History is filled with the rise and fall of civilizations. Some left behind vast empires, while others vanished without a clear explanation. These ancient societies once flourished but met mysterious and sudden ends. Their ruins still inspire curiosity, leaving us wondering what truly happened. This article explores a few civilizations whose disappearances continue to baffle historians and archaeologists alike.
The Indus Valley Civilization
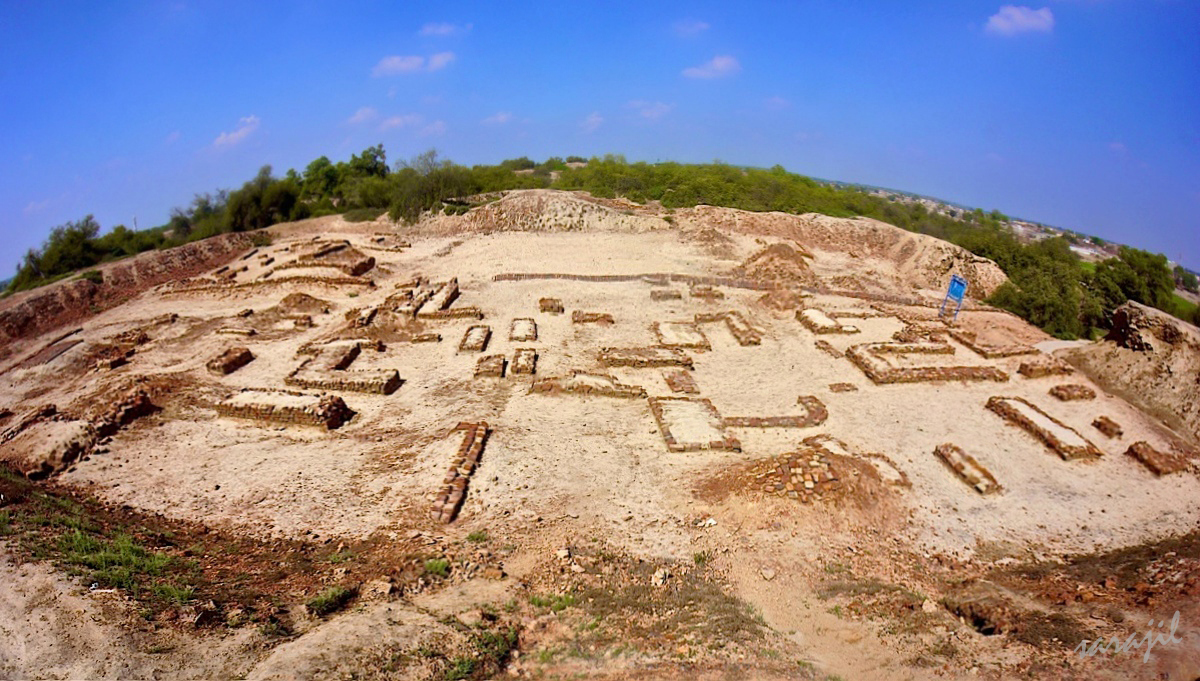

The Indus Valley Civilization thrived around 2500 BCE in what is now Pakistan and northwest India. Known for its advanced city planning, the society had well-laid streets, sophisticated drainage systems, and impressive architecture. However, by 1900 BCE, the civilization began to decline mysteriously. Many theories attempt to explain their disappearance, from climate change to invasions, but none offer a definitive answer. Despite extensive research, the exact reason for the downfall of this once-great civilization remains unknown.
The Maya Civilization
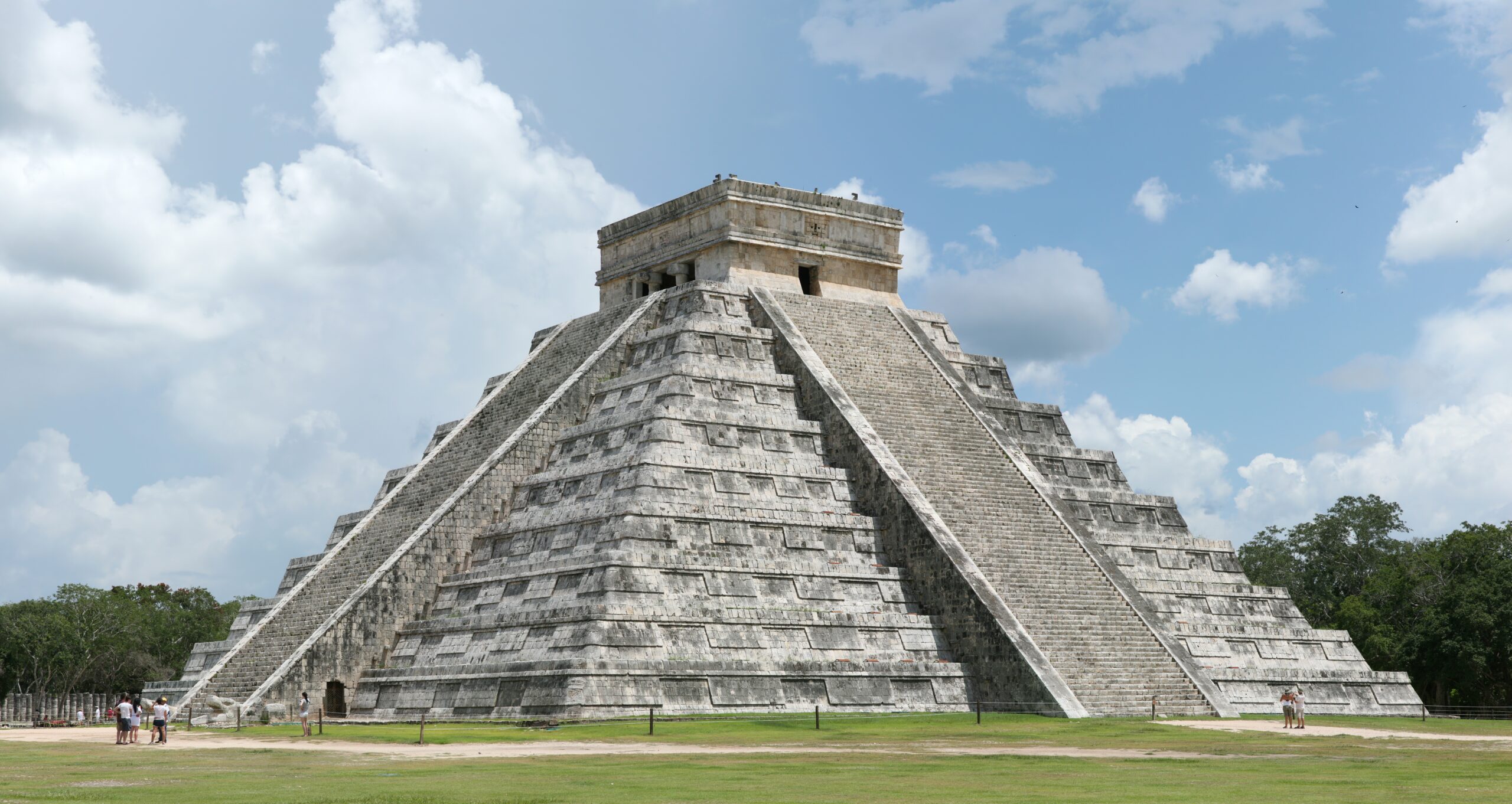

