Social movements have been a driving force behind significant changes in societies across the globe. From demanding equality and justice to reshaping political systems, these movements represent the voices of people standing up for their rights and values. While each movement arises from unique circumstances, their impacts often extend far beyond their origins, influencing cultures, policies, and even global perspectives. In this list, we’ll explore 18 social movements that have transformed the world, showcasing their lasting legacies and how they have shaped the societies we live in today.
Civil Rights Movement (United States)

The Civil Rights Movement in the U.S. marked a pivotal point in the struggle for racial equality. Sparked by decades of segregation and disenfranchisement, this movement fought for African Americans’ rights through nonviolent protests, legal challenges, and grassroots organizing. Key figures like Martin Luther King Jr. and Rosa Parks became symbols of resistance. The movement led to landmark legislation, including the Civil Rights Act of 1964 and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. Its success inspired other human rights movements globally. Although progress has been made, the fight for racial equality in the U.S. continues today.
Suffragette Movement (United Kingdom)

The Suffragette Movement in the UK revolutionized women’s rights by demanding the right to vote. Spearheaded by figures like Emmeline Pankhurst, these women used both peaceful protests and militant tactics to challenge gender inequality. Their efforts led to the Representation of the People Act in 1918, which granted voting rights to some women over 30. This victory was later expanded, allowing all women equal voting rights by 1928. The movement’s impact was felt globally, inspiring women’s suffrage campaigns in other nations. It marked the beginning of a broader struggle for gender equality across all spheres of life.
Anti-Apartheid Movement (South Africa)

The Anti-Apartheid Movement sought to dismantle institutionalized racial segregation and discrimination in South Africa. Started in the mid-20th century, it gained global support as activists, both within South Africa and internationally, demanded an end to apartheid. Nelson Mandela emerged as a central figure after enduring 27 years in prison for his efforts to bring equality to the country. The movement culminated in the 1994 democratic elections, which saw Mandela elected as South Africa’s first Black president. The end of apartheid has since allowed South Africa to build a multiracial democracy, though the legacies of inequality persist.
LGBTQ+ Rights Movement (Global)
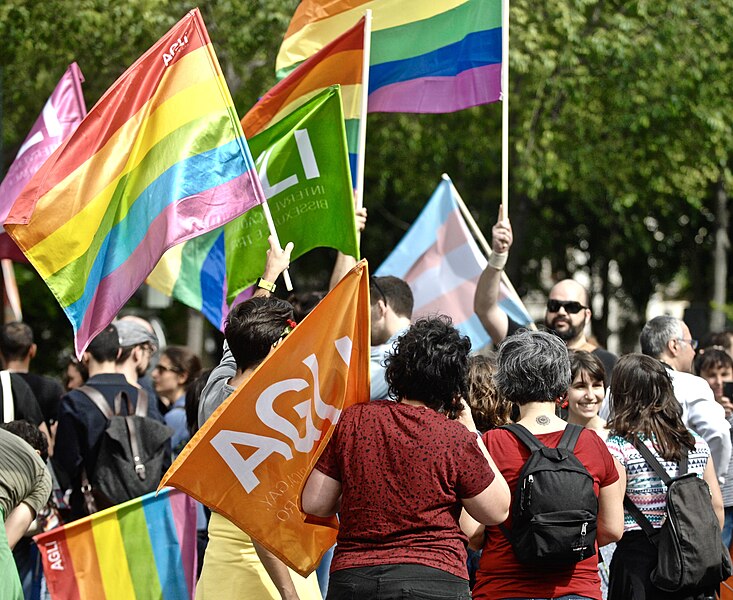

