Throughout history, empires have risen and controlled vast territories, leaving an undeniable mark on world culture, politics, and economics. These massive states, through conquest and colonization, have shaped the world map and influenced generations. Their territorial dominance and cultural impacts were profound.
British Empire

At its peak in 1920, the British Empire was the largest empire in history, controlling nearly 35.5 million square kilometers—almost a quarter of the world’s land. It spanned across North America, Australia, Africa, the Indian subcontinent, and parts of the Caribbean and Pacific islands. This empire, reigning from the late 16th century to the mid-20th century, played a pivotal role in shaping global trade and diplomacy. The phrase “the empire on which the sun never sets” became synonymous with Britain’s vast territorial holdings. Its influence on language, governance, and economics still resonates across former colonies.
Mongol Empire

The Mongol Empire, founded by Genghis Khan in 1206, quickly became the largest contiguous empire in world history, covering over 24 million square kilometers. Stretching from Eastern Europe across Central Asia to the Sea of Japan, the Mongols unified a diverse array of cultures under a single administration. This empire existed until 1368 and is remembered for its highly skilled cavalry and brutal military campaigns. However, the Mongols also facilitated trade across the Silk Road, promoting cultural exchanges and advancing communication networks across Asia and Europe.
Russian Empire

The Russian Empire, established by Peter the Great in 1721, extended across 22.8 million square kilometers at its peak in the early 20th century. It encompassed much of Eastern Europe, Central Asia, Siberia, and parts of North America, with Alaska being a notable territory before its sale to the United States. The empire persisted until the Russian Revolution in 1917, marking its collapse. It was characterized by territorial expansion, with significant military conquests of neighboring lands and aggressive colonization. The Russian Empire’s political, cultural, and social influence shaped much of Eurasian history.
Qing Dynasty

The Qing Dynasty, ruling from 1644 to 1912, was China’s last imperial dynasty and one of its most expansive. At its peak, it controlled over 14.7 million square kilometers, encompassing modern China, Mongolia, Taiwan, Tibet, and parts of Central Asia. The Qing oversaw significant territorial expansion through military conquests, solidifying China’s borders. It maintained a highly organized bureaucracy and is known for its cultural achievements, but internal strife and external pressures eventually led to its decline. Despite its fall, the Qing Dynasty’s legacy is still felt in China’s territorial integrity and cultural heritage.
Spanish Empire
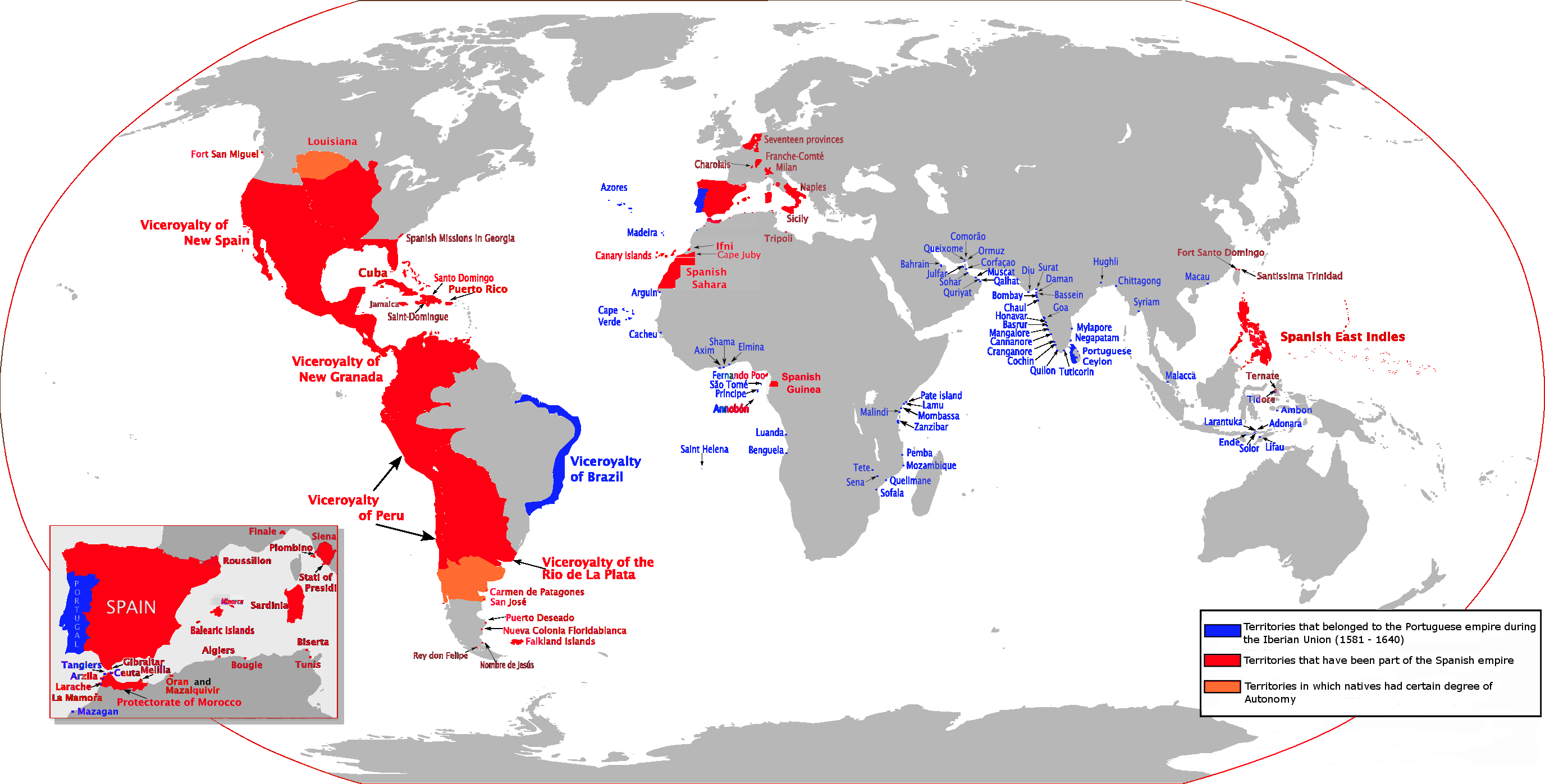
The Spanish Empire, founded in the late 15th century, was one of the first truly global empires, reigning over 13.7 million square kilometers at its height in the 18th century. Spanning Europe, the Americas, Asia, and Africa, it played a crucial role in the Age of Exploration. Territories included present-day Mexico, much