The Maya civilization was a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in what is now southern Mexico, Guatemala, and Belize. Known for their advancements in writing, astronomy, and architecture, the Maya built massive stone pyramids and complex city-states. Around the 9th century, many of these city-states were abandoned. Environmental degradation, droughts, and internal strife are among the many theories proposed to explain their mysterious collapse. However, no single explanation fully accounts for the sudden disappearance of this powerful culture.
The Ancestral Puebloans (Anasazi)
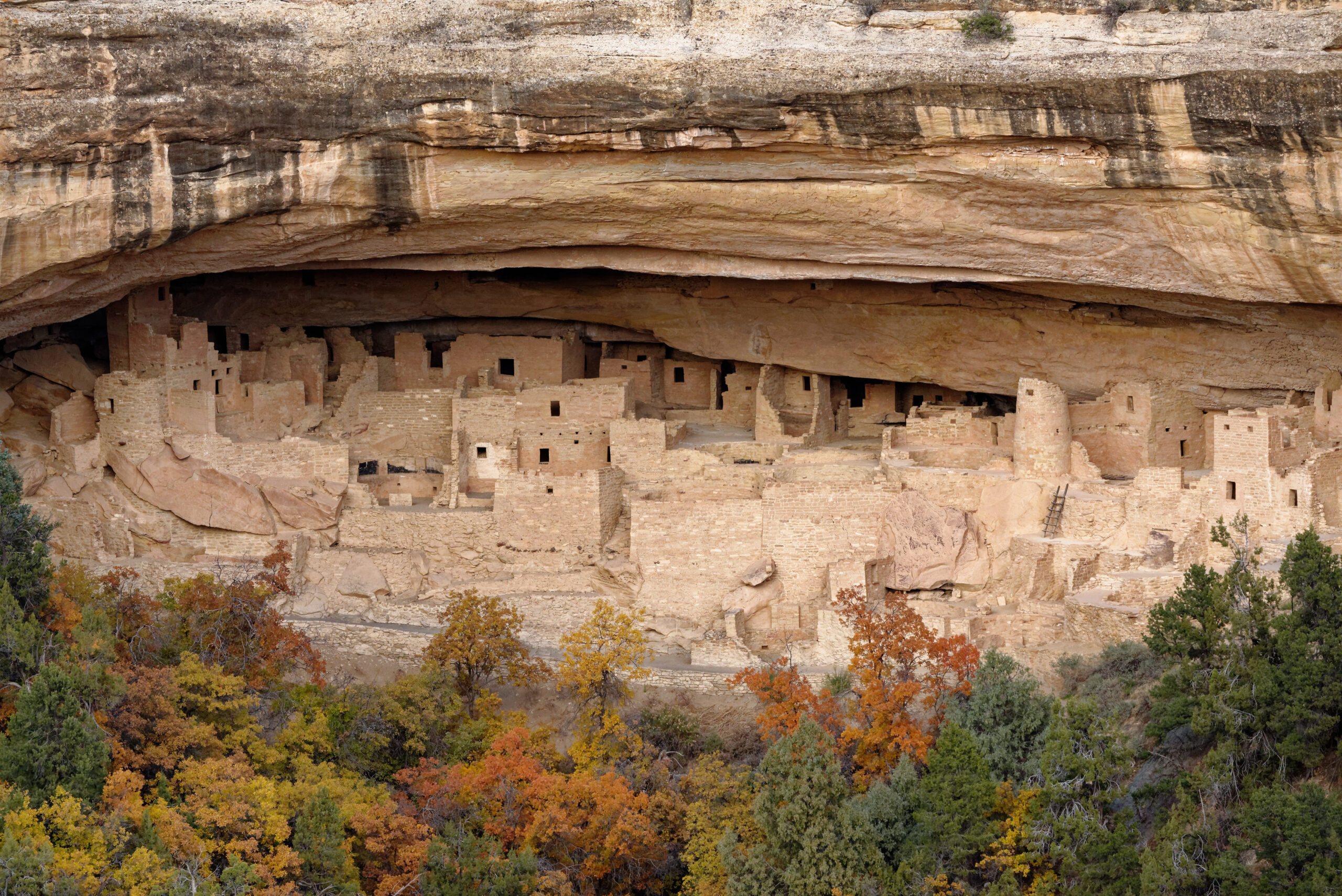

The Ancestral Puebloans, also known as the Anasazi, lived in the southwestern United States. They are famous for their impressive cliff dwellings and intricate pottery. This civilization reached its height between 900 and 1150 CE, but by 1300 CE, many of their settlements were mysteriously abandoned. Scholars believe prolonged drought, resource depletion, and social conflicts may have driven them to relocate or collapse entirely. The exact reasons, however, remain a subject of debate.
The Mycenaeans
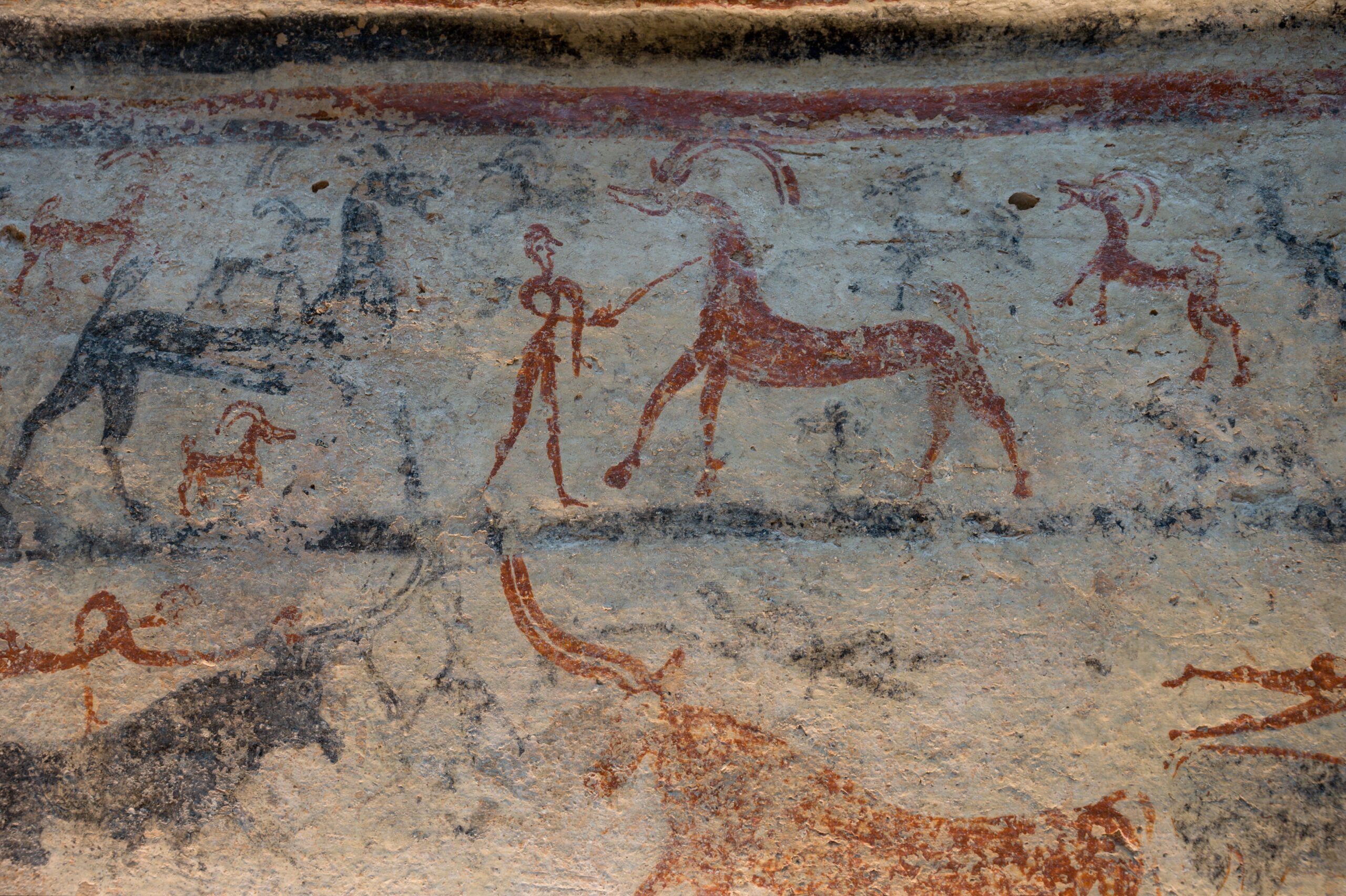

The Mycenaeans were a powerful civilization in ancient Greece that thrived from around 1600 to 1100 BCE. They were known for their influence on Greek culture, including their contributions to language, art, and military tactics. Despite their strength, the Mycenaeans suddenly vanished after the fall of their great cities. Possible explanations include invasions by the mysterious “Sea Peoples,” internal rebellion, or natural disasters like earthquakes. Yet, the true cause of their disappearance remains elusive.
The Minoans
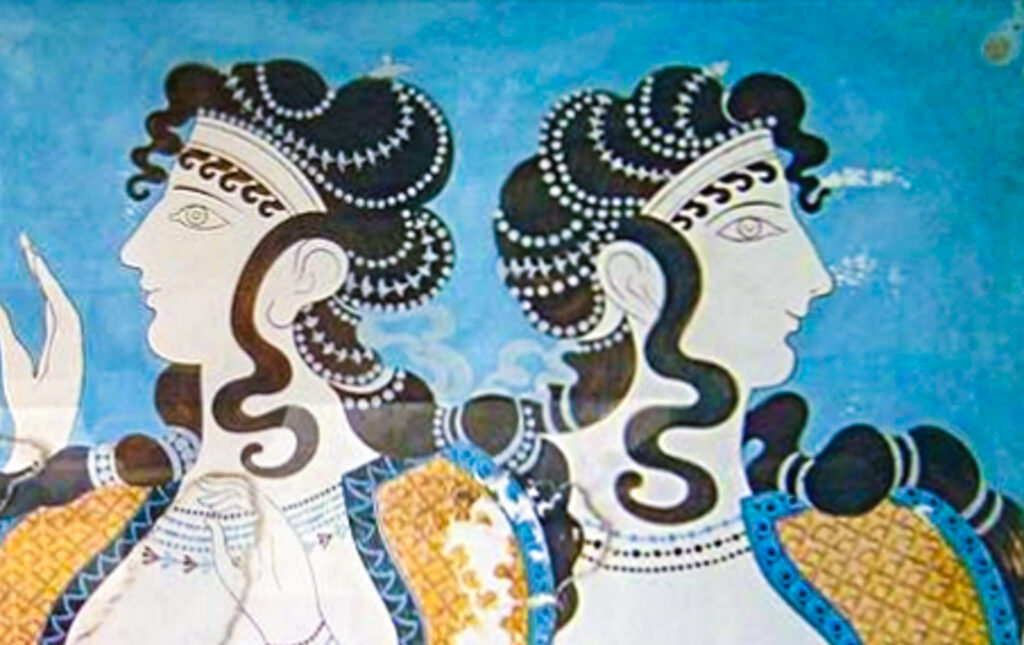

