In the vast expanse of the universe, stars fill the night sky with their steady glow. Yet, among the countless stars we see, some are extraordinarily rare, presenting unique characteristics and intriguing mysteries. This article explores the 12 rarest types of stars, each a cosmic marvel in its own right, revealing the diversity and wonder of the celestial bodies that light up our galaxy. From the turbulent magnificence of hypergiants to the enigmatic nature of neutron stars, join us on a journey through the most unusual stars in the cosmos
Wolf-Rayet Stars
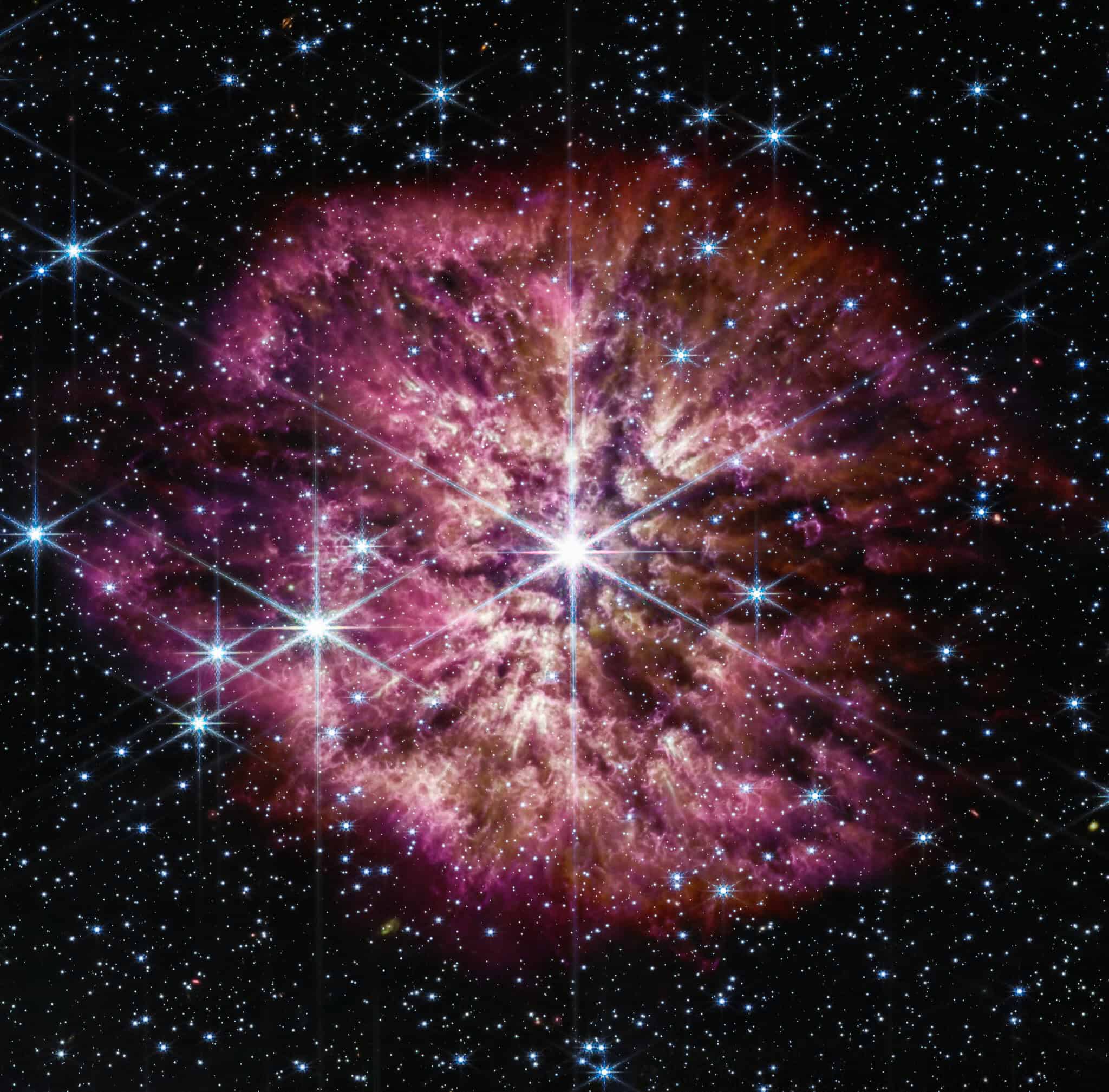

Wolf-Rayet stars are among the rarest and most massive stars in the universe, characterized by their strong stellar winds and extremely high temperatures. These stars have shed much of their hydrogen, exposing the hotter, inner layers that burn heavier elements like carbon and oxygen. They often signal the final stages before a supernova, and their scarcity is due to their short lifespan and the specific conditions required for their formation.
Magnetars

Magnetars are a type of neutron star with the most powerful magnetic fields known in the universe, billions of times stronger than any man-made magnet. These rare stars are thought to form from the supernovae of massive stars. Their extreme magnetic fields heat the surface to up to 18 million degrees Fahrenheit and power intense bursts of X-rays and gamma rays.