of South America, the Philippines, and parts of Italy and the Netherlands. The empire was a key player in global trade, particularly through its control of silver from the Americas, which fueled European economies. Despite its gradual decline in the 19th century, the Spanish Empire’s influence in language, religion, and culture remains strong across its former colonies today.
Umayyad Caliphate
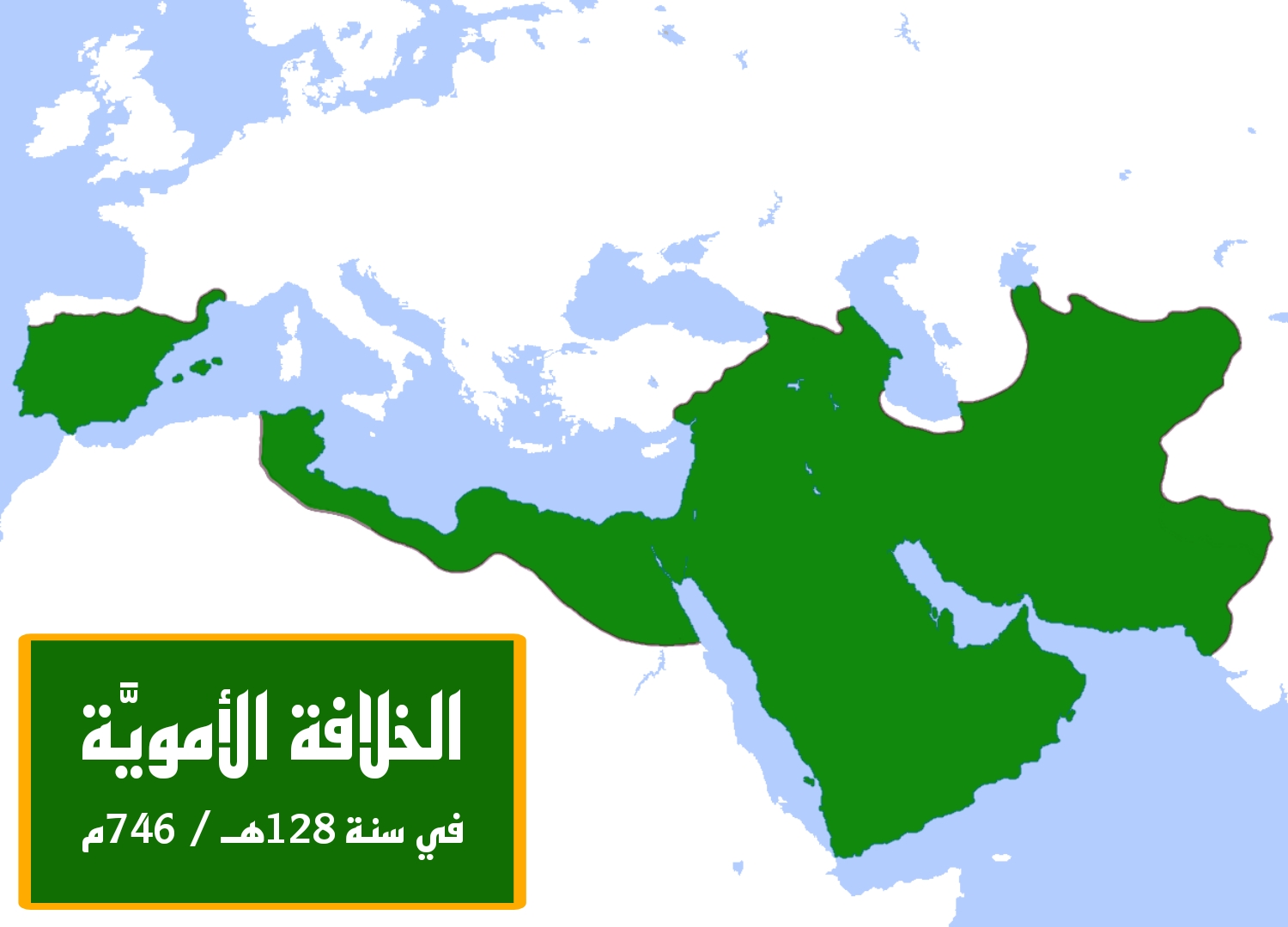
The Umayyad Caliphate, which lasted from 661 to 750 AD, was one of the largest and most powerful Islamic empires. At its peak, it covered around 11 million square kilometers, stretching from Spain in the west to India in the east. Its rapid expansion was marked by significant conquests in North Africa, the Iberian Peninsula, and Persia. The Umayyad dynasty played a crucial role in spreading Islam and facilitating trade across its vast territories. Its administrative innovations helped unify diverse cultures under one rule, leaving a lasting legacy in the Muslim world.
Yuan Dynasty

The Yuan Dynasty, established by Kublai Khan in 1271, ruled China and vast territories across Asia until 1368. At its peak, it controlled over 13 million square kilometers, encompassing present-day China, Mongolia, Korea, and parts of Southeast Asia. The Yuan Dynasty marked the first time a non-Han ethnic group, the Mongols, ruled all of China. This period saw significant advances in trade and communication, with the dynasty playing a pivotal role in linking the East and West along the Silk Road. Despite its eventual fall, it left a profound influence on Chinese history.
