The universe is filled with wonders that stretch the boundaries of our understanding, with some phenomena still leaving scientists mystified. From black holes speeding through space to planets that roam without stars, each discovery brings new questions about how the cosmos works. While we’re learning more every day, many of these oddities defy easy explanations, keeping astronomers searching for answers. Some may hint at forces we’re just beginning to uncover, while others might reveal unexpected behaviors in stars, galaxies, or even the very fabric of space. As technology advances, our view of the universe expands, but the mysteries only grow deeper. Here, we dive into some of the strangest phenomena in space that continue to puzzle even the most seasoned experts.
The Runaway Black Hole
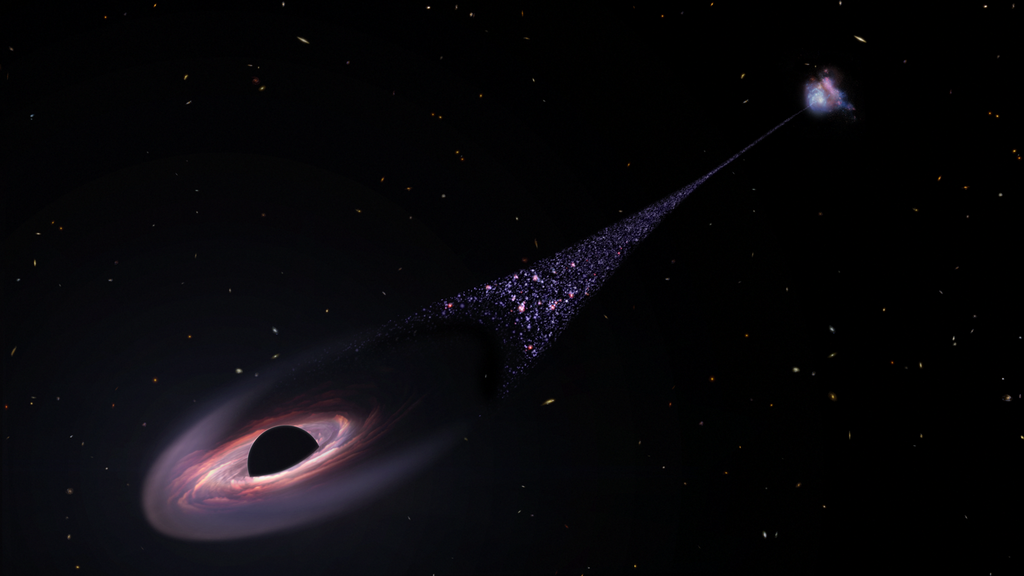
In 2023, astronomers observed an extraordinary event: a “runaway” black hole moving away from its galaxy at unprecedented speed. This colossal black hole, believed to be around 20 million times the mass of our Sun, is speeding through space at 4,500 times the speed of sound. Trailing behind it is a bright stream of stars stretching over 200,000 light-years, believed to have formed in its wake. It likely got “kicked” from its home by interactions with other black holes or galaxies in a complex gravitational dance. As black holes are generally gravitational anchors within galaxies, observing one on the run has baffled scientists. They think it was once in a binary orbit with another black hole until a third joined, causing one to be expelled. Confirming this would show that black holes are capable of breaking free and venturing independently through space, something scientists had previously only speculated. This unprecedented discovery sheds light on the interactions of black holes within galaxies. Astronomers continue to study this rogue black hole for further clues about galactic dynamics and black hole physics.