Blue Stragglers
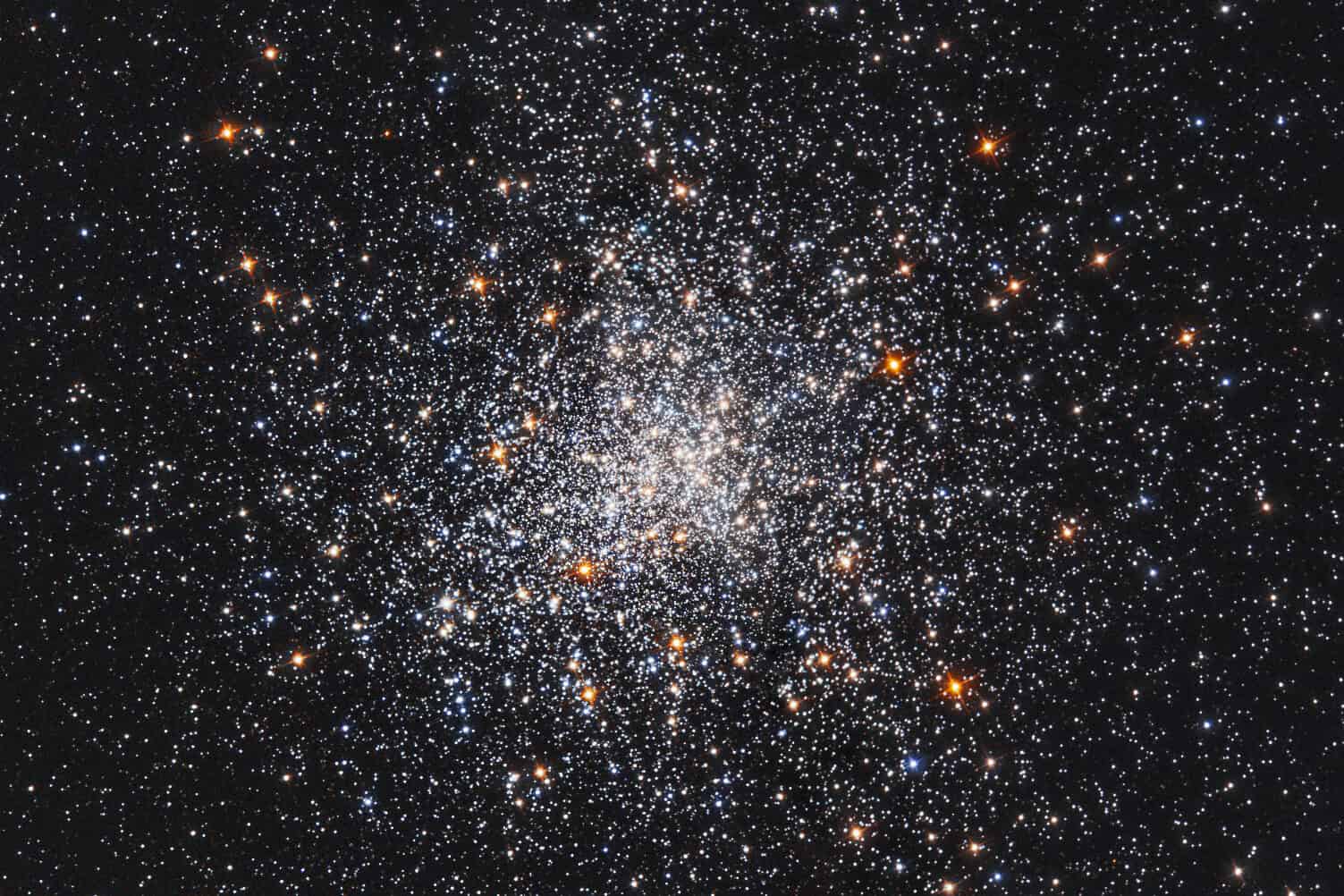

Found in globular clusters and some open clusters, blue stragglers appear younger and more luminous than the other stars in their environment. They are thought to form through interactions with other stars, either by colliding and merging with another star or by drawing material off a companion star, giving them a “second life” that makes them stand out as anomalously young.
Carbon Stars

Carbon stars are a rare type of asymptotic giant branch star whose atmosphere contains more carbon than oxygen, which results in the formation of carbon compounds such as soot, leading to a strikingly red appearance. They represent a brief and unusual phase in the life cycle of a dying star where nuclear fusion creates an excess of carbon.
Neutron Stars
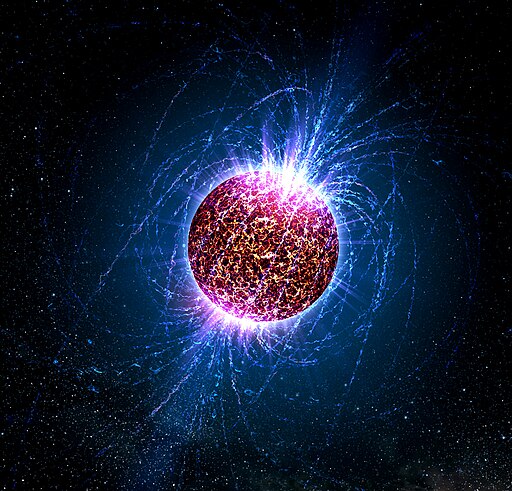

Neutron stars are the remnants of large stars that have undergone a supernova explosion. They are incredibly dense, with a teaspoon of neutron star material weighing about 6 billion tons. Neutron stars are rare due to the specific mass range needed for their formation, making them extraordinary laboratories for studying the laws of physics under extreme conditions.