Abbasid Caliphate
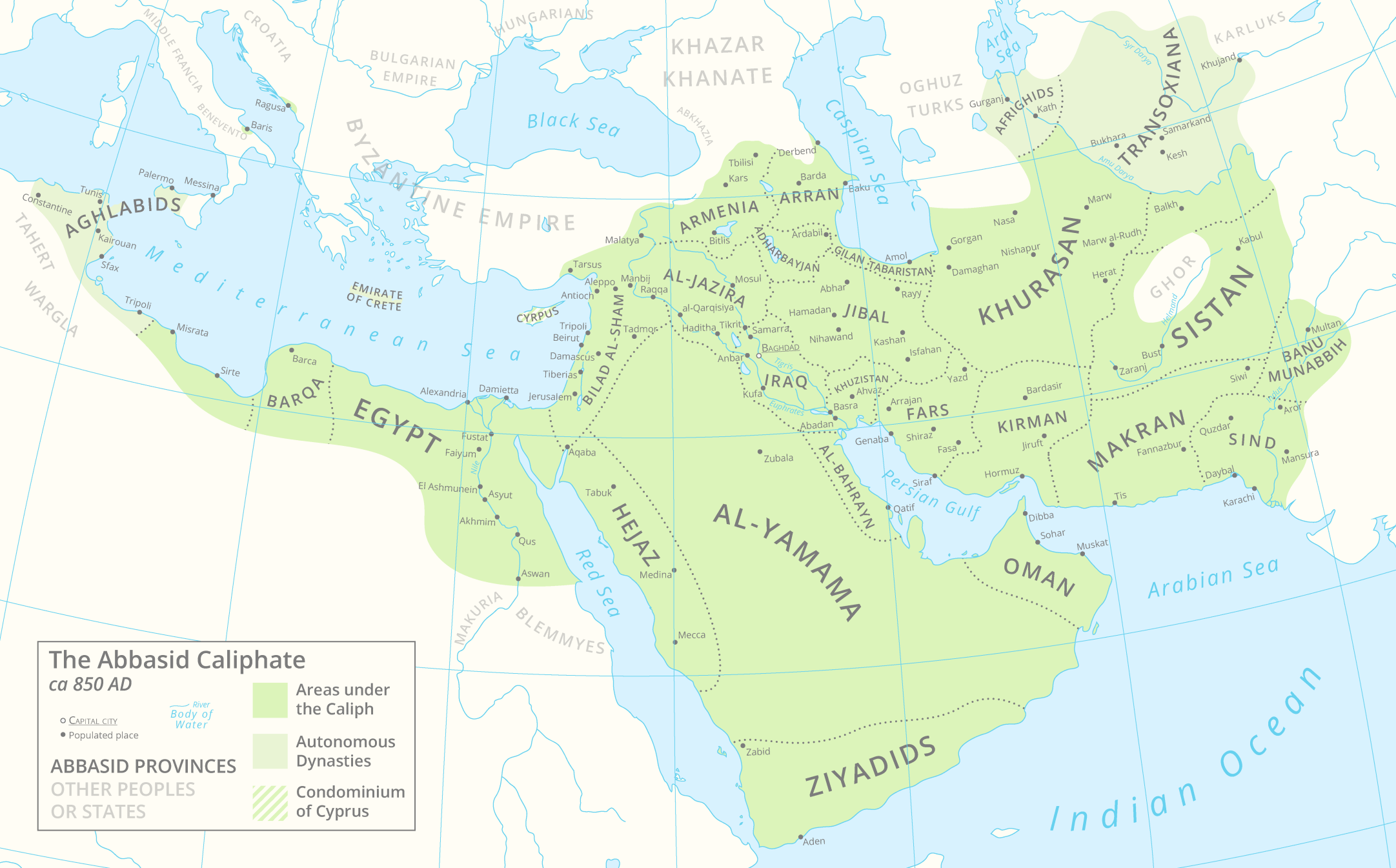
The Abbasid Caliphate, which reigned from 750 to 1258 AD, controlled one of the largest empires in history, covering around 10 million square kilometers. At its height, it stretched from North Africa to Central Asia, with its capital in Baghdad becoming a center of learning and culture. The Abbasid period is often considered the Islamic Golden Age due to its advancements in science, mathematics, and the arts. The empire’s decline came after invasions by the Mongols, but its cultural and intellectual contributions had a lasting impact on the world.