Odd Radio Circles (ORCs)
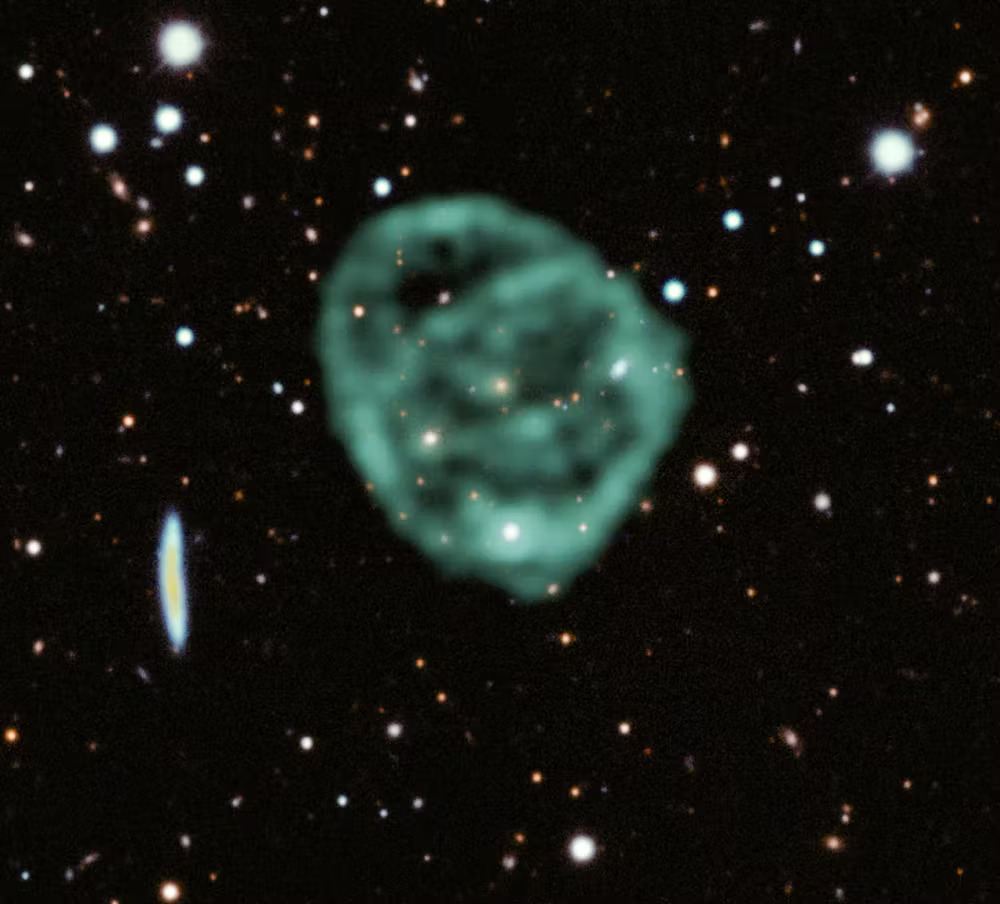
Astronomers have detected unusual structures called Odd Radio Circles (ORCs), which are large, mysterious rings of radio waves. First discovered in 2019 by the Australian Square Kilometer Array Pathfinder, they are rare, with only a handful spotted in deep space. Each ORC is roughly one million light-years in diameter and displays a distinct, circular radio pattern visible only through radio telescopes. Researchers are still uncertain about their origin, with some theories suggesting they might be shockwaves from galactic events, like the merger of supermassive black holes. However, this hypothesis remains unproven, and they continue to puzzle scientists. Another idea is that these circles result from unusual stellar explosions or magnetic field phenomena. Despite their mystery, they have sparked significant interest, as they could represent new structures previously unseen in the cosmos. Scientists are hopeful that future discoveries will reveal more of them, allowing them to determine a common factor or event that causes these strange formations. Advanced telescopes under construction may be instrumental in solving this cosmic enigma.