The LGBTQ+ Rights Movement has sought to secure equality and end discrimination for individuals of diverse sexual orientations and gender identities. Beginning in the mid-20th century, activists fought for visibility, legal rights, and acceptance, often in the face of intense societal prejudice. Key moments include the 1969 Stonewall Riots in New York, which ignited global advocacy for LGBTQ+ rights. Over time, this movement has led to the legalization of same-sex marriage in many countries and increased protections for LGBTQ+ individuals. Although progress has been significant, the fight against discrimination continues worldwide. The movement has reshaped conversations around gender and sexuality, fostering greater acceptance.
The Feminist Movement (Global)
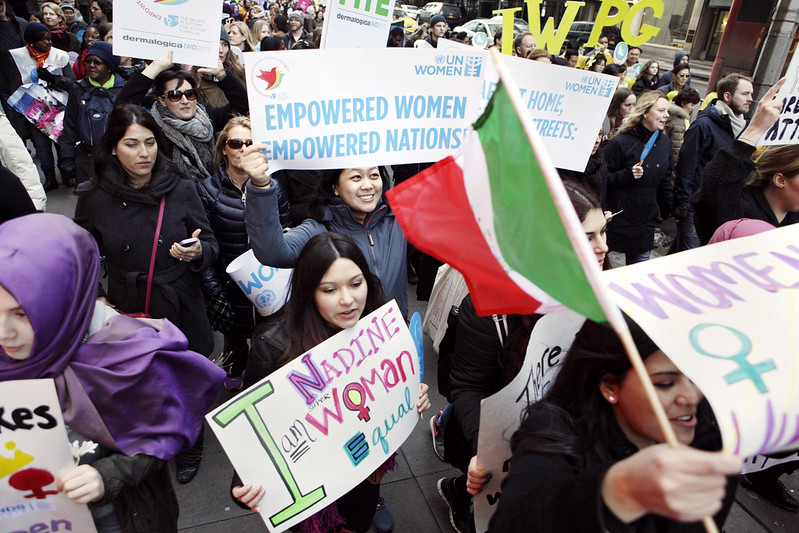

The Feminist Movement, with roots in the late 19th century, has fought for women’s rights across social, political, and economic domains. Feminists have challenged traditional gender roles, advocating for equal pay, reproductive rights, and the eradication of gender-based violence. The movement has evolved through multiple waves, with the second wave in the 1960s focusing heavily on workplace equality and reproductive freedoms. Feminism’s influence extends beyond the West, shaping policies and laws globally that have improved gender equality. Yet, the fight is far from over, as many women around the world continue to face systemic oppression. Feminism remains a driving force for gender justice.
The Environmental Movement (Global)

The Environmental Movement emerged in response to growing concerns over pollution, resource depletion, and environmental degradation. Throughout the 20th century, environmental activists called for greater accountability from corporations and governments in preserving natural ecosystems. Landmark events like the first Earth Day in 1970 and the establishment of the UN’s climate conferences have helped raise awareness. This movement led to the creation of policies such as the Clean Air Act and the Paris Agreement, aiming to combat climate change. The push for sustainability continues to be a major focus. Today, the movement’s influence can be seen in everyday actions, from recycling to renewable energy use.
The Indian Independence Movement (India)

The Indian Independence Movement was a decades-long struggle to free India from British colonial rule. Key figures like Mahatma Gandhi advocated for nonviolent resistance through movements such as the Salt March and the Quit India Movement. Over time, this widespread civil disobedience put increasing pressure on British authorities. Finally, in 1947, India achieved independence, ending nearly 200 years of British control. This movement not only shaped India’s future but also inspired other countries to challenge colonial rule. Today, India’s Independence Day is celebrated as a symbol of national pride and resilience.
The Black Lives Matter Movement (United States and Global)
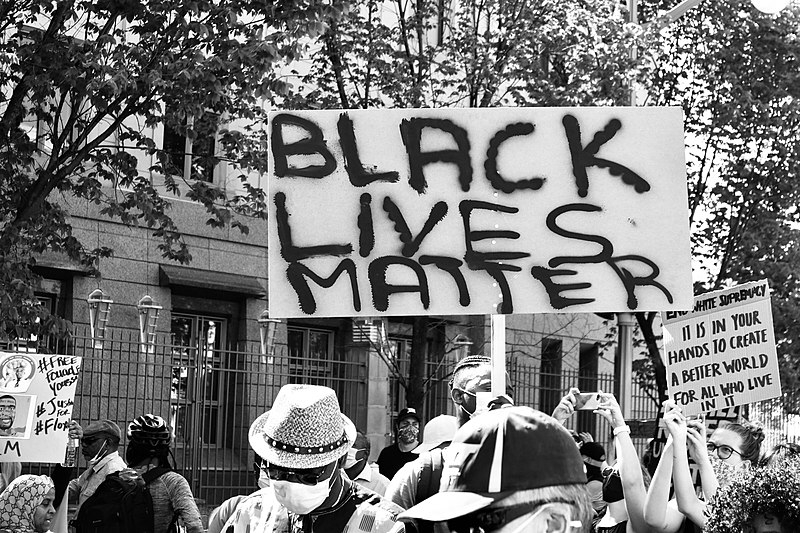
The Black Lives Matter (BLM) Movement was born out of the frustration over police violence and systemic racism in the U.S. It began in 2013 after the acquittal of George Zimmerman in the shooting death of Trayvon Martin, a Black teenager. BLM has since grown into a global movement, focusing on issues such as police brutality, racial inequality, and mass incarceration. Protests following the deaths of George Floyd and Breonna Taylor in 2020 brought the movement back into the international spotlight. BLM has influenced policy changes, though the conversation around racial justice remains ongoing. Its digital presence has empowered activists worldwide to demand change.
The Arab Spring (Middle East and North Africa)
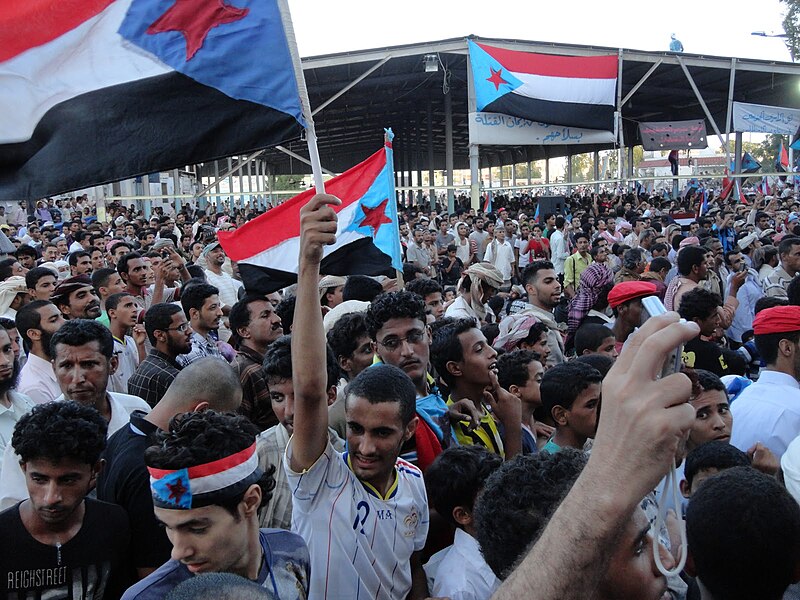