The Minoan civilization, based on the island of Crete, was one of the earliest in Europe. Flourishing around 2000 BCE, the Minoans were skilled in trade, art, and architecture, with a strong maritime presence. However, by 1450 BCE, their society began to decline rapidly. Theories for their downfall range from volcanic eruptions and tsunamis to invasion by the Mycenaeans. While many believe these events contributed, the exact cause of their mysterious disappearance is still unclear.
The Nabateans
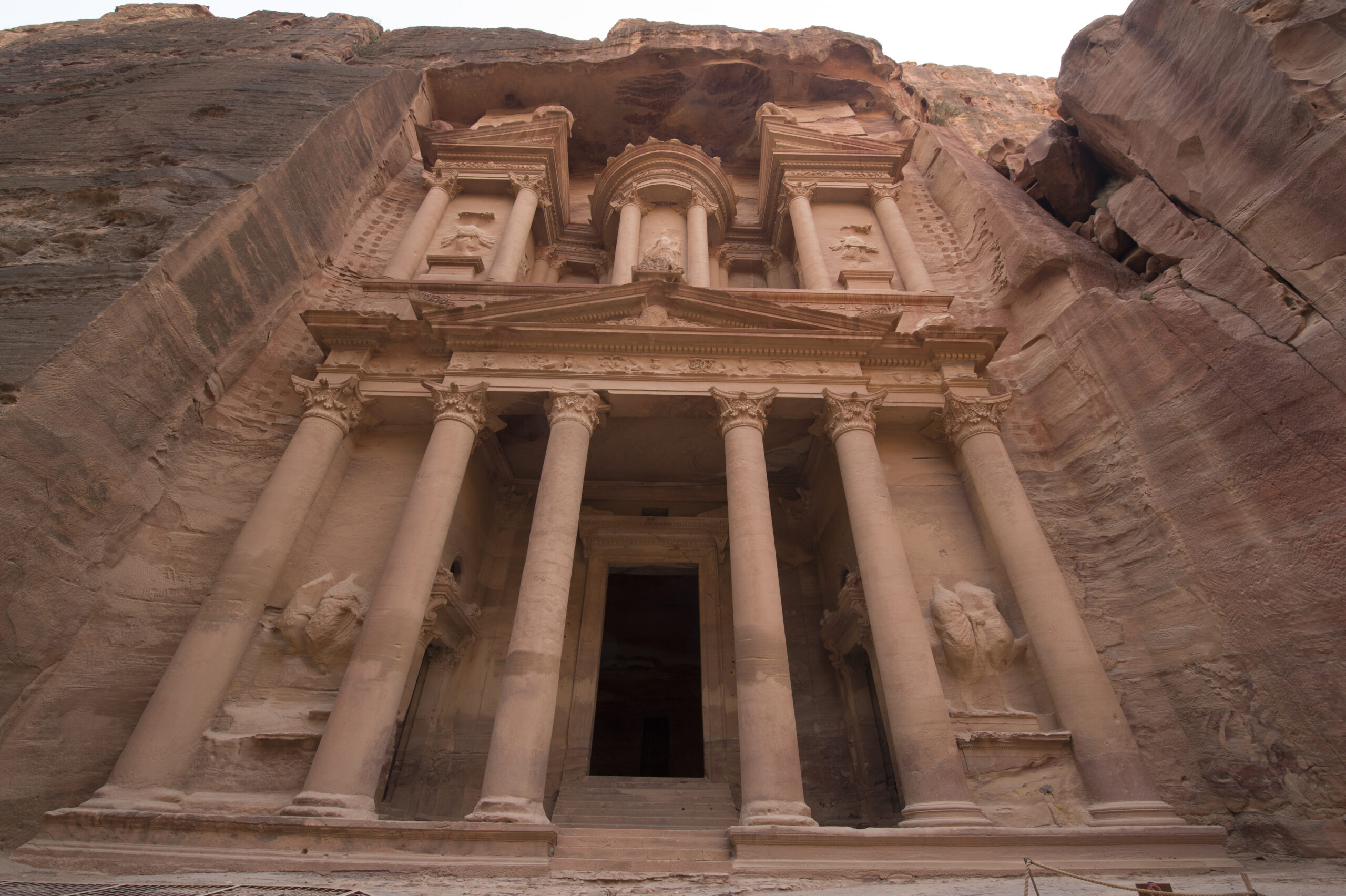

The Nabateans were an ancient Arab people who established the city of Petra, now in modern-day Jordan, around the 4th century BCE. They became wealthy through trade and their control of key routes between the Arabian Peninsula and the Mediterranean. By the 2nd century CE, the Nabateans mysteriously vanished, leaving Petra to fall into ruins. Some scholars believe their collapse was due to changes in trade routes and Roman annexation, but no single explanation fully accounts for their disappearance.
The Khmer Empire
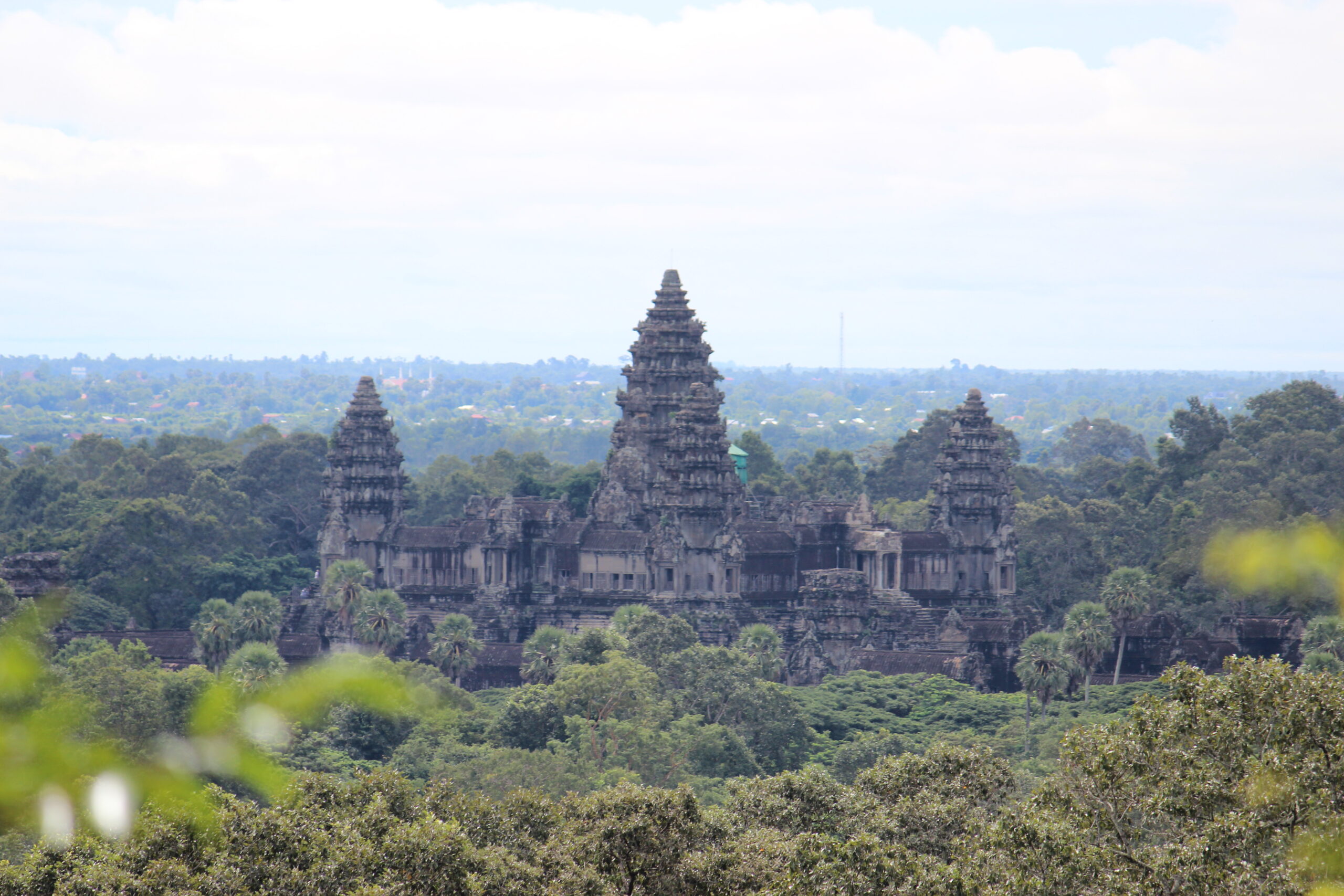

