The night sky has always been a source of wonder and mystery, offering more than just the stars and the moon. Beyond the usual celestial sights, there are rare and unusual phenomena that can take your breath away. From the vibrant colors of the Northern Lights to the fleeting appearance of a moonbow, these events are as fascinating as they are beautiful. In this article, we’ll explore some of the most uncommon and awe-inspiring phenomena that can be seen when you look up after dark.
Aurora Borealis (Northern Lights)
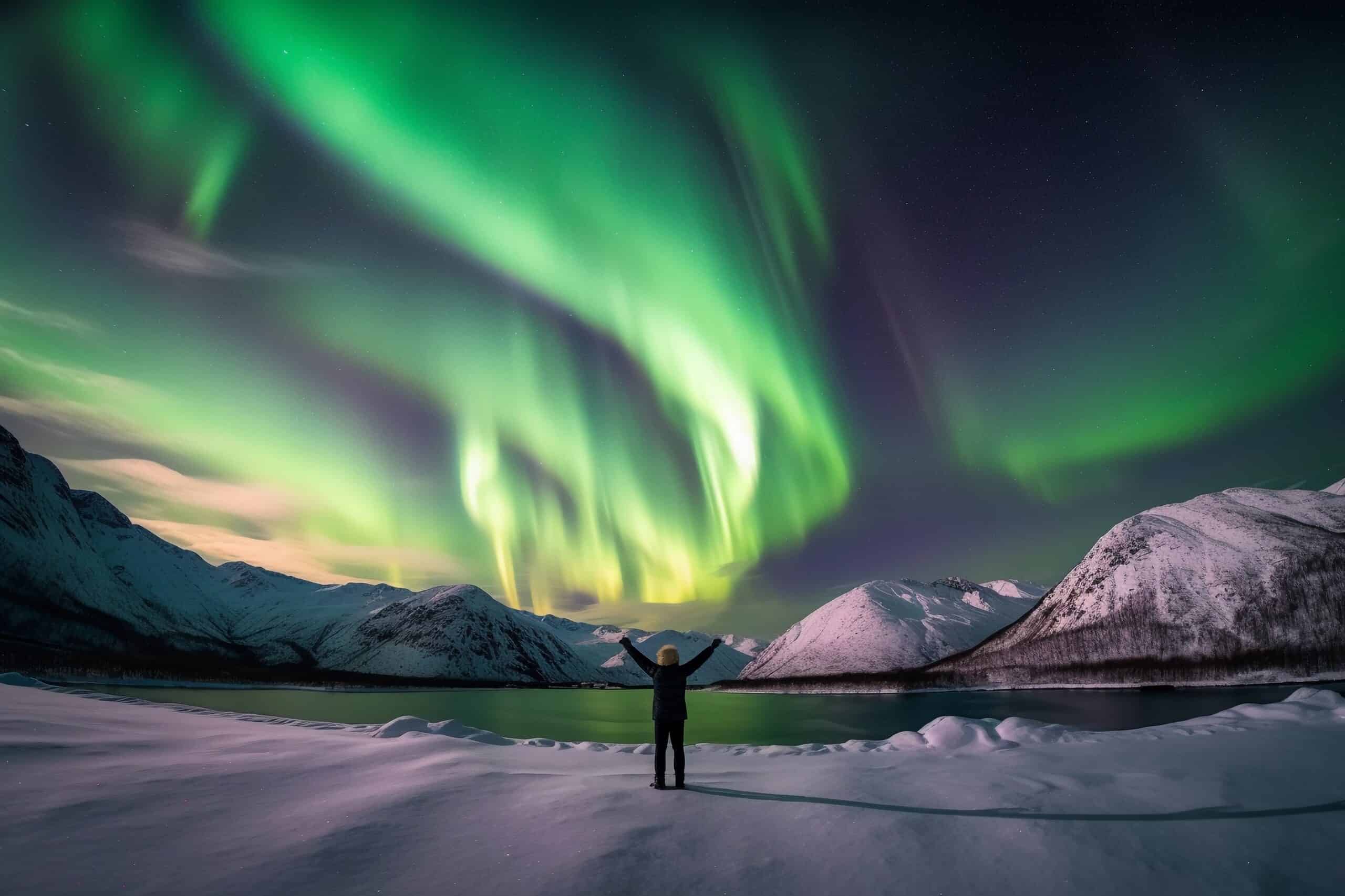