The Arab Spring was a series of anti-government protests that spread across the Middle East and North Africa beginning in 2010. Fueled by frustration over corruption, unemployment, and human rights abuses, the movement sought to overthrow authoritarian regimes. It began in Tunisia and quickly spread to Egypt, Libya, Syria, and beyond. While some countries, like Tunisia, saw positive changes, others descended into civil war. The Arab Spring remains one of the most significant political movements in recent history. Its legacy continues to impact the region, with ongoing struggles for democracy and human rights.
The Me Too Movement (Global)

The Me Too Movement erupted globally in 2017, after sexual misconduct allegations against high-profile figures surfaced. Founded by activist Tarana Burke, it initially aimed to support survivors of sexual violence, particularly women of color. The hashtag #MeToo, popularized by actress Alyssa Milano, empowered countless individuals to share their stories of harassment and abuse. This movement led to widespread conversations about workplace harassment, sexual misconduct, and the abuse of power. It resulted in the downfall of many prominent figures and sparked new legislation aimed at protecting survivors. Today, the movement remains a force for advocating for systemic change and accountability.
The Disability Rights Movement (Global)
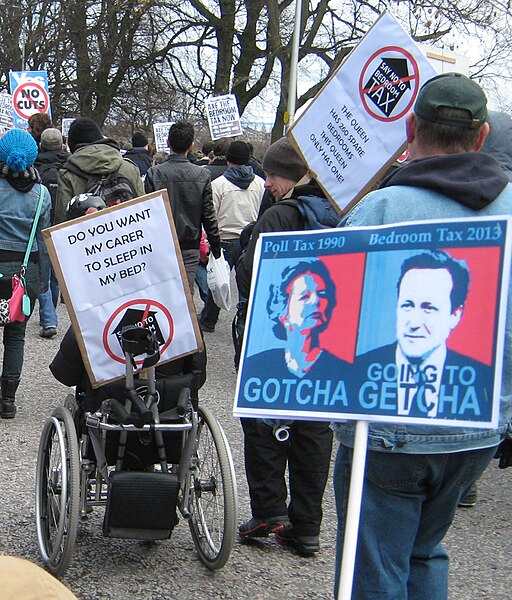