The Khmer Empire, once a dominant force in Southeast Asia, thrived from the 9th to the 15th century. At its peak, the empire built the famous Angkor Wat, showcasing its architectural brilliance. However, by the mid-15th century, the empire suddenly declined, and its cities were abandoned. Theories suggest that factors like overpopulation, environmental degradation, or shifting trade routes may have contributed to its downfall. Despite these possible explanations, the exact reasons for the collapse of the Khmer Empire remain unclear.
The Cucuteni-Trypillia Culture
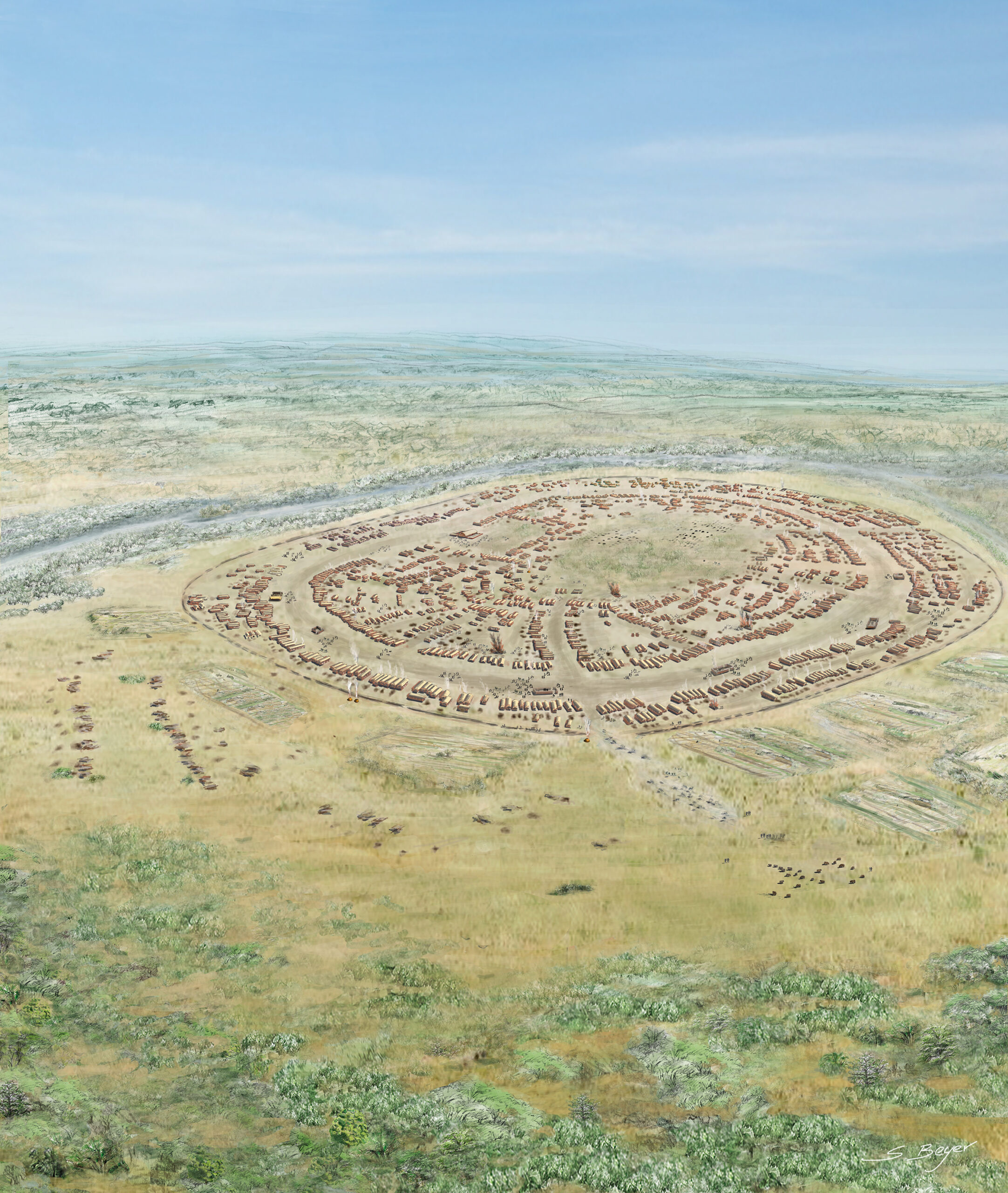
The Cucuteni-Trypillia culture, which existed from 5500 to 2750 BCE, spanned parts of modern-day Ukraine, Moldova, and Romania. This culture is known for its large settlements and beautifully decorated pottery. Mysteriously, the Cucuteni-Trypillia people abandoned their large settlements every few centuries, burning their homes before moving. By 2750 BCE, this practice stopped, and the culture disappeared altogether. Some researchers believe climate changes or invasion by outside groups may have caused the decline, but no definitive cause has been identified.
The Hittites
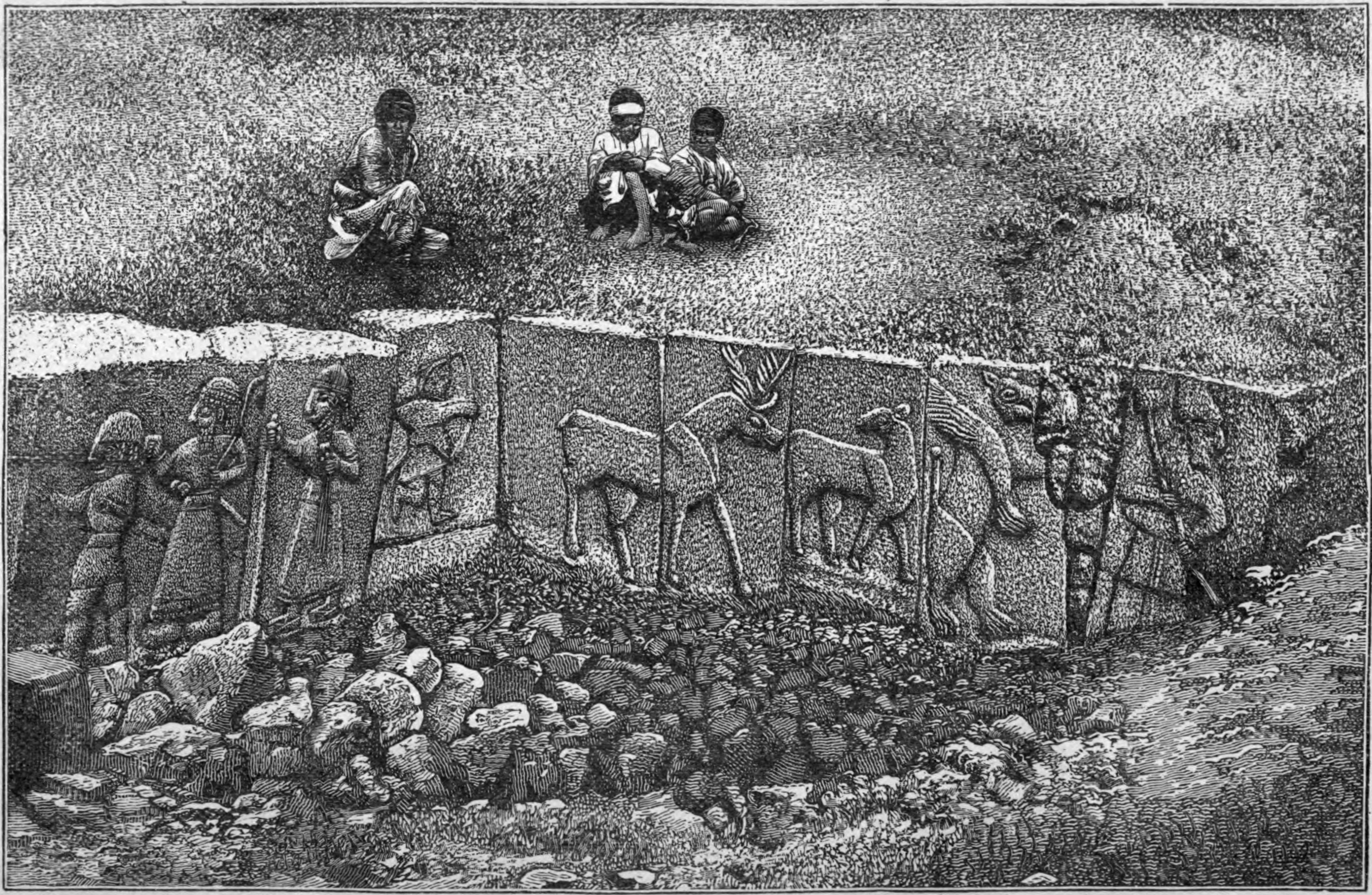