The Aurora Borealis is a dazzling natural light display that occurs near the polar regions. Caused by the interaction between solar wind and the Earth’s magnetic field, these lights create vibrant waves of green, pink, and violet in the sky. The phenomenon is typically visible in high-latitude regions such as Norway, Canada, and Alaska. Though the lights appear as if they’re dancing across the sky, they are actually a complex play of charged particles colliding with atmospheric gases. This breathtaking sight is often sought after by skywatchers and photographers alike.
Aurora Australis (Southern Lights)
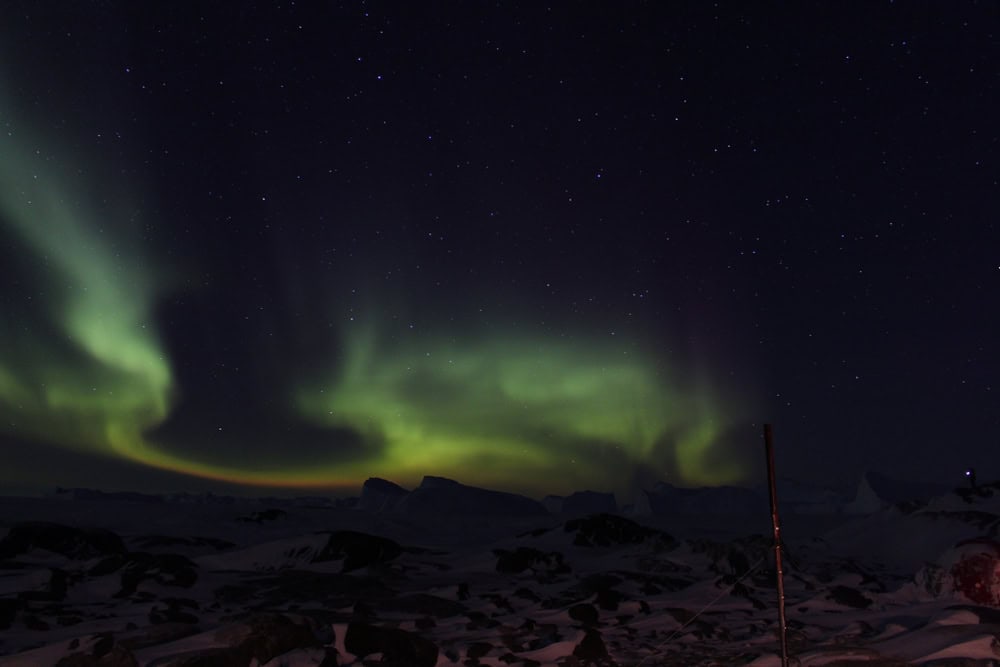

Similar to its northern counterpart, the Aurora Australis illuminates the southern skies with its ethereal glow. This rare phenomenon is best observed from southern latitudes like Antarctica, New Zealand, and Tasmania. Its striking colors and movements are due to the same mechanism that causes the Aurora Borealis. The light display varies in intensity and color, depending on solar activity and atmospheric conditions. Observing the Aurora Australis is a truly unforgettable experience for those fortunate enough to witness it.
Green Flash
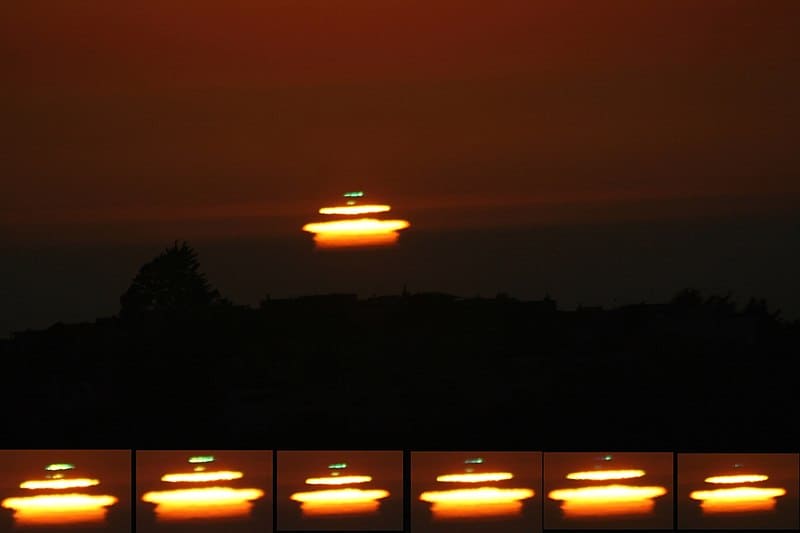