The Disability Rights Movement has worked to end discrimination and improve access for people with disabilities. Activists have pushed for laws that ensure equal rights, accessibility, and inclusion in public spaces. Major victories include the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the U.S., which became law in 1990, and similar legislation across the globe. This movement has helped break down societal barriers, ensuring that people with disabilities are seen as equal members of society. Public spaces, education, and workplaces are now more accessible due to these efforts. The movement continues to evolve, advocating for more nuanced understandings of disability rights.
The Peasant Movement (Mexico)
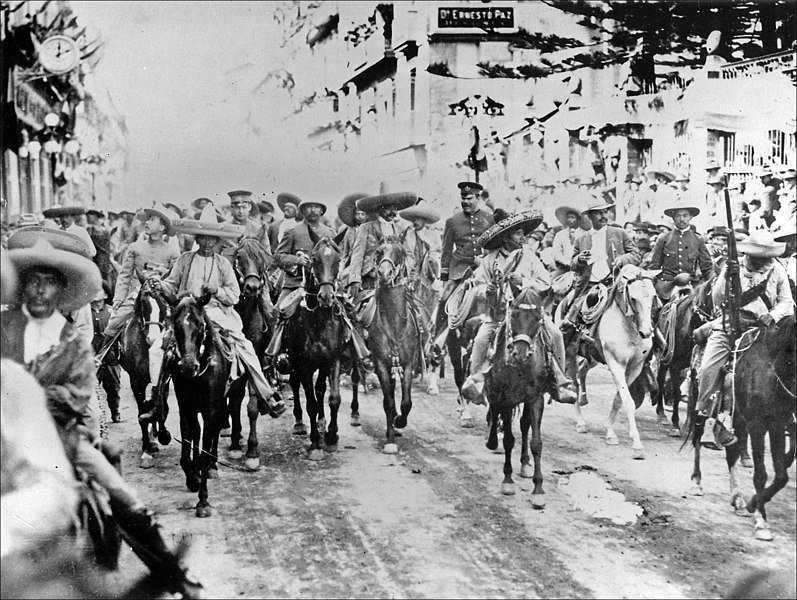

The Peasant Movement in Mexico, most notably led by Emiliano Zapata during the Mexican Revolution, sought land reform and rights for rural farmers. The movement arose out of frustration with the inequality of land distribution under the regime of Porfirio Díaz. Through armed struggle, peasants sought to redistribute land from large haciendas to the poor. Zapata’s influence can still be seen in modern Mexican politics, especially in the ongoing fight for indigenous and peasant rights. Land reform laws were passed in the decades following the revolution, though challenges persist. Today, Zapata remains a symbol of agrarian reform and resistance.
The Labor Movement (Global)

The Labor Movement, emerging during the Industrial Revolution, sought to improve working conditions, wages, and labor rights. Workers in factories, mines, and other industries formed unions to fight against exploitation by powerful employers. Strikes and protests, often met with violent opposition, were central to labor activism. Over time, the movement achieved major victories, such as the eight-hour workday, minimum wage laws, and workplace safety regulations. In many countries, these reforms transformed the workplace, ensuring greater dignity for workers. The movement continues today, focusing on issues such as wage inequality and workers’ rights in the gig economy.
The Chilean Student Protests (Chile)

In 2011, Chilean students launched massive protests demanding education reform. The movement, led primarily by university students, argued that the country’s education system was underfunded and too privatized, perpetuating inequality. Through strikes, marches, and occupations, students called for free, quality public education. The protests were successful in bringing the issue to the forefront of national debate. Over the following years, several reforms were introduced, making education more accessible. However, the fight for a more equitable education system continues as social inequalities remain a pressing issue in Chilean society.
The Occupy Movement (Global)

The Occupy Movement began in 2011 in New York City’s financial district with the slogan “We are the 99%.” It sought to highlight economic inequality, corporate greed, and the influence of money in politics. Activists set up camps in public spaces, including Zuccotti Park, demanding action on wealth disparity. Although the movement’s encampments were eventually dismantled, Occupy influenced public discourse on economic inequality. It also paved the way for future movements, such as those focused on student debt and healthcare reform. The movement’s legacy persists in discussions of wealth redistribution and economic justice.
The Women’s March (Global)
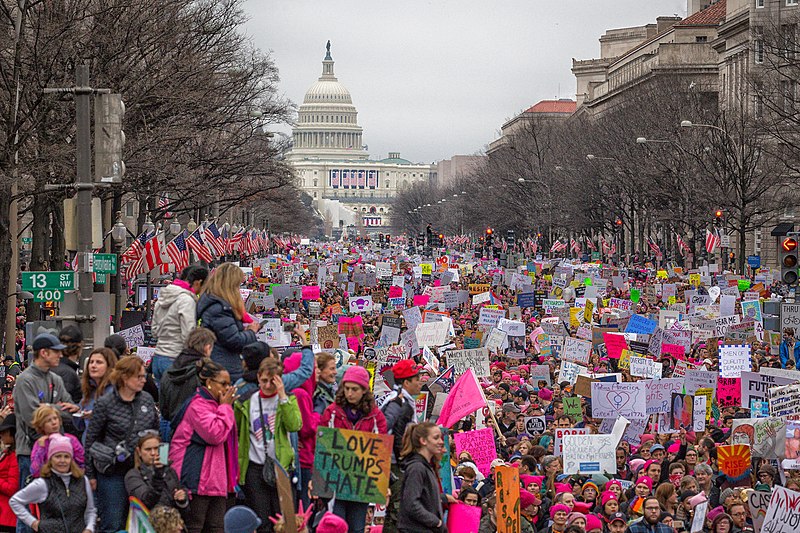