The Fermi Bubbles
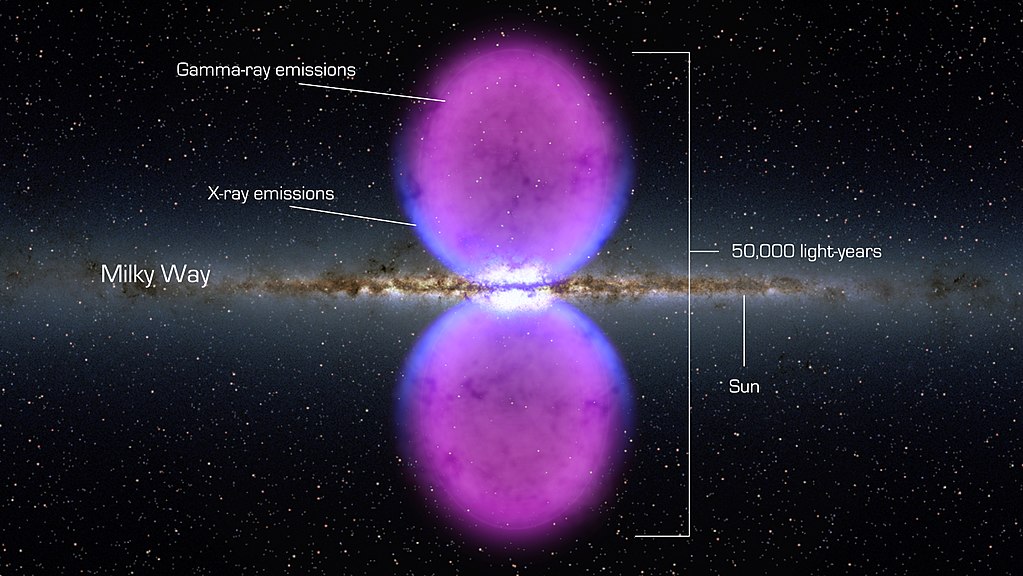
In 2010, scientists using NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope discovered enormous, bubble-like structures extending from the Milky Way’s center. Named Fermi Bubbles, these two bubbles span about 50,000 light-years and are visible only in gamma-ray wavelengths. They are believed to be remnants of a powerful event in the galaxy’s past, possibly an explosion caused by the supermassive black hole at the Milky Way’s core. The energy required to create these bubbles would have been enormous, but the exact cause remains a mystery. One theory posits that they resulted from intense star formation activities, releasing vast quantities of energy and cosmic rays. Despite this, the true origin of the Fermi Bubbles is still a puzzle, as no similar phenomenon has been observed in nearby galaxies. Their symmetrical shape and size suggest a dramatic, organized event rather than a random cosmic burst. Scientists are investigating whether black hole activity or other galactic interactions could produce similar gamma-ray structures elsewhere. Continued studies are key to determining whether they are unique to our galaxy.
Dark Matter

One of the most enduring mysteries in astronomy, dark matter makes up about 25% of the universe, yet it remains unseen and undetectable by conventional telescopes. It is inferred from its gravitational effects on galaxies and stars, as it neither emits nor absorbs light. This mysterious substance is thought to be composed of particles that interact differently than regular matter, explaining its elusive nature. While scientists have proposed various candidates for dark matter particles, none have been confirmed, leaving its composition unknown. Observations show that it plays a crucial role in galaxy formation and stability, affecting how stars cluster and move. Without it, galaxies as we know them would not exist, as there wouldn’t be enough gravitational force to bind stars together. Its existence is one of the major pieces missing in our understanding of the cosmos. Researchers continue to develop new methods to detect it directly, hoping to solve one of the universe’s most profound mysteries. Despite decades of research, this invisible substance remains one of the most enigmatic components of the universe.