The Green Flash is a fleeting optical phenomenon that occurs just after sunset or right before sunrise. For a brief moment, the top edge of the sun appears green due to the refraction of light in the Earth’s atmosphere. This rare event is best observed from a clear horizon over an ocean or desert. While it only lasts for a few seconds, the Green Flash has inspired countless myths and stories throughout history. Observers need a clear view and quick eyes to catch this elusive sight.
Zodiacal Light
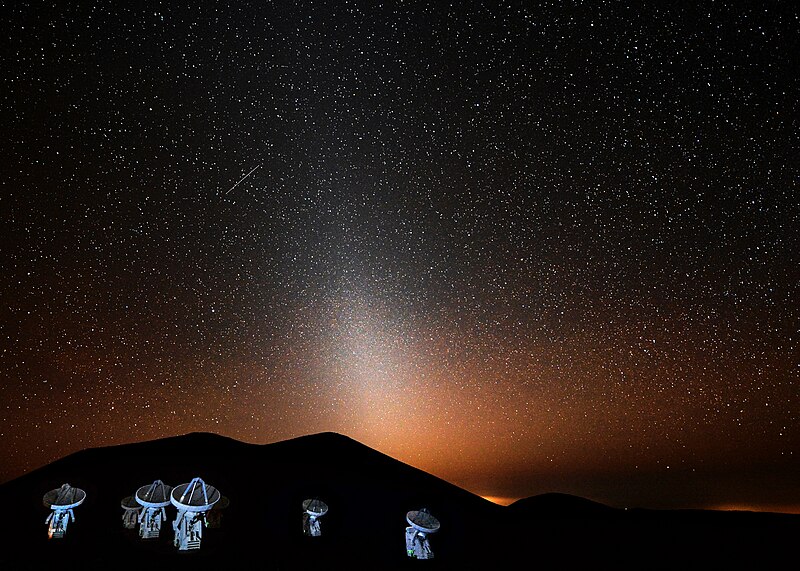

Zodiacal Light is a faint, triangular glow that extends from the horizon along the zodiac in the early morning or late evening sky. It is caused by sunlight scattering off interplanetary dust particles in the solar system. This glow is most visible in regions with dark, clear skies and little light pollution. The phenomenon is best observed during the spring and autumn months when the ecliptic is most perpendicular to the horizon. Stargazers often mistake Zodiacal Light for the Milky Way, but its origin is much closer to home.
Gegenschein
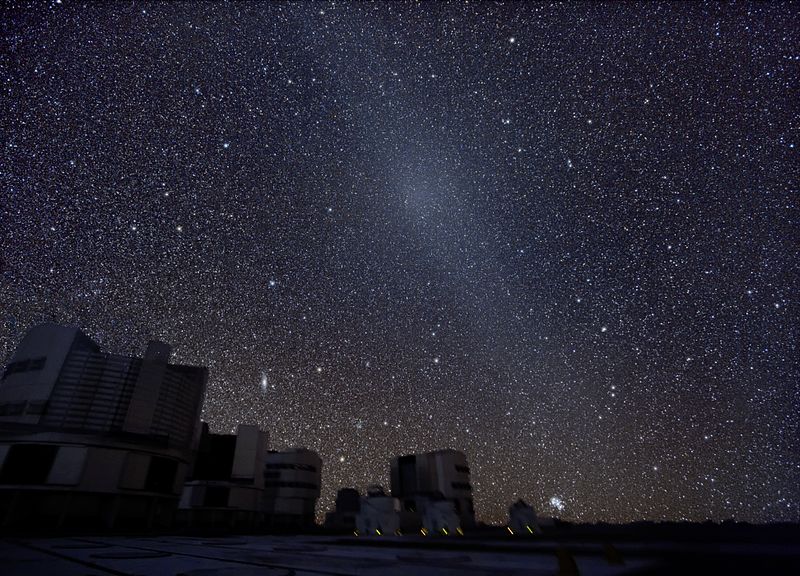

