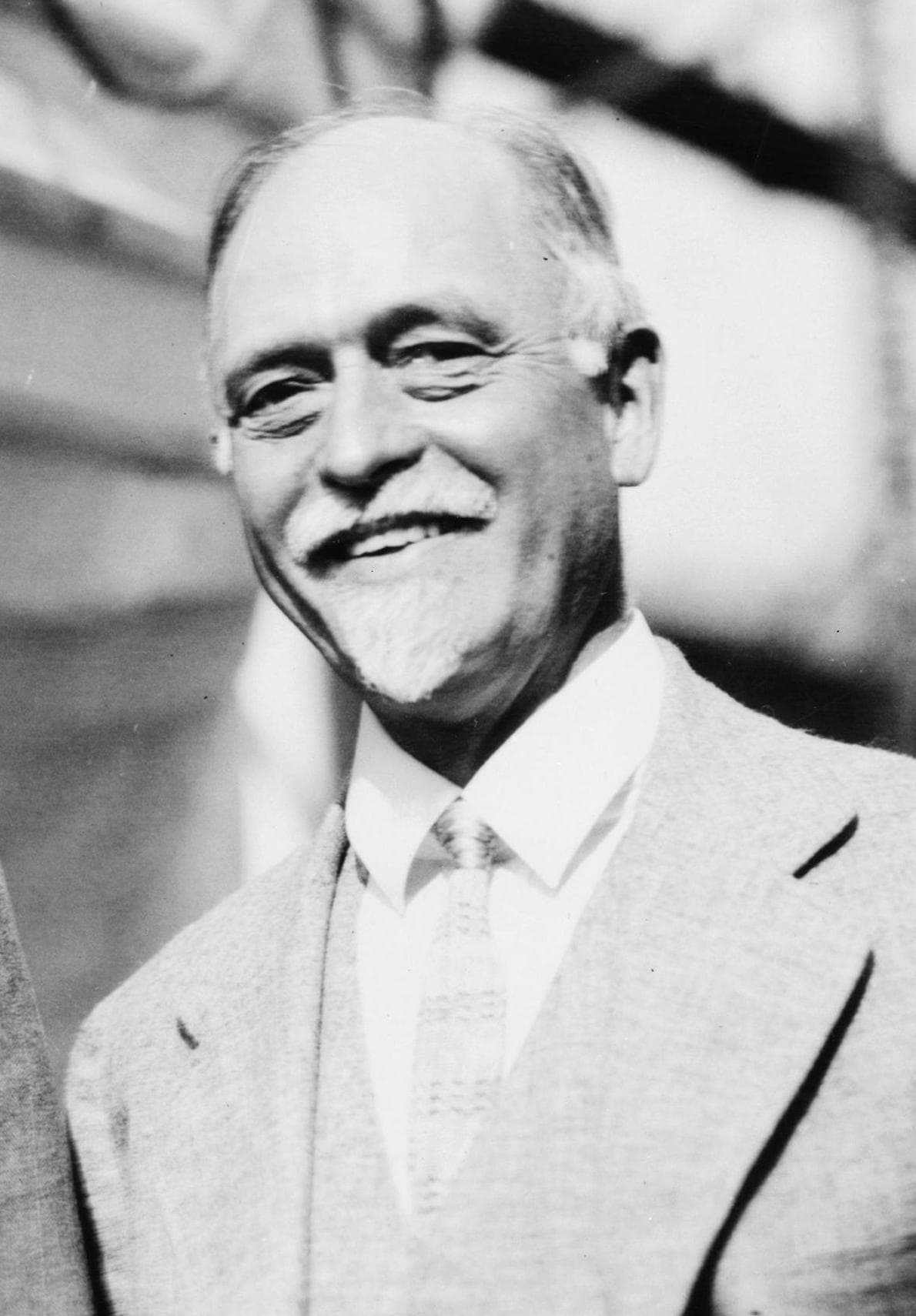

Irving Fisher was an American economist known for his work on interest rates and inflation. He developed the Fisher equation, which links nominal interest rates to real interest rates and inflation. Fisher’s theories on monetary economics laid the groundwork for modern financial economics. Despite some setbacks during the Great Depression, his ideas have had a lasting impact. Fisher’s contributions remain central to understanding inflation and interest rates.
Thorstein Veblen