Ottoman Empire
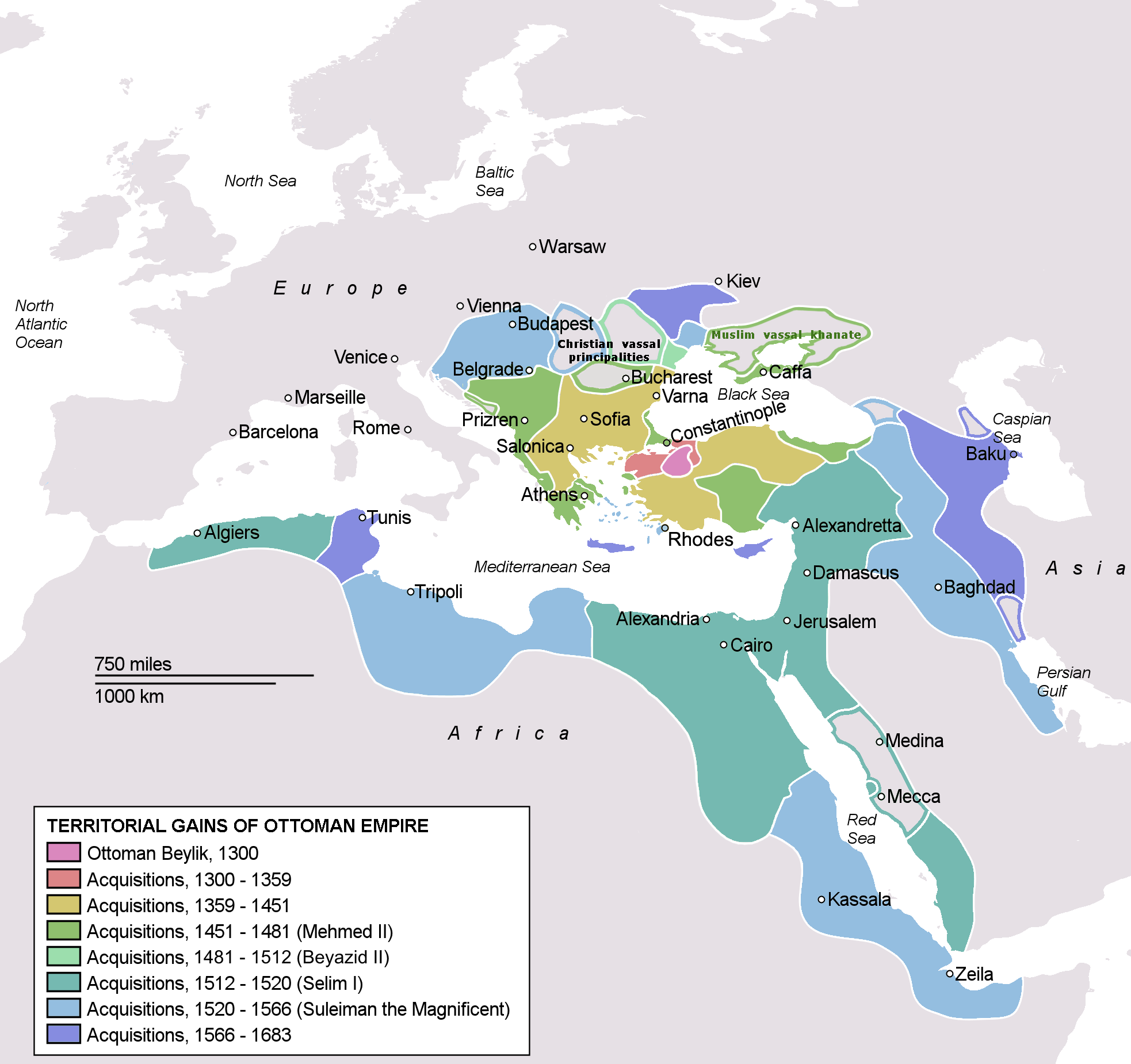
The Ottoman Empire, founded in 1299 and lasting until 1922, was one of the longest-lasting empires in history. At its height in the 17th century, it spanned over 5.2 million square kilometers, encompassing Southeast Europe, Western Asia, and North Africa. The Ottomans ruled over a diverse population with a highly centralized government. Their military strength, particularly their naval power, enabled them to control important trade routes. The fall of the Ottoman Empire after World War I marked the end of one of the most influential empires in global history.