Gegenschein, also known as “counterglow,” is a subtle brightening of the sky directly opposite the Sun, visible only in very dark skies. This glow is caused by sunlight reflecting off dust particles in space, similar to Zodiacal Light but fainter and more diffuse. Gegenschein is best observed in rural areas far from city lights, and even then, it requires a trained eye and ideal conditions. The phenomenon is a reminder of the delicate interplay between light and dust in our solar system. Its elusive nature makes it a rare treat for dedicated skywatchers.
Noctilucent Clouds
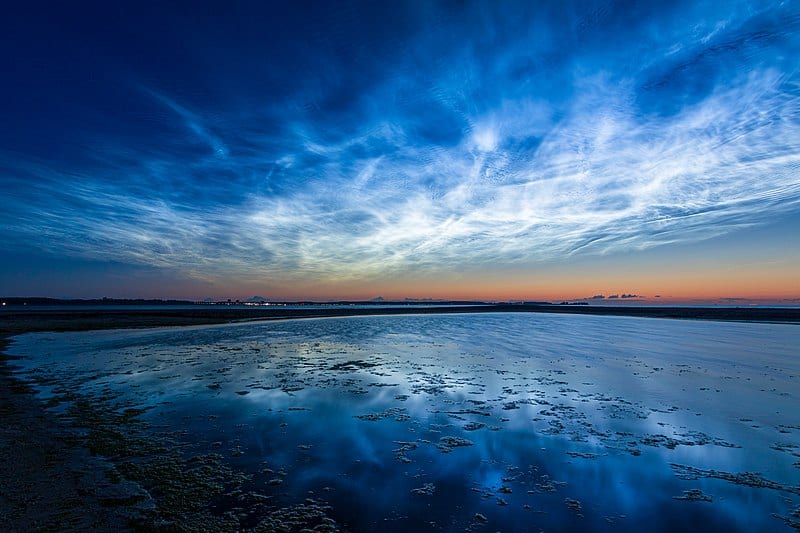

Noctilucent clouds are the highest clouds in the Earth’s atmosphere, located in the mesosphere at altitudes of around 80 kilometers. These clouds are composed of tiny ice crystals that reflect sunlight, making them glow brightly against the darkening sky. They are typically visible during the summer months at high latitudes, just after sunset or before sunrise. Noctilucent clouds are rare and their formation is not fully understood, adding an element of mystery to their appearance. Their shimmering, silver-blue hues create an otherworldly spectacle.
Airglow
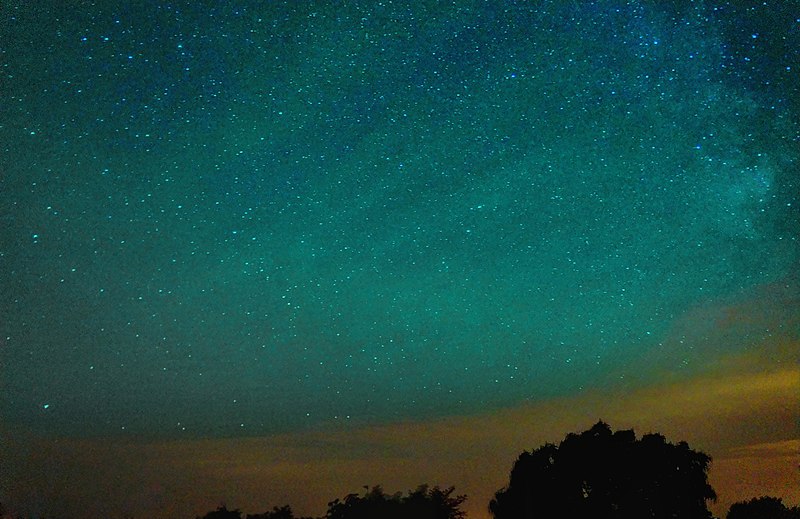

Airglow is a faint emission of light by Earth’s atmosphere, occurring even in the absence of direct sunlight. This phenomenon is caused by various chemical reactions in the upper atmosphere, where atoms and molecules emit light as they return to their ground state. Unlike the Aurora, which is more dynamic, airglow is a constant, subtle glow that can be seen on clear, dark nights. It is most noticeable in remote areas with minimal light pollution. Though often overlooked, airglow contributes to the natural light of the night sky.
Moonbow
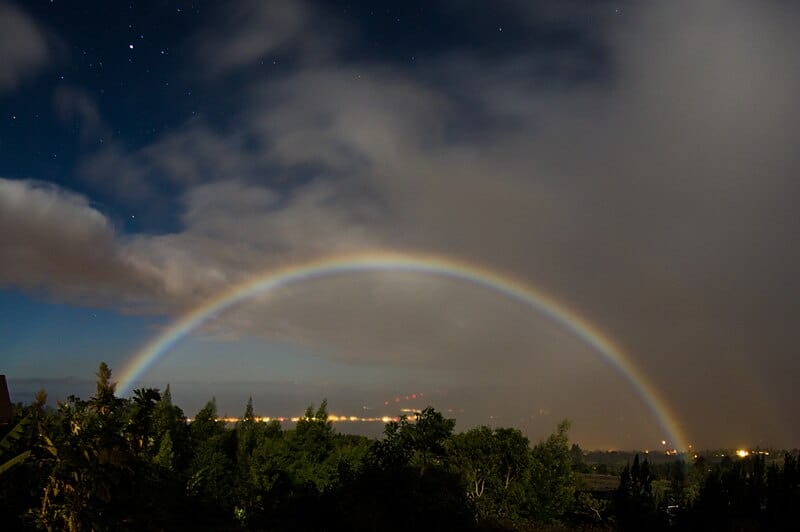