The Hittites were a powerful ancient civilization based in Anatolia (modern-day Turkey), reaching their height around 1600 BCE. They were known for their military prowess, use of iron, and legal systems. Around 1200 BCE, the Hittite empire mysteriously collapsed, along with several other great civilizations of the time. Some historians believe invasions by the mysterious Sea Peoples, internal strife, or natural disasters contributed to their downfall. Despite these theories, the sudden disappearance of the Hittites remains unresolved.
The Aksumite Empire
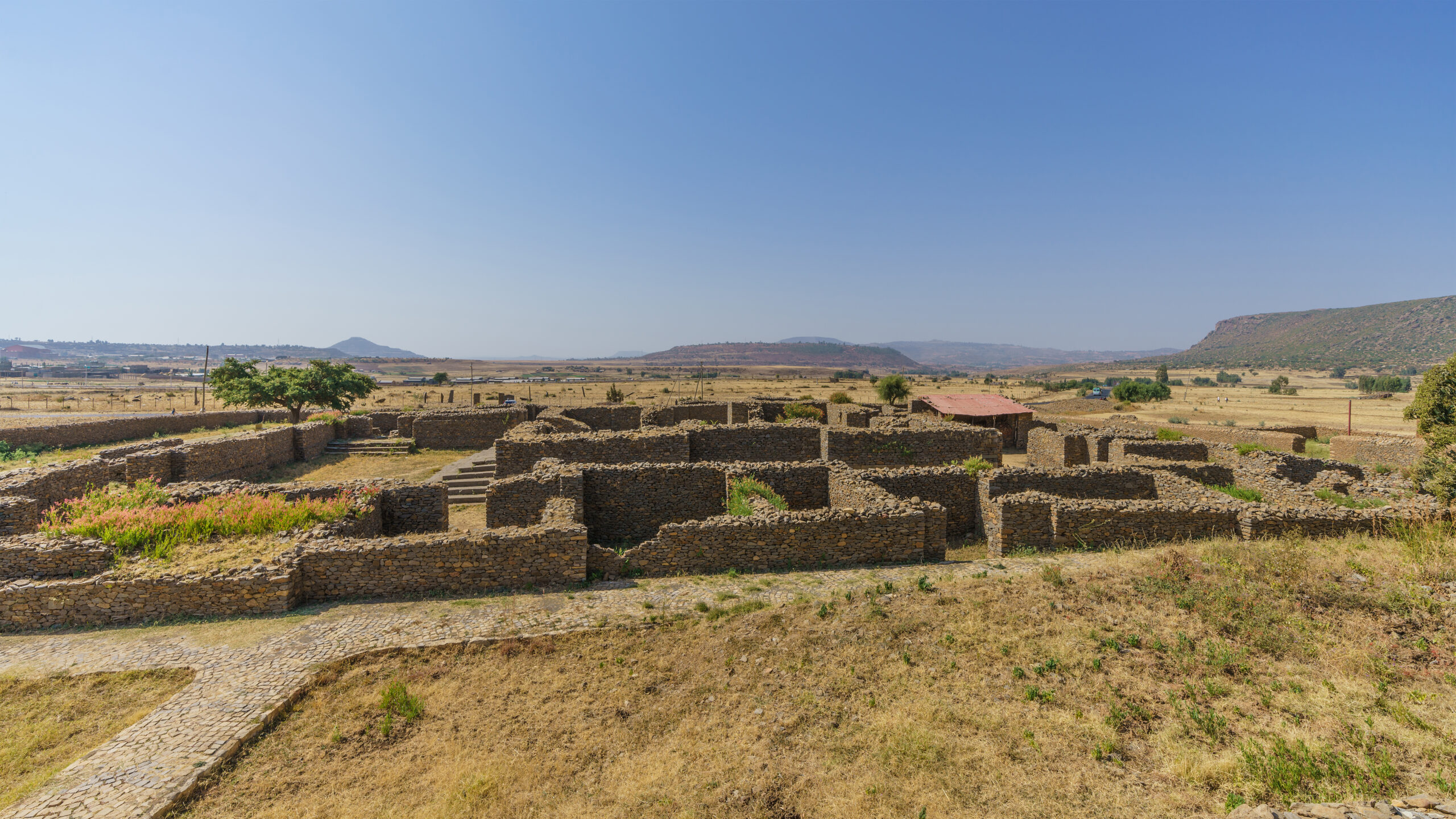

The Aksumite Empire, located in present-day Ethiopia and Eritrea, was a significant power from the 1st to the 7th century CE. It was known for its impressive obelisks, trade dominance, and early adoption of Christianity. By the 8th century, the empire began to decline, and by the 10th century, it had largely disappeared. Environmental degradation, shifting trade routes, and religious conflicts are thought to have played a role. However, the exact cause of the Aksumite Empire’s disappearance is still debated by scholars.
The Rapa Nui (Easter Island)
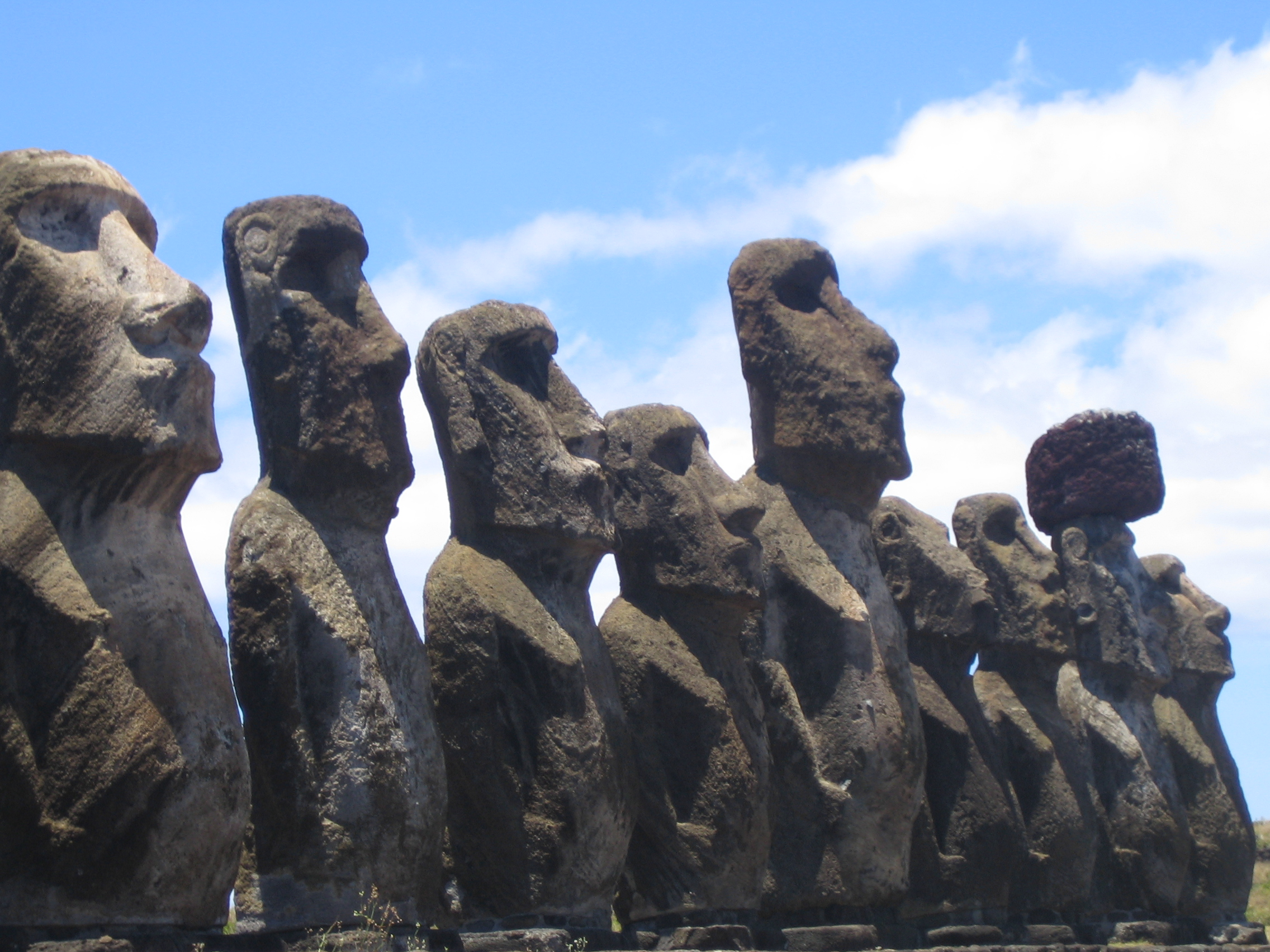