White Dwarfs
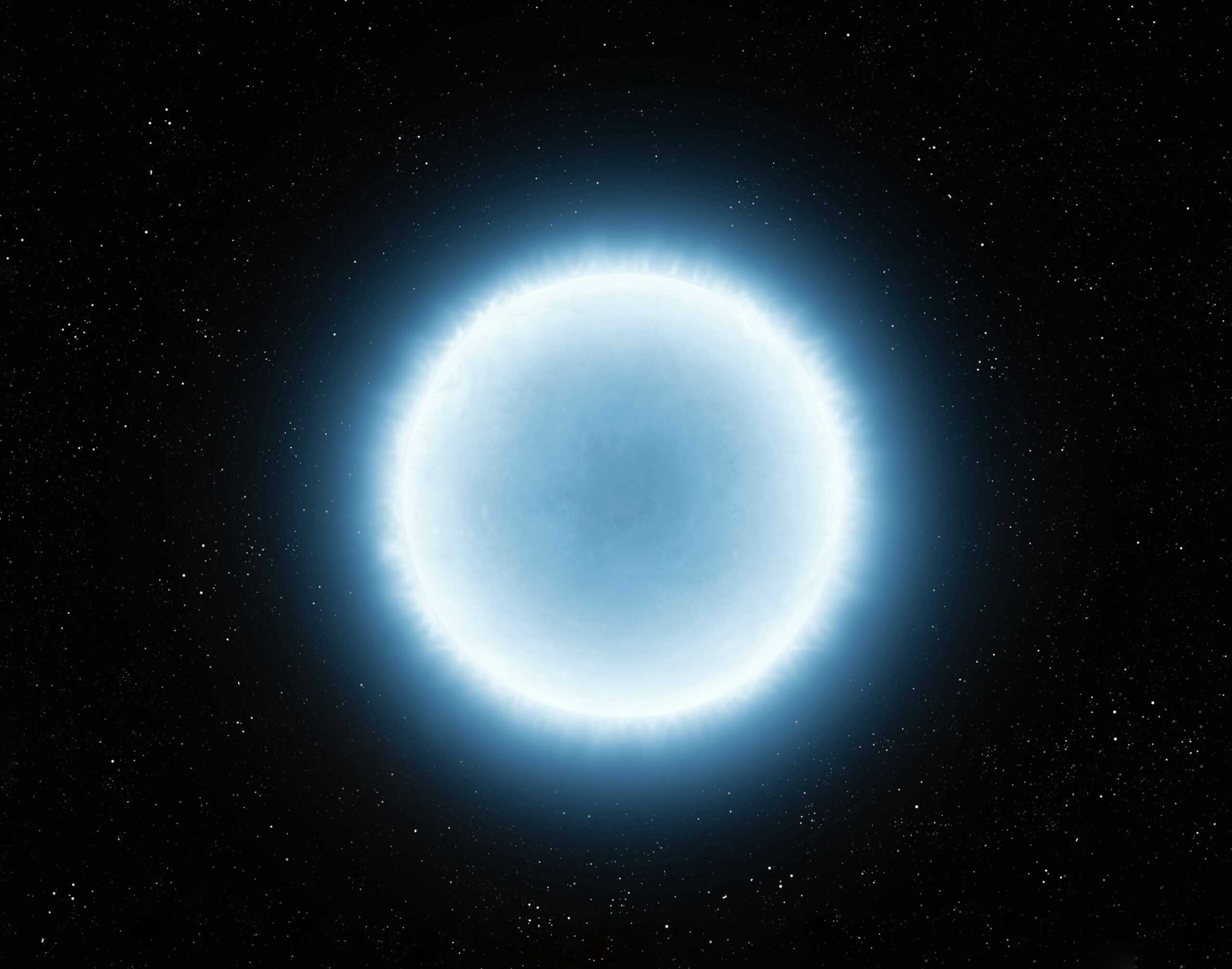

Although more common than some of the other star types on this list, white dwarfs are fascinating due to their role in understanding stellar evolution. These are the remnants of medium-sized stars that have exhausted their nuclear fuel and shed their outer layers. They are characterized by their small size but high density and gradually cool and fade over billions of years.