A moonbow, also known as a lunar rainbow, is a rare type of rainbow that occurs at night. It is formed in the same way as a regular rainbow, through the refraction, dispersion, and reflection of light, but the light source is the moon rather than the sun. Moonbows are typically seen in areas with waterfalls or after rainfall when the moon is bright, often near full. The phenomenon appears more white than colorful due to the low light intensity, though some colors may be visible with longer exposure photography. Moonbows are a stunning and elusive sight that many stargazers dream of witnessing.
Earthshine
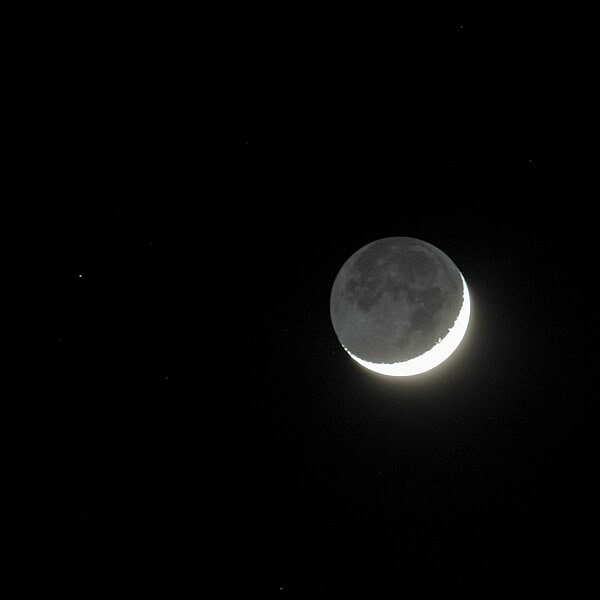

Earthshine is the soft, faint glow visible on the dark side of the Moon, illuminated by sunlight reflected from the Earth. This phenomenon is often called “the old moon in the new moon’s arms” and is most noticeable when the Moon is a thin crescent. Earthshine occurs because the Earth reflects sunlight much more effectively than the Moon, lighting up the lunar surface. The best time to observe Earthshine is during the waxing or waning phases of the Moon. This gentle illumination creates a beautiful and serene view for skywatchers.
Steve (Strong Thermal Emission Velocity Enhancement)
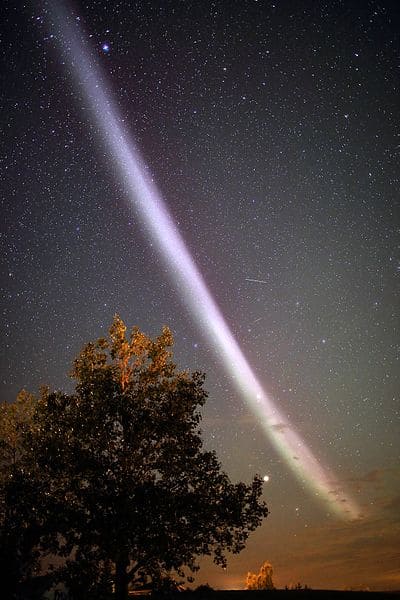