The Moon’s Magnetic Field
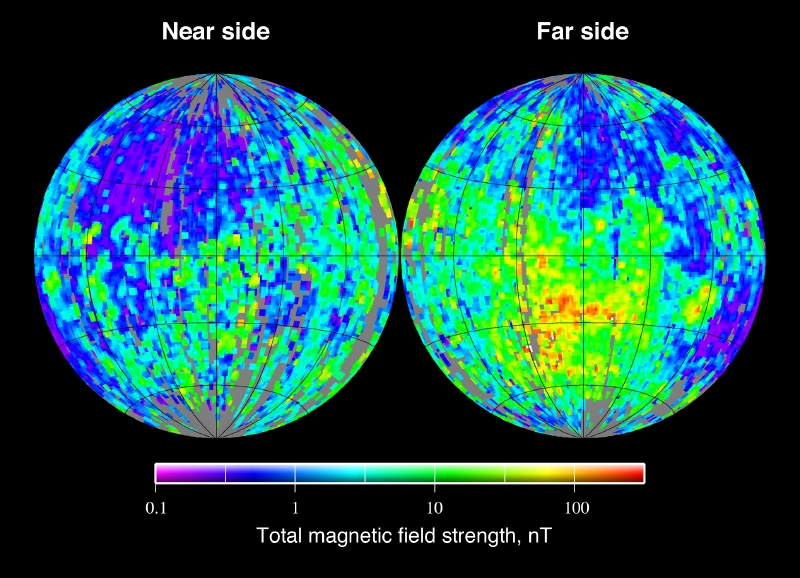
The Moon’s magnetic field has long baffled scientists, as only parts of its crust seem to retain magnetic properties. Unlike Earth, the Moon lacks a strong global magnetic field, yet certain areas show evidence of past magnetism. Some researchers theorize that this residual magnetism could be due to ancient asteroid impacts that heated and magnetized parts of the lunar surface. Others suggest the magnetic field may have resulted from smaller, isolated regions with volcanic activity. Recent computer simulations propose that a large asteroid collision roughly 4.5 billion years ago may have scattered magnetic materials across the Moon’s surface. The remnants of this impact could explain the magnetic field inconsistencies found today. Still, the origins of these magnetic anomalies are unclear, as no large-scale lunar magnetic field appears to exist now. Future missions to it may provide clues about the cause of its partial magnetism, helping scientists understand more about planetary magnetic fields.
The Great Attractor
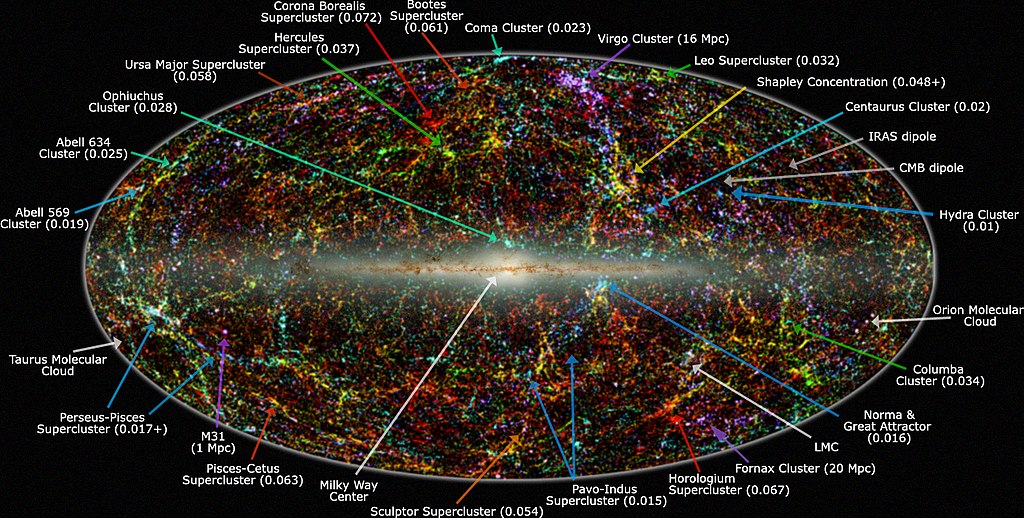
The Great Attractor is an enormous gravitational anomaly that pulls galaxies, including our own, toward a region of space known as the “Zone of Avoidance.” Located roughly 150 million light-years away, it has a gravitational force so strong that it influences the movement of galaxies over vast distances. Despite its effect on galactic motion, the exact nature of it remains unknown due to the dense clouds of gas and dust in the Milky Way’s plane, which obscure it from view. Scientists suspect it might be a dense cluster of galaxies, though its scale and composition are difficult to determine. Theories include a supercluster of dark matter or massive galactic structures that create a gravitational pull. Advanced infrared and X-ray telescopes have allowed for limited observations, yet it remains mysterious. Scientists hope future telescopes will allow them to peer through the galactic plane and uncover what truly lies at the heart of this cosmic anomaly.