The Rapa Nui civilization, located on Easter Island, is famous for its massive stone statues, known as moai. This Polynesian society thrived from the 12th to the 17th century. However, by the 18th century, the civilization was in decline, and many of its structures were left abandoned. Deforestation, overpopulation, and conflicts over resources are believed to have contributed to their downfall. Still, the complete reasons behind the disappearance of the Rapa Nui people remain uncertain.
The Sumerians
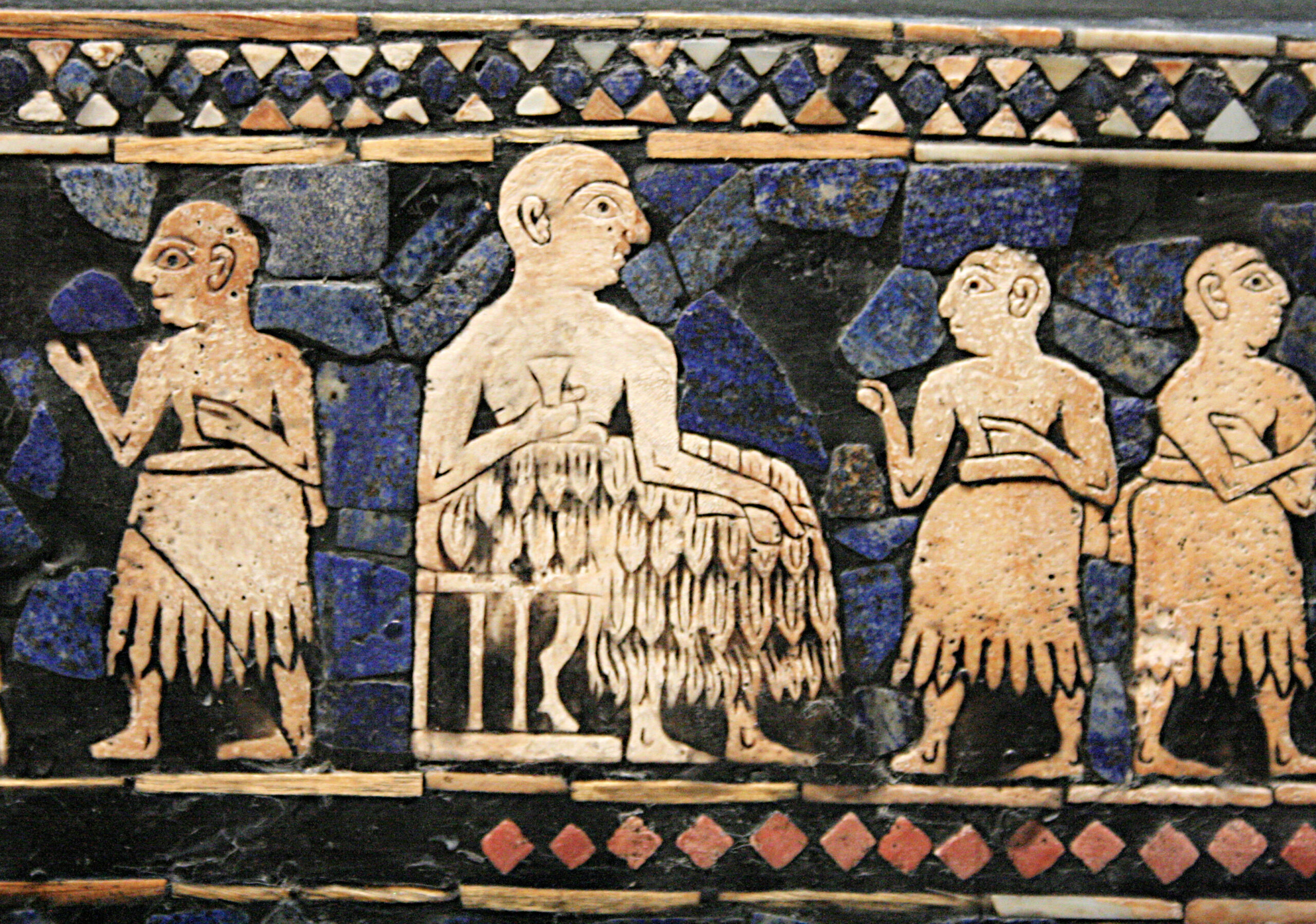

The Sumerians, one of the earliest known civilizations, thrived in Mesopotamia around 4500 BCE. They are credited with creating the first system of writing, cuneiform, and established complex cities like Ur and Uruk. Their advanced knowledge of irrigation, agriculture, and trade made them a dominant force in the ancient world. However, by 2000 BCE, their civilization began to decline. Many believe constant warfare, environmental changes, and internal conflicts led to their downfall. Despite their disappearance, their innovations shaped future civilizations.
The Nok Culture
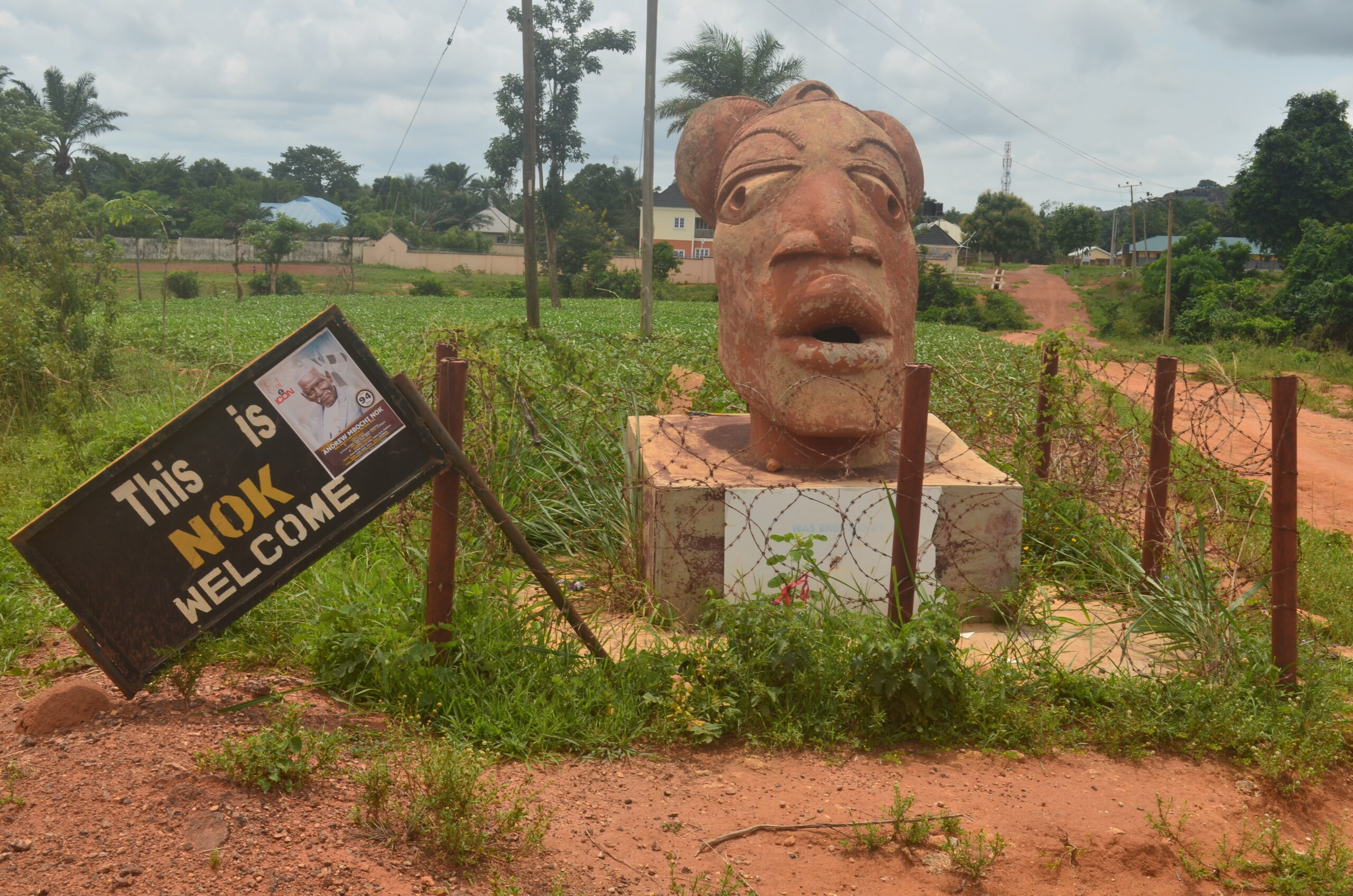