Steve is a recently discovered atmospheric phenomenon that appears as a narrow, purplish arc of light in the night sky. Unlike the Aurora, Steve is not caused by solar wind particles but by streams of fast-moving ions in the Earth’s magnetosphere. The phenomenon was first reported by amateur aurora chasers and later confirmed by scientists. Steve is typically seen in the same regions as the Aurora Borealis but is much rarer. The distinct color and shape of Steve make it a unique and intriguing sight.
Belt of Venus
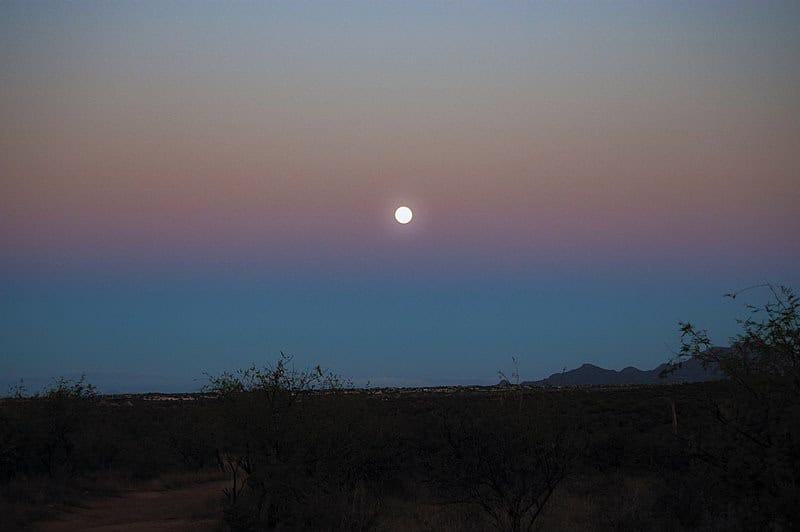

The Belt of Venus is a phenomenon that occurs shortly after sunset or before sunrise, where a pinkish or purplish band appears just above the horizon opposite the sun. This band is caused by the backscattering of reddened sunlight by the Earth’s atmosphere. Below the Belt of Venus, the sky often appears a deeper blue or gray due to the Earth’s shadow. The phenomenon is best observed in clear, flat areas where the horizon is unobstructed. The soft, pastel colors of the Belt of Venus create a beautiful and tranquil atmosphere at twilight.
Lunar Corona
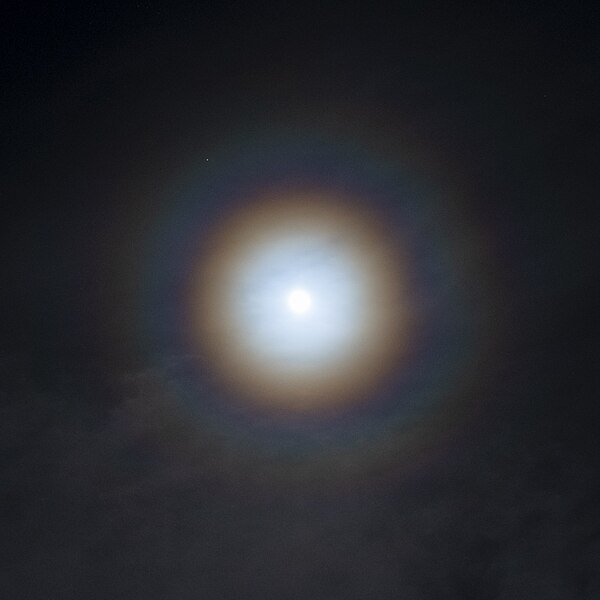