Hypergiants
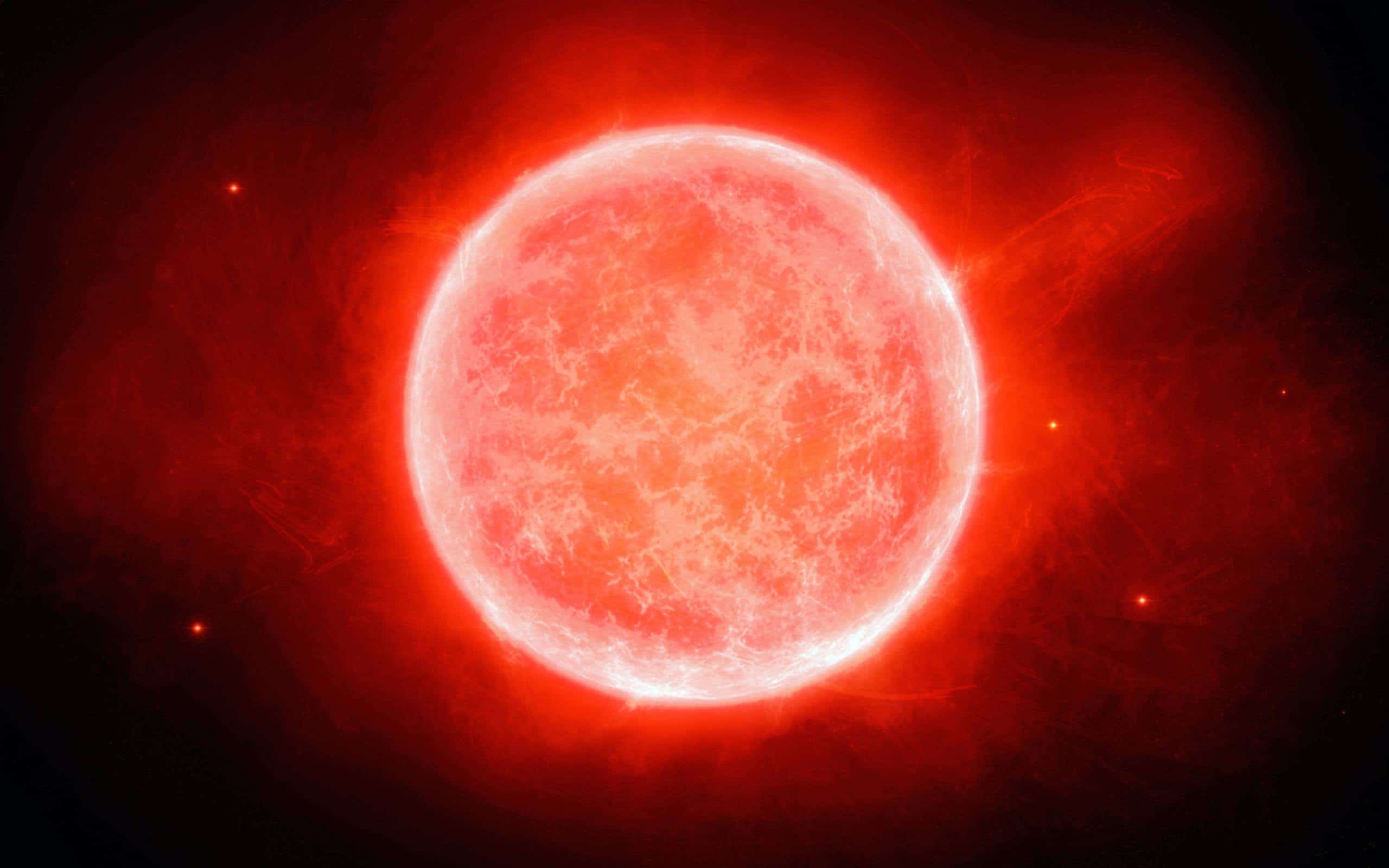
Hypergiants are exceedingly rare due to their extreme luminosity, mass, and size, which place them at the upper limits of stellar evolution. These stars live fast and die young, often leading to spectacular supernovae. Hypergiants like Eta Carinae can be millions of times as luminous as the Sun and exhibit complex and violent changes in their atmospheres.