The Nok culture thrived in West Africa, primarily in modern-day Nigeria, from around 1000 BCE to 300 CE. They are best known for their distinctive terracotta sculptures, which reflect an advanced artistic ability. The Nok people were also pioneers in iron smelting, making them one of the earliest iron-working cultures in sub-Saharan Africa. By 300 CE, the civilization mysteriously vanished, and the reason remains unclear. Some scholars suggest environmental changes or overuse of resources, but no definitive evidence exists to explain their disappearance.
The Etruscans
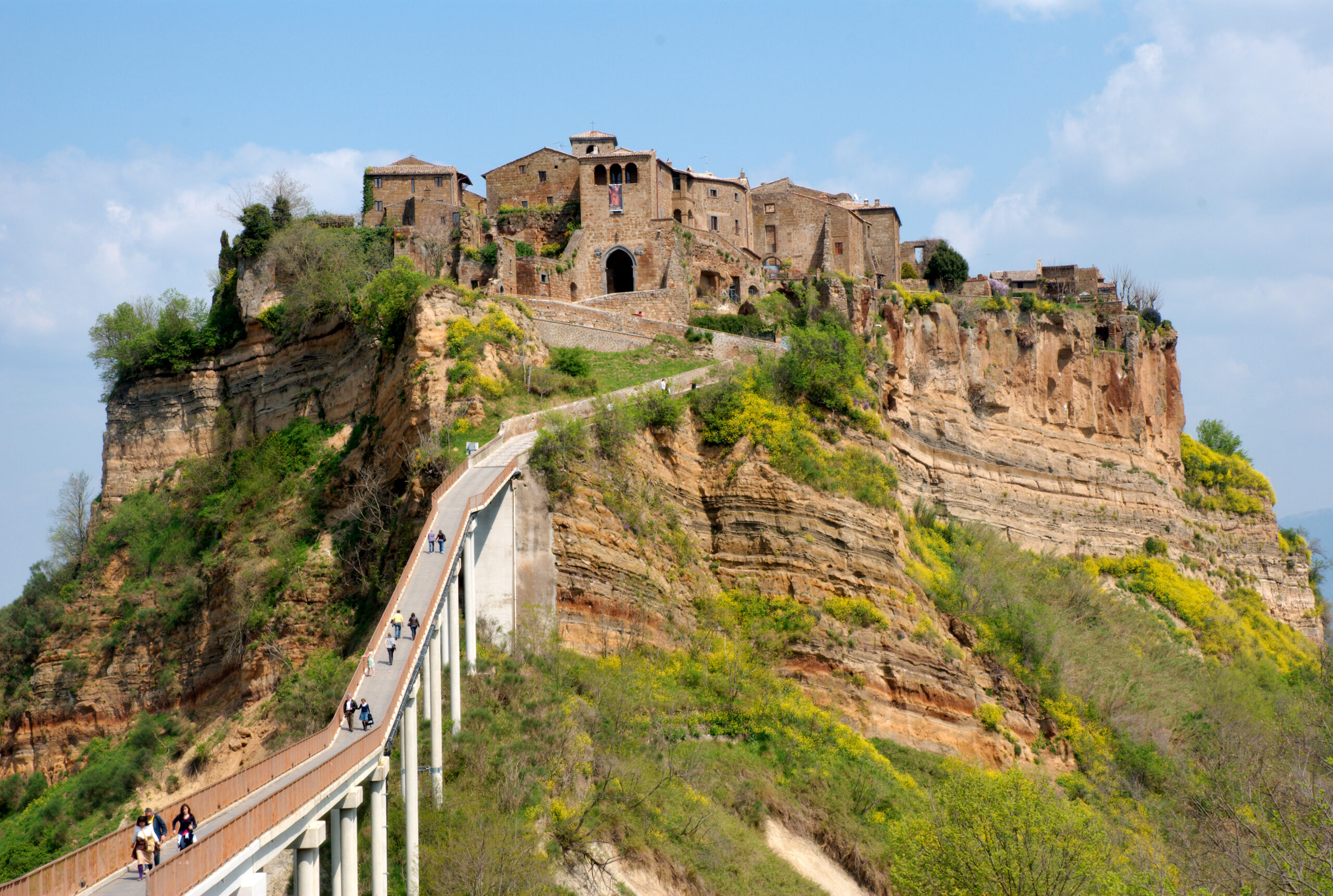

The Etruscans dominated central Italy before the rise of Rome, flourishing between the 8th and 3rd centuries BCE. They were known for their sophisticated society, impressive art, and strong influence on early Roman culture. Despite their power, the Etruscans mysteriously faded into history by the 3rd century BCE, as they were gradually absorbed by the growing Roman Republic. It is believed that military defeats and assimilation into Roman society caused their decline, but many aspects of their disappearance remain uncertain.
The Tiwanaku Empire
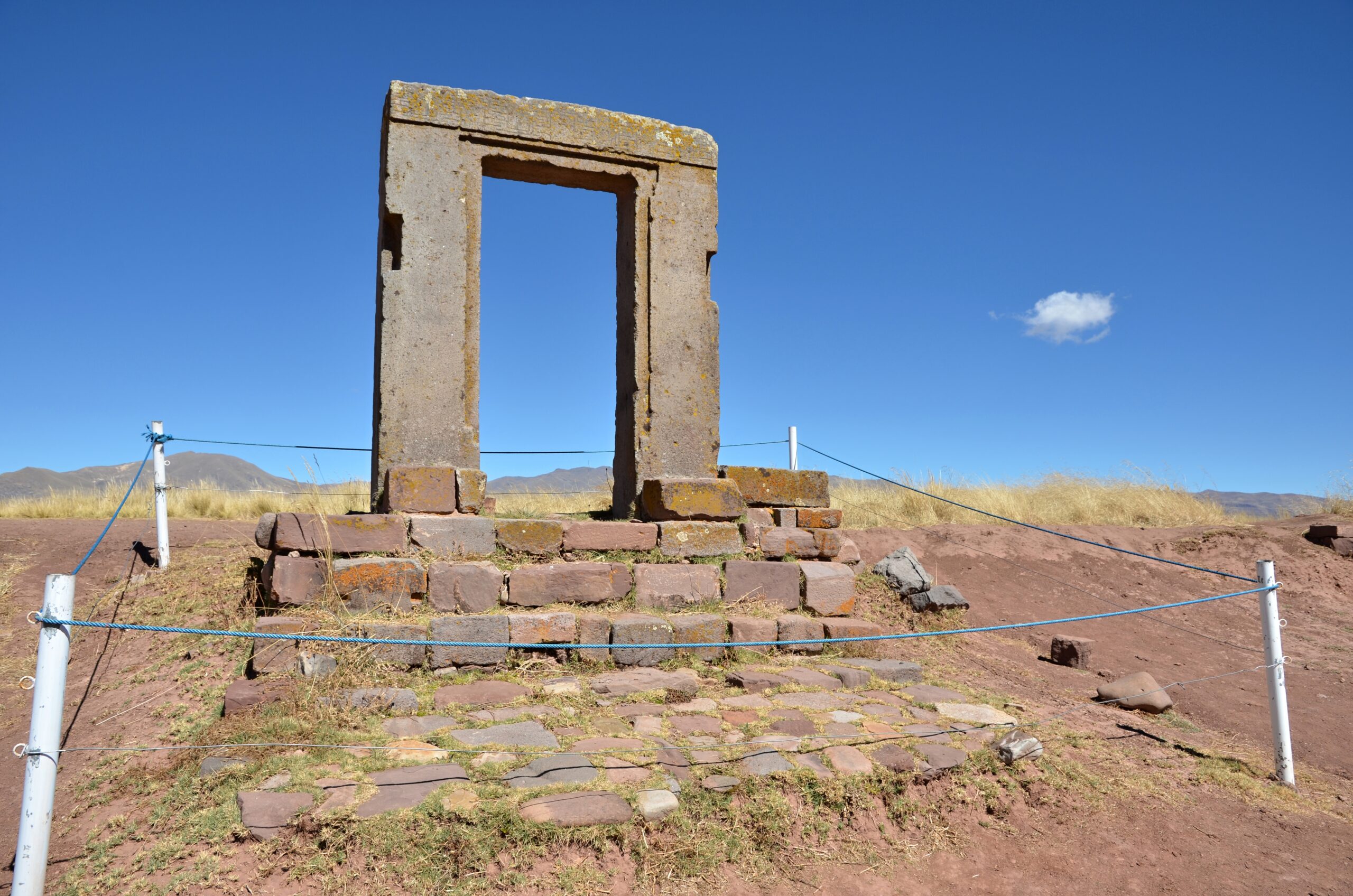