A lunar corona is a rare optical phenomenon where a halo of light, often with faint colors, surrounds the moon. It is caused by the diffraction of moonlight by tiny water droplets or ice crystals in the Earth’s atmosphere. The result is a series of concentric, colorful rings encircling the moon, with the innermost ring typically being bluish-white. Lunar coronas are best observed during thin cloud cover when the moon is bright. This phenomenon adds a mystical quality to the night sky, captivating those lucky enough to see it.
Glory
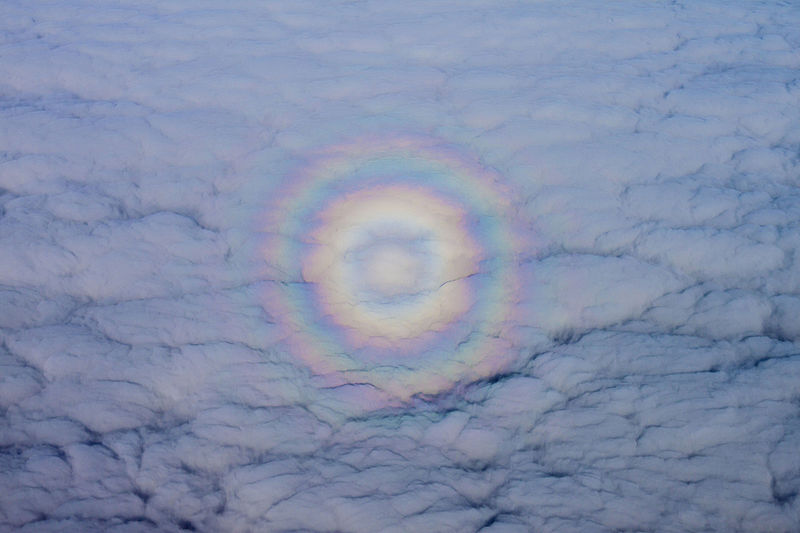
A glory is an optical phenomenon that appears as concentric rings of colored light surrounding the shadow of an observer’s head, typically seen from high altitudes or in misty conditions. It is caused by the diffraction, reflection, and backscattering of light by tiny water droplets. Glories are most often observed by pilots flying above clouds or by hikers on mountaintops looking down into fog. The rings can vary in size and intensity, depending on the observer’s altitude and the size of the water droplets. Glories are a beautiful and rare manifestation of light interacting with the atmosphere.
Red Sprites
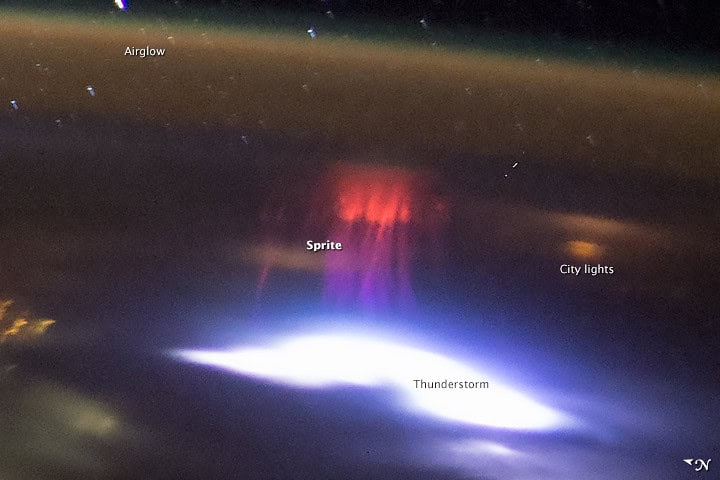

Red sprites are another type of TLE, appearing as large, red flashes above thunderstorms. These electrical discharges occur at altitudes of 50 to 90 kilometers and are usually triggered by positive lightning strikes from the storm below. Sprites can take on various shapes, including jellyfish, carrots, and columns, depending on atmospheric conditions. Like elves, sprites are brief and often difficult to observe without specialized cameras. Their discovery has revealed more about the mysterious electrical activities taking place high above thunderstorms.
Blue Jets
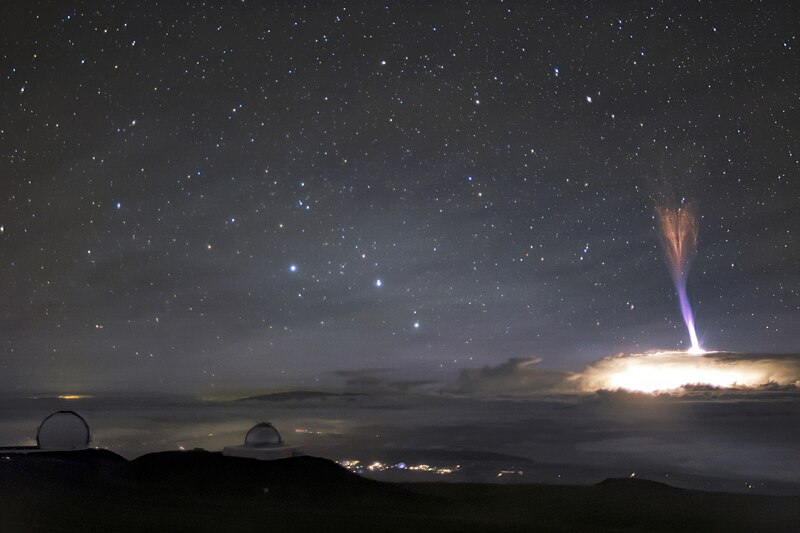