Cepheid Variables
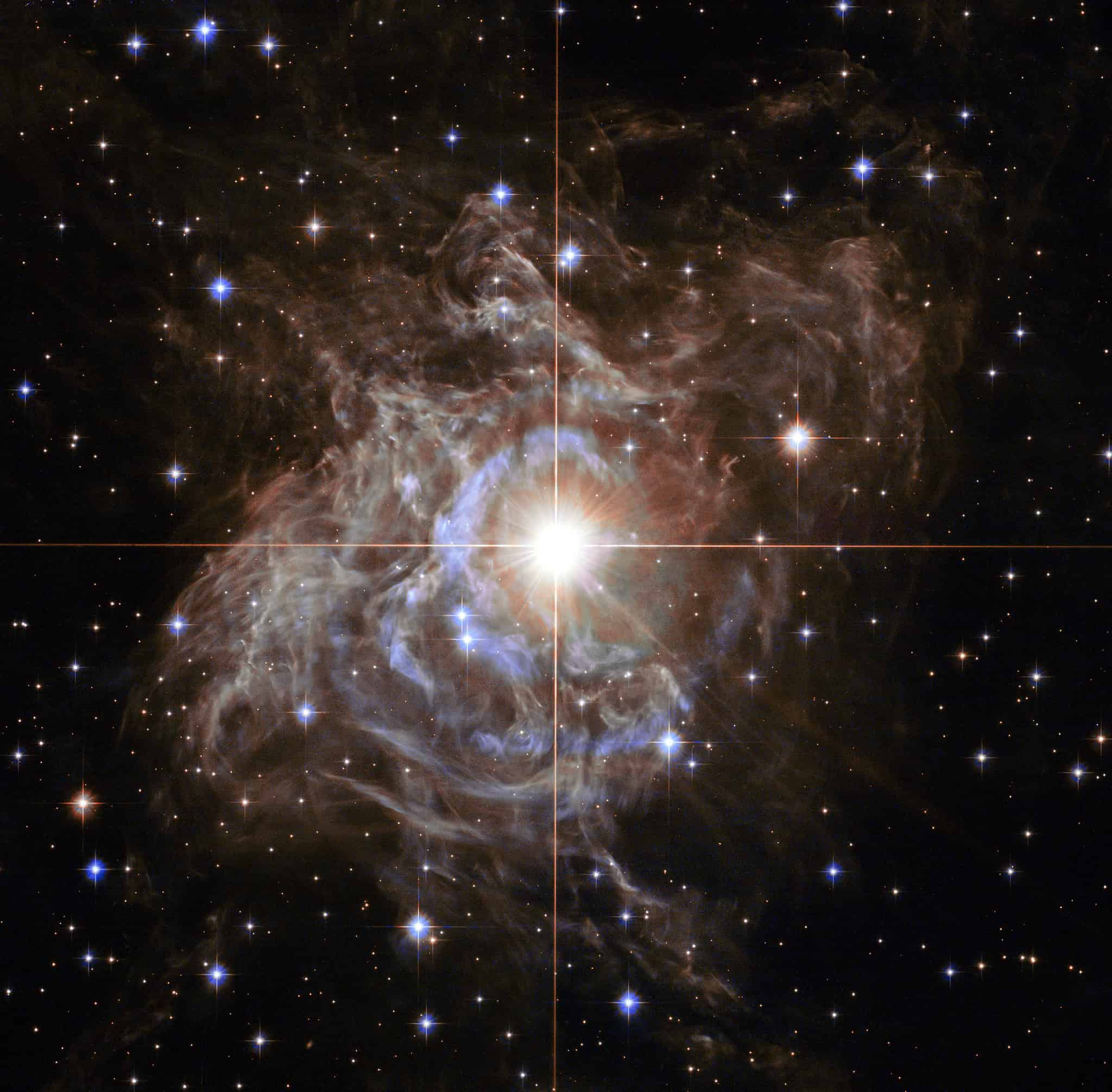

Cepheids are a rare type of star known for their pulsations, which have periods ranging from days to months. These stars expand and contract in a regular pattern, making them crucial as standard candles for measuring cosmic distances. Their rarity is due to the precise conditions needed for a star to enter the pulsation phase of its life cycle.
R Coronae Borealis Stars
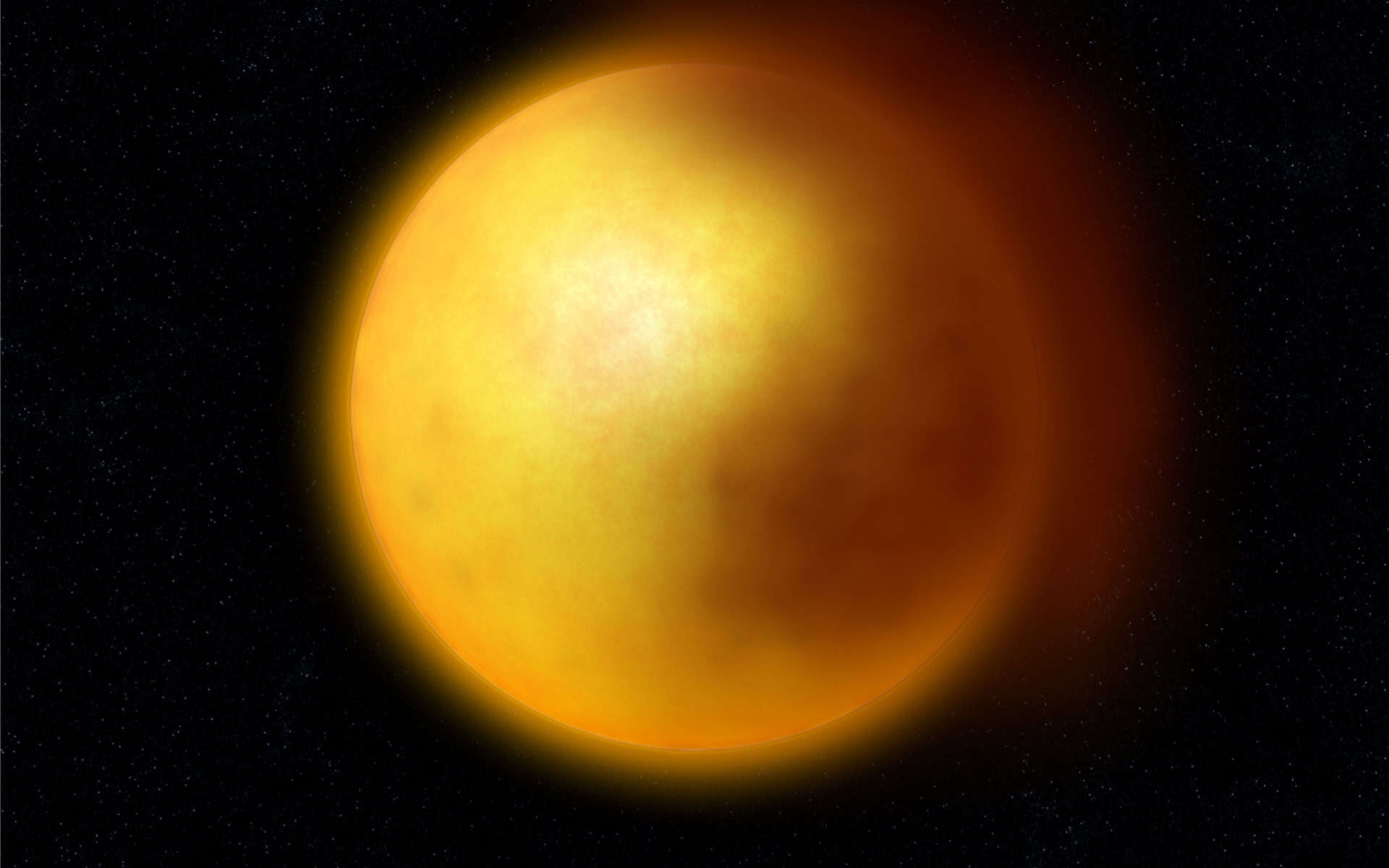

These rare stars are notable for their irregular and dramatic decreases in brightness, dropping as much