Thorstein Veblen was an American economist and sociologist who introduced the concept of conspicuous consumption. He critiqued the social and economic practices of the wealthy in his book “The Theory of the Leisure Class.” Veblen’s work explored the relationship between economic behavior and social structures. His ideas influenced both economics and sociology, particularly in the study of consumer behavior. Veblen’s critiques of capitalism continue to resonate today.
Friedrich List
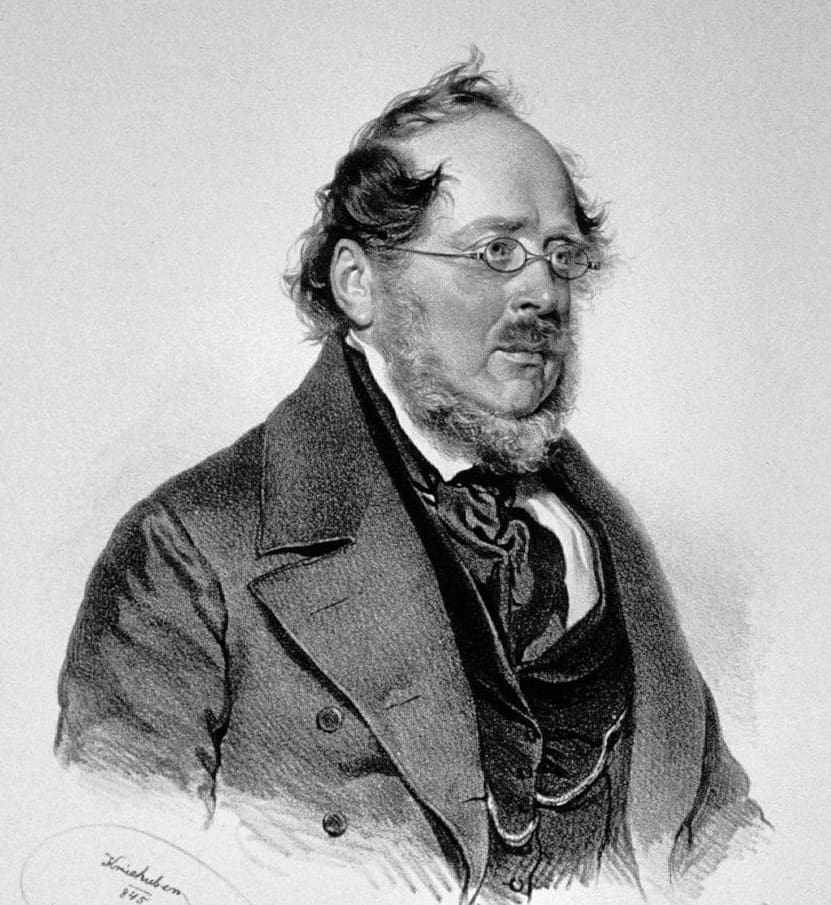
Friedrich List was a German economist who advocated for protectionism and economic nationalism. He argued that nations should protect their industries through tariffs and government intervention until they become competitive. List’s ideas were influential in shaping economic policies in Germany and the United States. His work laid the foundation for the concept of economic development and industrial policy. List’s theories are still relevant in discussions of trade and development.
Arthur Cecil Pigou

Arthur Cecil Pigou was a British economist who developed the concept of externalities. He argued that markets do not always allocate resources efficiently, particularly when external costs or benefits are involved. Pigou’s work laid the foundation for welfare economics and the study of market failures. His ideas have influenced environmental economics, particularly in the design of policies to address pollution. Pigou’s contributions remain central to understanding the role of government in correcting market failures.
This article originally appeared on Rest.orgar.
More from Rarest.org
1943 Washington Quarter Value Guide

The 1943 Washington quarter is made of 90% silver and 10% copper. The same composition was used from 1932 to 1964. Read More.
1944 Liberty Half Dollar Value Guide

Once dubbed as the most beautiful coin in US history, the 1944 Walking Liberty half dollar is undoubtedly a much sought-after collector’s item. Read More.
1942 Mercury Dime Value Guide
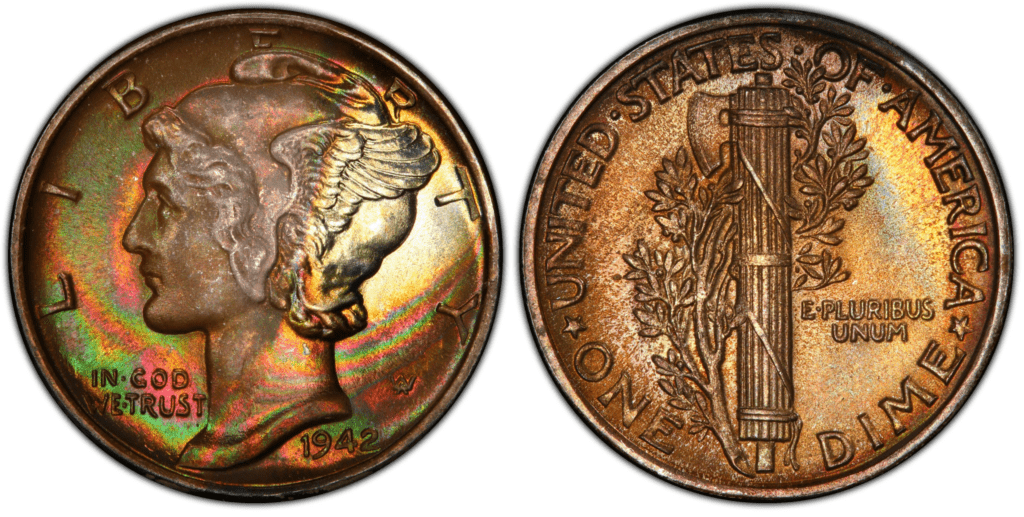

The 1942 Mercury dime, often known as the Winged Liberty Head dime and part of the 90% silver coin series, is a favorite among collectors and dealers. Read More.