Rogue Planets

Rogue planets, or free-floating planets, are worlds that wander the galaxy without orbiting a star. Detected in the Milky Way and beyond, they exist independently, likely ejected from their home star systems. Recent observations suggest there could be trillions of them in our galaxy alone. The James Webb Space Telescope recently discovered hundreds of Jupiter-sized rogue planets, raising questions about how they form and survive in the cold of interstellar space. Some theories suggest they may have formed from collapsing gas clouds, similar to stars, but on a smaller scale. They are difficult to detect due to their faint visibility, as they don’t reflect light from a nearby star. They remain one of space’s strangest mysteries, challenging our understanding of planetary formation. Further studies on them may provide insights into the early chaotic dynamics of star systems, revealing why some worlds are forced into isolation.
Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs)
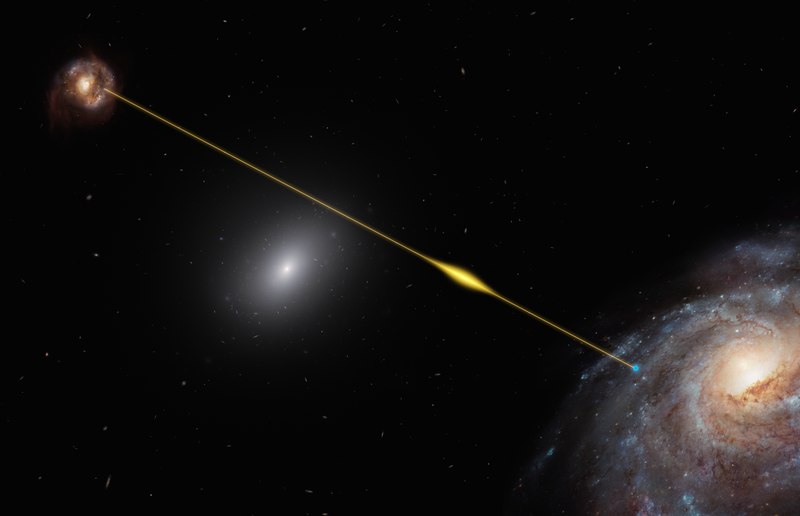

Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) are powerful, millisecond-long pulses of radio waves detected from distant galaxies. Discovered in 2007, they are among the most intense sources of radio energy in the universe, yet their origins remain largely unknown. Some are one-time events, while others repeat, suggesting different possible sources. Theories for their origin include neutron stars, magnetars, or even exotic phenomena like colliding black holes. Despite numerous detections, each one seems to have a unique signature, complicating attempts to classify them. In recent years, scientists have identified repeating patterns in certain FRBs, hinting at possible periodic events or sources. Yet, without a consistent pattern among all of them, understanding their cause remains a complex challenge. Further monitoring of these may unlock clues about their sources, helping scientists decipher one of the universe’s most intense phenomena.