as several magnitudes for periods from months to years. This phenomenon is caused by clouds of carbon dust formed in the star’s atmosphere, obscuring the star from view.
OH/IR Stars
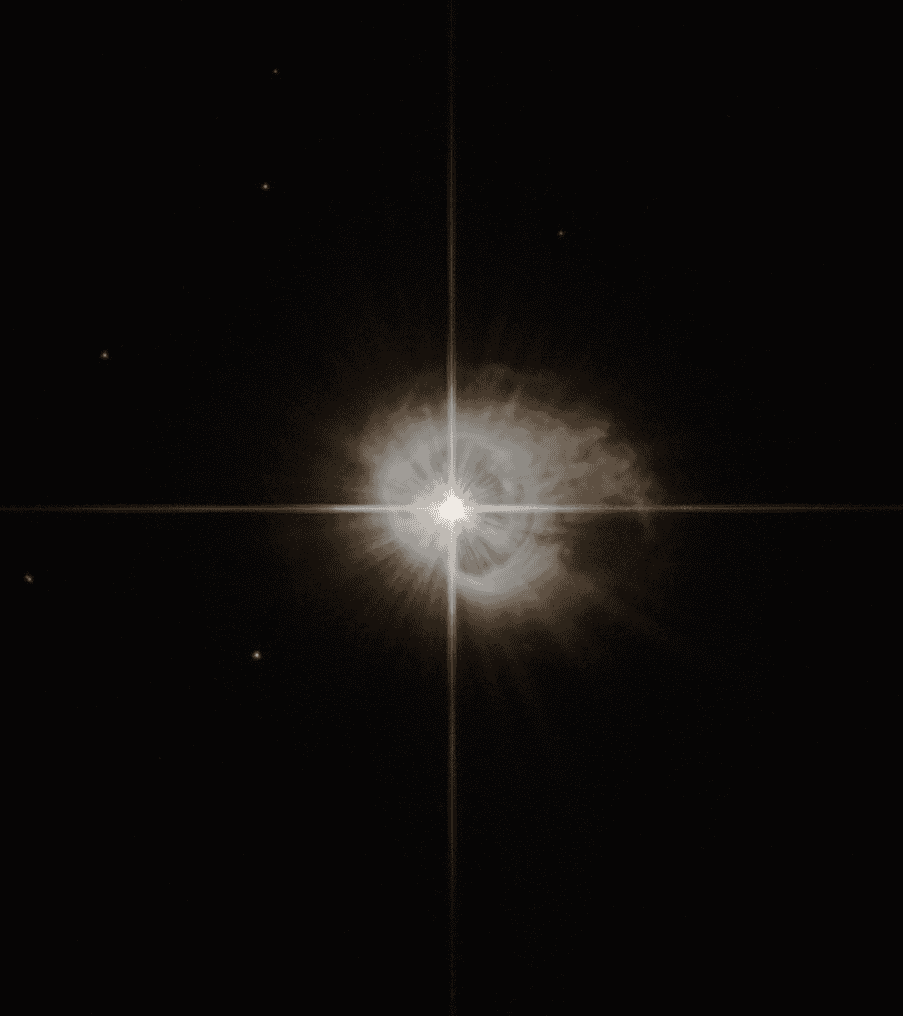

These are a late type of Mira variable stars with extremely strong oxygen-hydroxyl emission lines in their spectra. They are enveloped in thick dust shells that they have ejected, and they are significant contributors to the dust found in the galaxy. OH/IR stars represent a short-lived transitional phase in the life of low to intermediate-mass stars.