Roman Empire
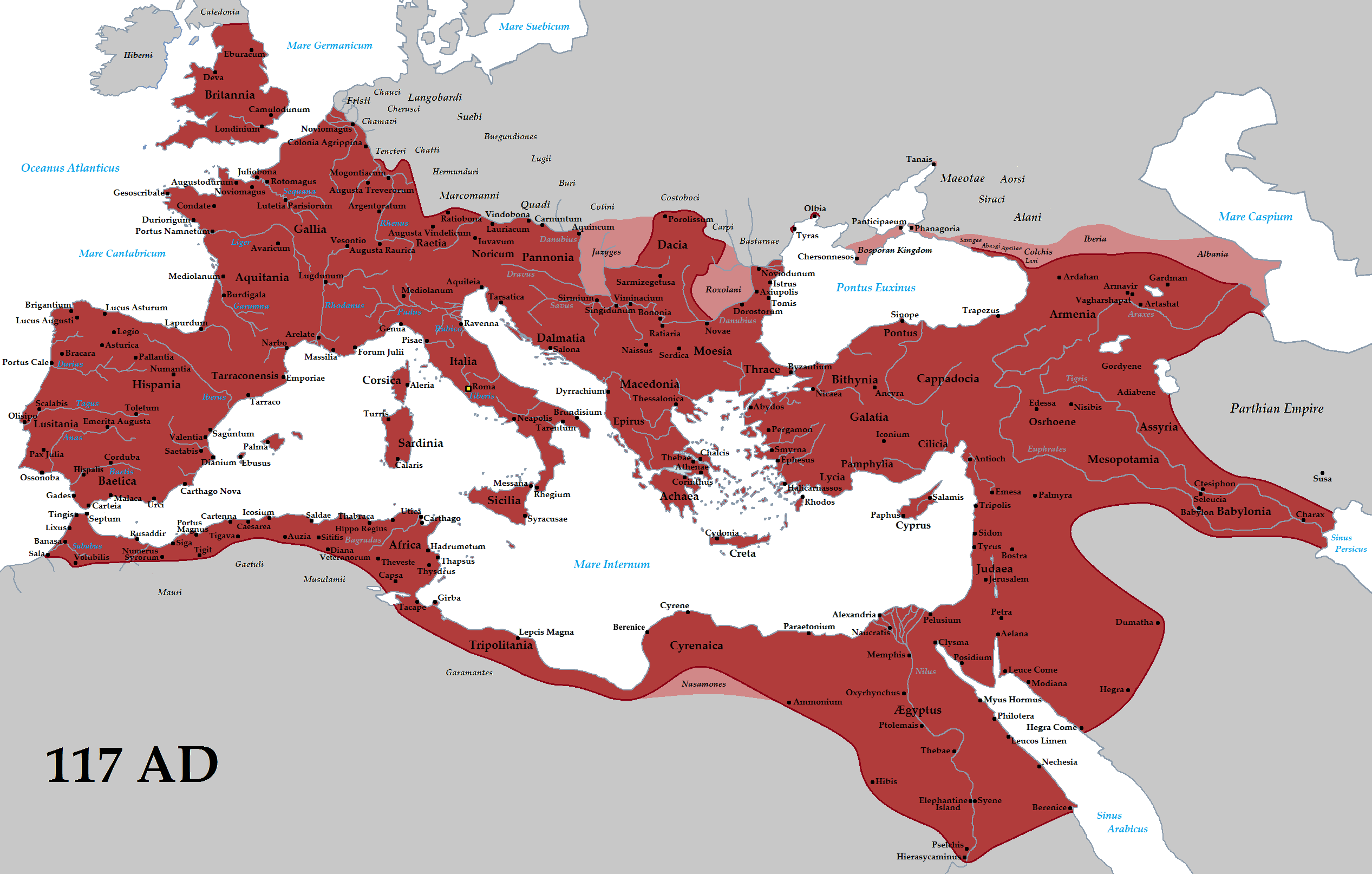
The Roman Empire, established in 27 BC, was one of the most significant empires in history, reaching its peak under Emperor Trajan in 117 AD. At its height, it controlled around 5 million square kilometers, including territories across Europe, North Africa, and the Middle East. The Roman Empire is renowned for its legal system, engineering feats, and military dominance. Despite its eventual division and fall in 476 AD, the Roman Empire’s cultural, architectural, and political legacies remain influential in modern society.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More from Rarest.org
14 Rare Gemstones Found Only in Specific Regions

Rare gemstones hold a special allure, not just for their beauty but for their scarcity. Found only in specific regions around the world, these stones are prized by collectors and jewelers alike. Read More.
13 Rare Flower Species That Bloom in Specific Microclimates

Some flowers are so rare that they can only bloom under very specific environmental conditions, known as microclimates. Read More.
8 Forgotten Action Movies That Pack a Punch

Action movies are often packed with adrenaline-fueled sequences, but some gems slip through the cracks over time. Read More.