Galactic Recycling
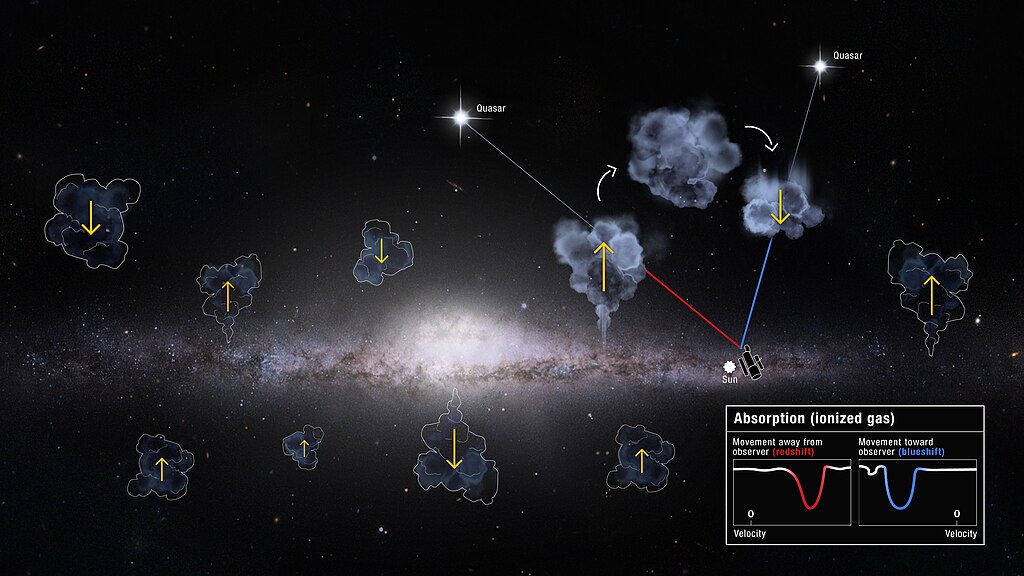
Galaxies like the Milky Way seem to produce new stars at a rate that would exhaust their gas reserves, yet they continue to thrive. This phenomenon, known as galactic recycling, suggests that galaxies may reuse gas they once expelled. Astronomers have observed flows of gas falling back into galaxies, refueling star formation processes and allowing them to “recycle” their materials. Some researchers believe that supernovae and stellar winds expel gas, which later cools and returns, supplying fresh material. This recycled gas is pulled back by galactic gravity, sustaining star formation cycles that could otherwise deplete. It offers a way for galaxies to continue creating stars beyond their estimated capacity. The process adds a new layer to our understanding of galaxy evolution, showing how matter in the universe may circulate. As telescopes become more advanced, astronomers hope to observe galactic recycling in action, providing insights into how galaxies sustain themselves across billions of years.
Gravitational Waves

Gravitational waves are ripples in spacetime caused by extreme cosmic events, such as merging black holes or neutron stars. First predicted by Einstein’s general theory of relativity, gravitational waves went undetected until 2015 when the LIGO observatory captured them for the first time. They provide a new way to observe the universe, as they can travel through matter undisturbed, unlike light. As gravitational waves pass, they subtly compress and stretch space, detectable by precise instruments on Earth. Their discovery has opened a new field of astronomy, allowing scientists to study events previously hidden, like black hole collisions. The observations of these have confirmed aspects of relativity, providing a deeper understanding of cosmic phenomena. Each wave detected offers insights into the most violent and energetic events in the universe. Future improvements in gravitational wave observatories will allow scientists to explore these ripples in even greater detail, potentially uncovering new aspects of space and time.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More from Rarest.org
16 Unique Marine Creatures Found in the Deepest Oceans

The deep ocean is one of the most mysterious and unexplored places on Earth, home to a fascinating array of marine creatures that have adapted to survive in its extreme conditions. From the eerie glow of bioluminescent fish to the ancient, armor-like shells of deep-sea crabs, these creatures are as unique as they are remarkable. Read More.
22 Eye-Catching Fish Species Found in Coral Reefs

Coral reefs are home to some of the most vibrant and diverse fish species in the world. These underwater ecosystems showcase a kaleidoscope of colors and fascinating behaviors that captivate anyone who visits. Read More.
15 Most Notable Scientific Discoveries in History

Throughout history, countless scientific discoveries have transformed the way we understand the world and shaped the course of human progress. From breakthroughs in medicine to revolutionary theories in physics, these discoveries have not only solved complex mysteries but also laid the groundwork for future innovations. Read More.