Luminous Blue Variables
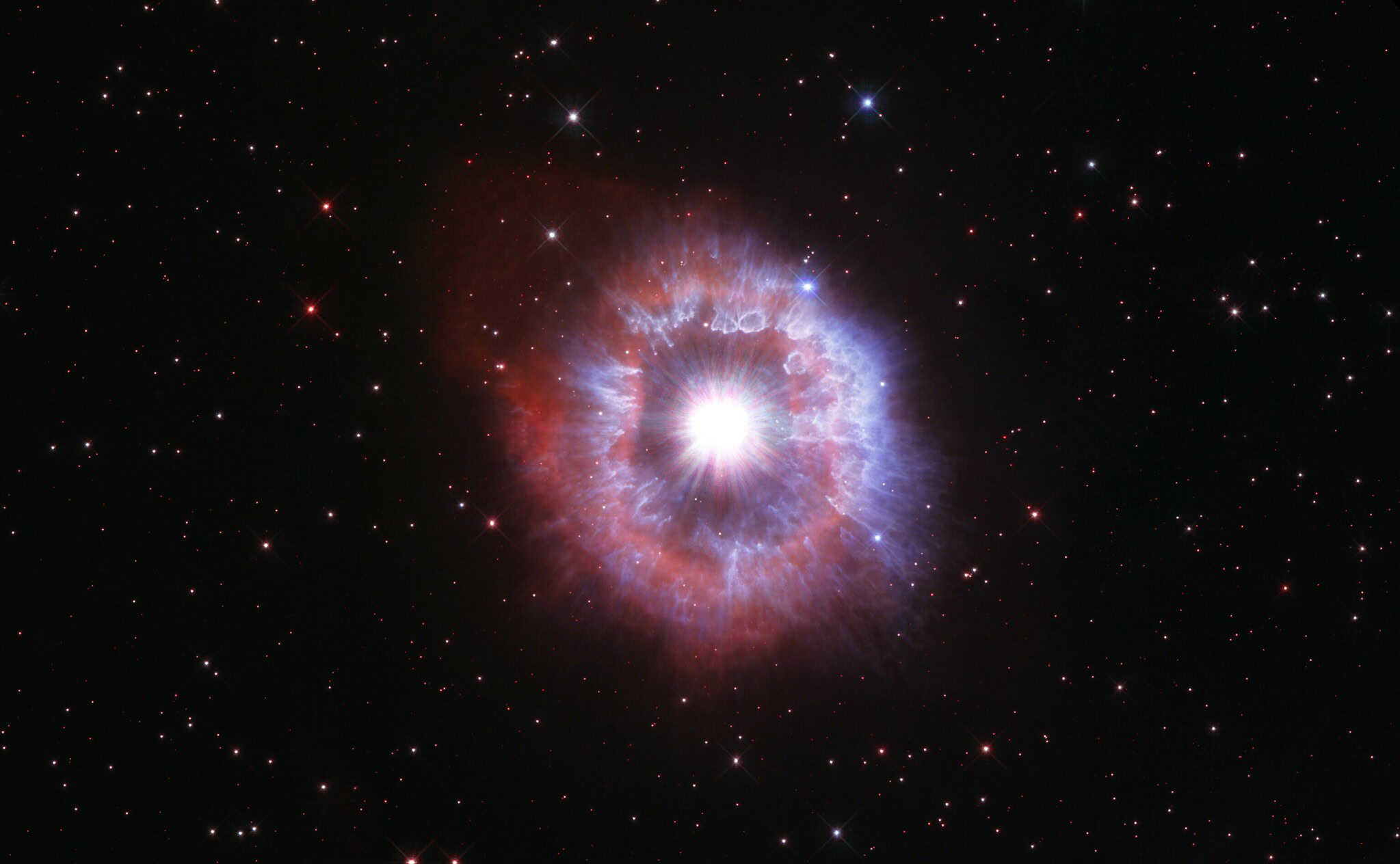
Luminous blue variables (LBVs) are massive stars that experience extreme changes in brightness and mass loss through violent outbursts. Their rarity and unpredictability make them intriguing objects for study, as they represent a critical phase in the life cycle of the most massive stars.