Blue jets are TLEs that occur above thunderstorms, shooting upward from the cloud tops into the stratosphere. They are typically bluish in color and can reach altitudes of up to 50 kilometers. Unlike sprites and elves, which are associated with positive lightning, blue jets are thought to be caused by different mechanisms within the storm. They are rarer and less understood than other TLEs, making them a subject of ongoing research. Observing blue jets is challenging, as they last only a few tenths of a second and are often masked by the brightness of the storm below.
Fire Rainbow (Circumhorizontal Arc)
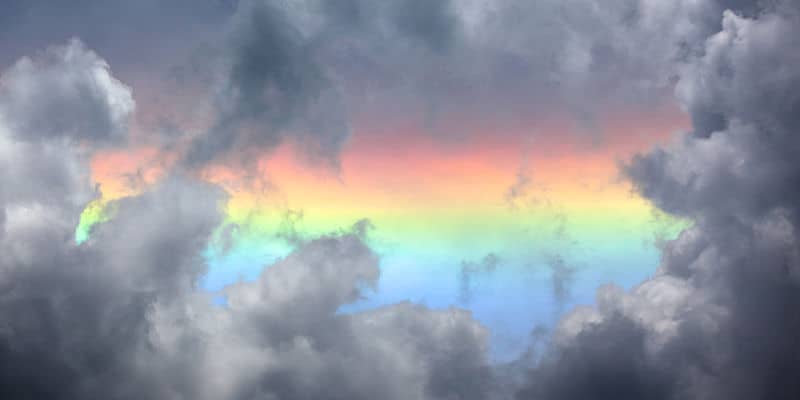

A fire rainbow, or circumhorizontal arc, is a rare optical phenomenon that appears as a multicolored band of light in the sky, parallel to the horizon. It is caused by the refraction of sunlight through ice crystals in high-altitude cirrus clouds. The phenomenon occurs only when the sun is high in the sky, typically during the summer months, and the ice crystals are aligned in a specific way. The resulting arc can resemble a rainbow or flames, hence the name “fire rainbow.” This dazzling display is often mistaken for an actual rainbow, but its formation and appearance are quite different.
Light Pillars
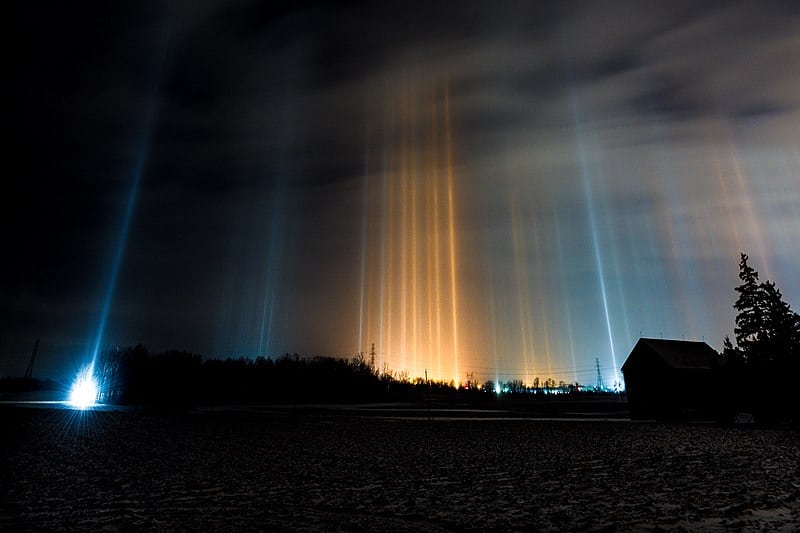

Light pillars are vertical columns of light that appear to extend above or below a light source, usually seen during cold weather. They are caused by the reflection of light from ice crystals in the atmosphere, which act like tiny mirrors. The light source can be the sun, moon, or even artificial lights from buildings or street lamps. Light pillars are best observed in polar regions or during winter in temperate zones. The phenomenon creates a stunning visual effect, with beams of light appearing to stretch into the sky.
Marfa Lights

The Marfa Lights are unexplained lights that appear near the town of Marfa in West Texas. They are described as glowing orbs of various colors that float above the desert, often moving erratically or splitting into multiple lights. The phenomenon has been observed for over a century, yet no definitive explanation has been found. Some theories suggest they are caused by atmospheric reflections, car headlights, or even geological activity. The Marfa Lights remain one of the most mysterious and intriguing night sky phenomena.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More From Rarest.Org
Gold coins have long been prized not just for their intrinsic value but also for their historical significance and beauty. Whether you’re a seasoned collector or an investor looking to diversify your portfolio, certain gold coins offer both solid investment potential and a fascinating glimpse into the past. Read more.
Exploring lost cities offers a fascinating glimpse into ancient civilizations that once thrived and then vanished, often hidden for centuries until rediscovered by modern explorers. These cities, from the dense jungles of Guatemala to the deserts of the Middle East, reveal incredible architectural feats, cultural achievements, and historical mysteries. Read more.
Discovering remote hot springs is like finding hidden gems in nature’s treasure trove. These secluded spots offer not just breathtaking scenery but also healing waters rich in minerals. Read more.