The Women’s March, first held in January 2017, became one of the largest protests in U.S. history, with over 5 million people participating globally. The march was a response to the election of Donald Trump and his controversial rhetoric toward women, immigrants, and other marginalized groups. The movement advocated for women’s rights, reproductive health, LGBTQ+ rights, and racial equality. The success of the initial march has led to subsequent annual events, with organizers expanding their focus to broader social justice issues. The Women’s March continues to be a platform for progressive advocacy worldwide. Its influence is felt in ongoing movements for equality and justice.
The Abolitionist Movement (United States)
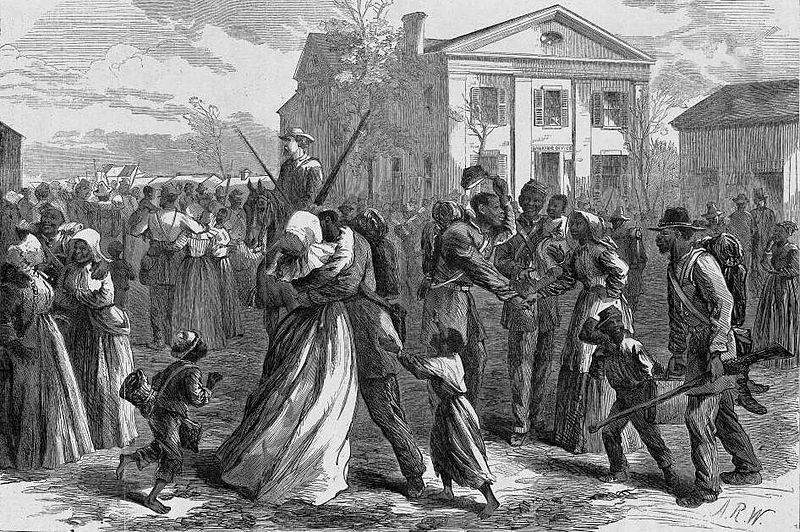

The Abolitionist Movement in the U.S. was a powerful force in the fight to end slavery. Beginning in the late 18th century, abolitionists, both Black and white, campaigned tirelessly through speeches, writings, and organizing. Figures like Frederick Douglass and Harriet Tubman became central to the movement’s success. The abolitionists’ efforts culminated in the Civil War and the eventual passage of the 13th Amendment in 1865, which formally abolished slavery. The movement not only ended legal slavery but also laid the groundwork for future civil rights struggles. Its legacy continues to inspire movements for racial justice.
The Anti-Nuclear Movement (Global)

The Anti-Nuclear Movement gained traction in the 1970s as concerns over the dangers of nuclear weapons and energy grew. Activists raised awareness of the catastrophic potential of nuclear power and fought against nuclear testing and plant construction. Incidents like the Chernobyl disaster in 1986 and the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster in 2011 fueled public opposition. Over time, the movement has successfully influenced policies to reduce nuclear arsenals and promote renewable energy alternatives. Today, it remains a critical voice in the fight against nuclear proliferation. The movement’s call for a world free of nuclear threats continues to resonate globally.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More From Rarest.Org
8 Greatest Underdog Stories in Professional Sports

Underdog stories in professional sports capture our imagination by showing us that anything is possible. These are the moments when teams and athletes overcome insurmountable odds to achieve greatness, defying expectations and creating unforgettable memories. Read more.
Many species around the world are facing the threat of extinction, but not all of them are well-known. While efforts to save popular animals like pandas and tigers often make headlines, lesser-known species are quietly disappearing at an alarming rate. Read more.
High-altitude regions around the world are home to some of the most unique and uncommon mammals on the planet. They have adapted to survive in the harsh, cold, and rugged environments of the world’s tallest mountains. Read more.