Yellow Hypergiants
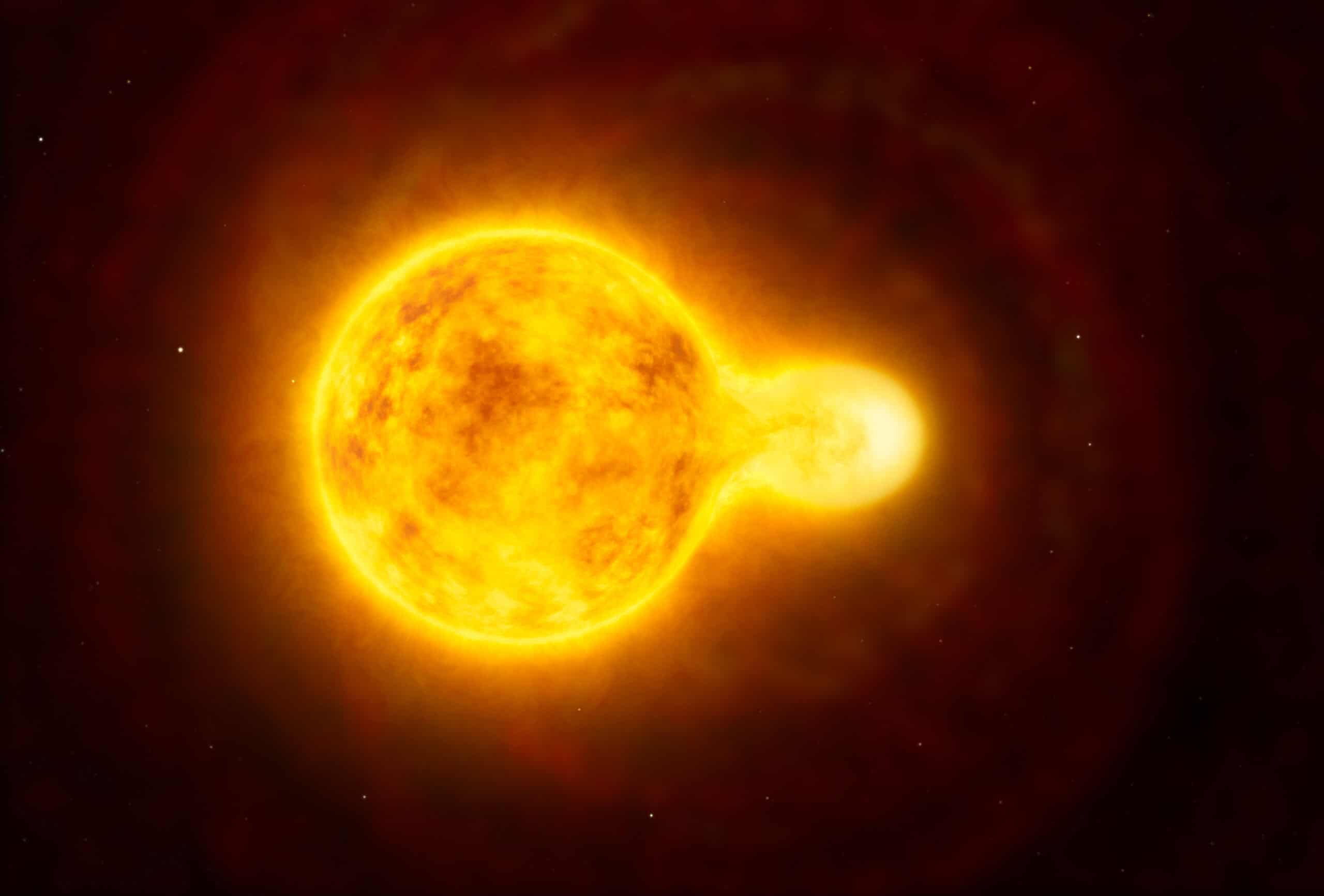

Yellow hypergiants are rare due to their extremely unstable nature and the rapid pace of their evolution. They are characterized by their massive size, high luminosity, and complex changes in their spectra. These stars are thought to be in a transitional phase, possibly on their way to becoming luminous blue variables or Wolf-Rayet stars.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org
More from Rarest.org
10 Rarest Crystals in the World

Crystals are some of the most widely collected items in the world because of their beauty. In recent years, crystal collecting has also increased in popularity because of the rise of alternative medicine. Read More
15 Rarest Metals in the World

In the realm of materials science and industry, certain metals stand out for their rarity, unique properties, and crucial roles in various technological advancements. Read More
1960 Lincoln Penny Value Guide
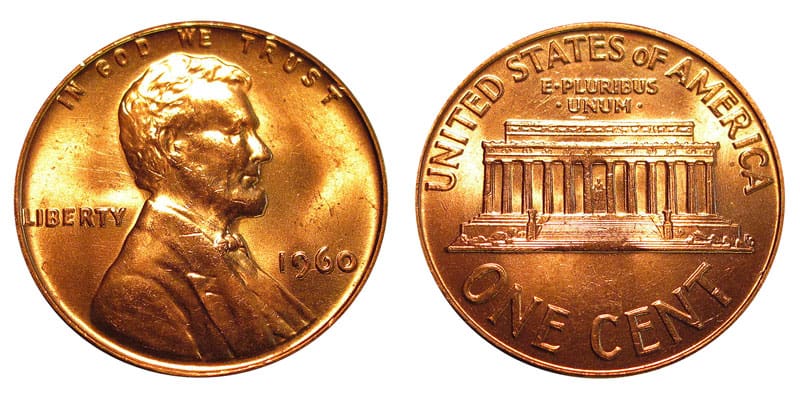

The 1960 penny is a 1-cent coin produced by the US Mint in 1960. As a 60-plus-year-old coin, the 1960 penny is quite popular among collectors. Read More