The Tiwanaku Empire flourished in the Andean region of South America from about 300 to 1000 CE. This pre-Incan civilization was known for its impressive stone architecture, complex agricultural techniques, and ceremonial centers near Lake Titicaca in present-day Bolivia. Around 1000 CE, Tiwanaku mysteriously declined, and its cities were abandoned. Some scholars believe prolonged droughts, resource depletion, or internal strife led to the empire’s fall. Despite these theories, the exact cause of the Tiwanaku Empire’s collapse remains unresolved.
The Nuragic Civilization
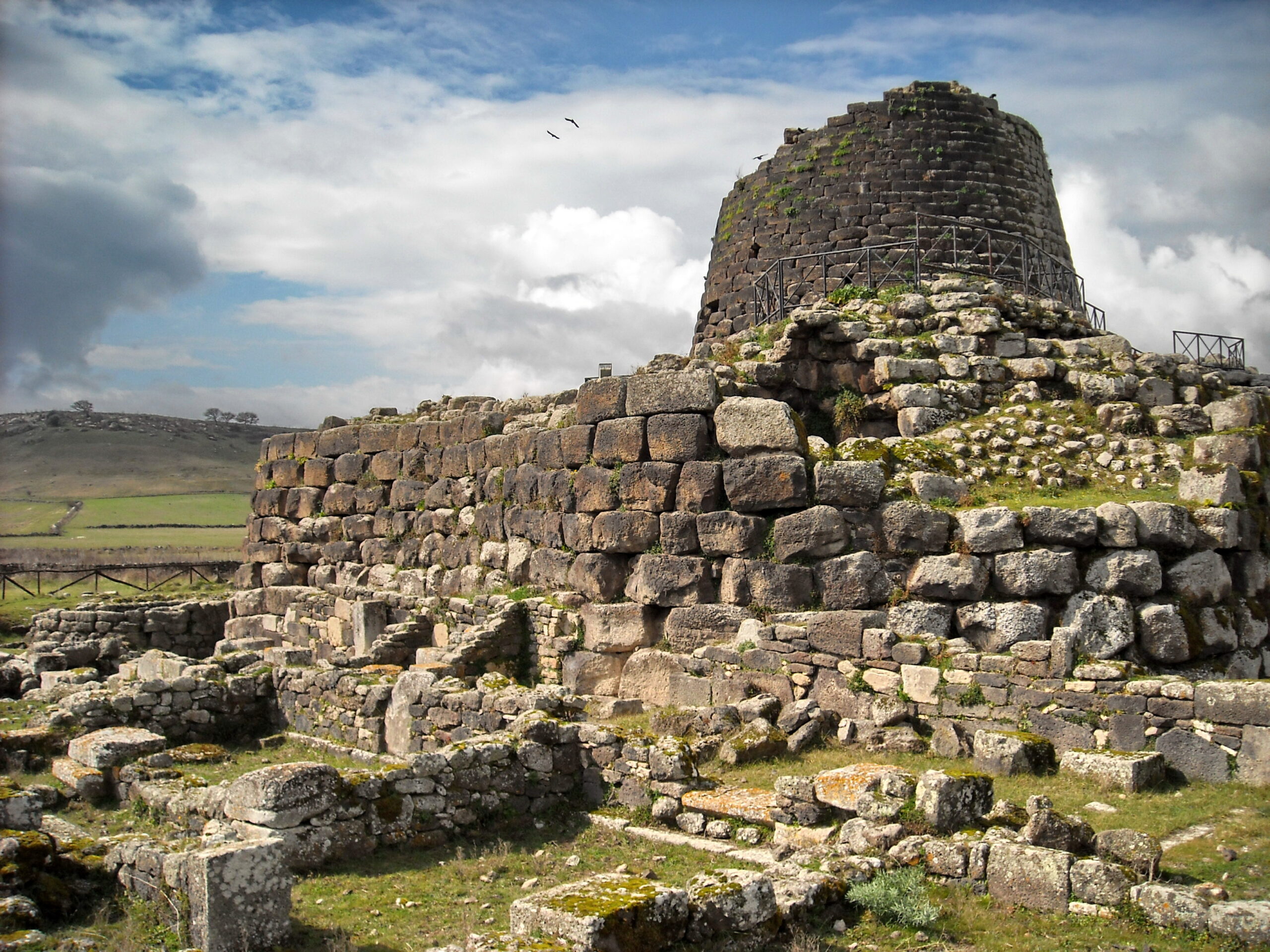

The Nuragic Civilization thrived on the island of Sardinia from around 1800 to 500 BCE. They are best known for their unique stone towers, called nuraghes, which are scattered across the island. This civilization built complex villages, engaged in trade, and developed a distinct culture. By the 6th century BCE, the Nuragic people began to disappear, with much of their society fading from history. The reasons for their decline are unclear, but external invasions, changing trade routes, or cultural assimilation may have played a role in their mysterious disappearance.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More from Rarest.org
22 Rare Marine Species Found in the Deepest Ocean Trenches
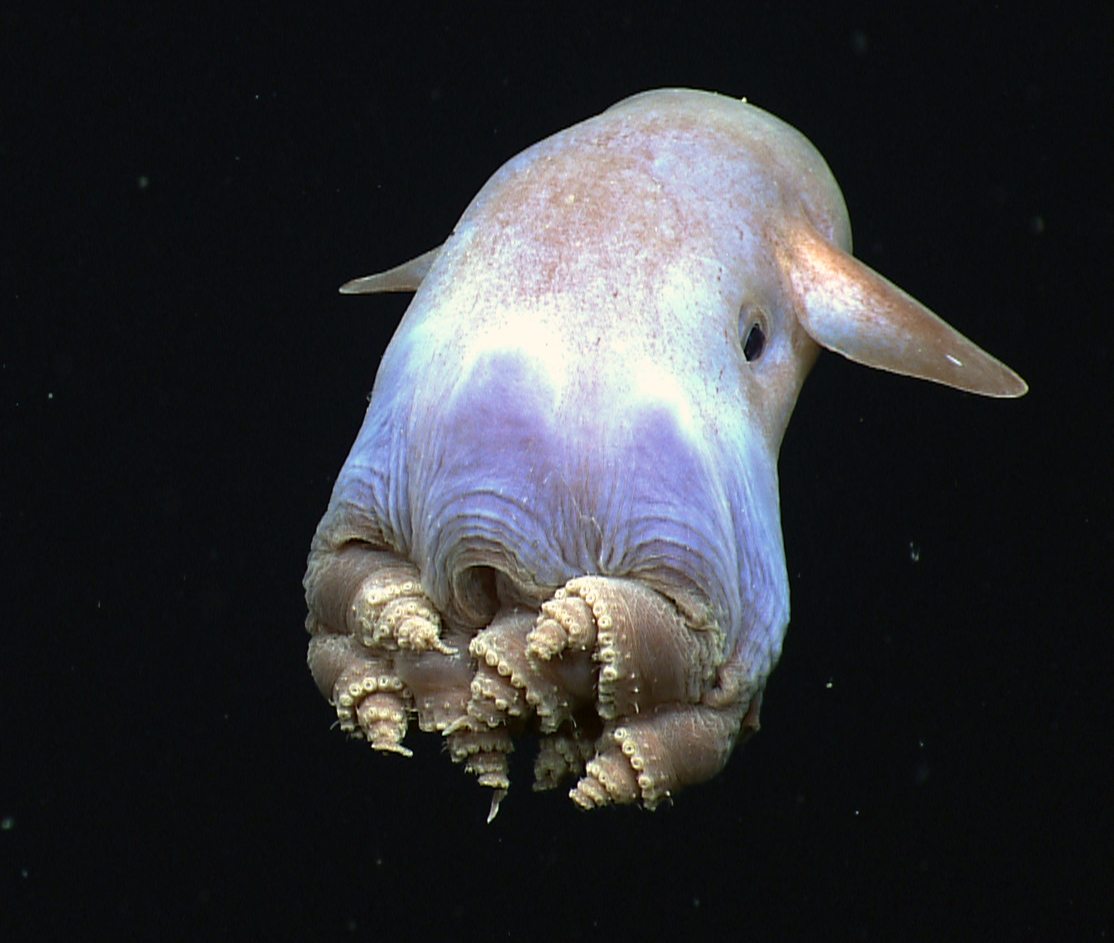

The deepest parts of the ocean are home to some of the most mysterious and fascinating creatures on Earth. Read More.
20 Rarest Chicken Breeds for Egg and Meat Production
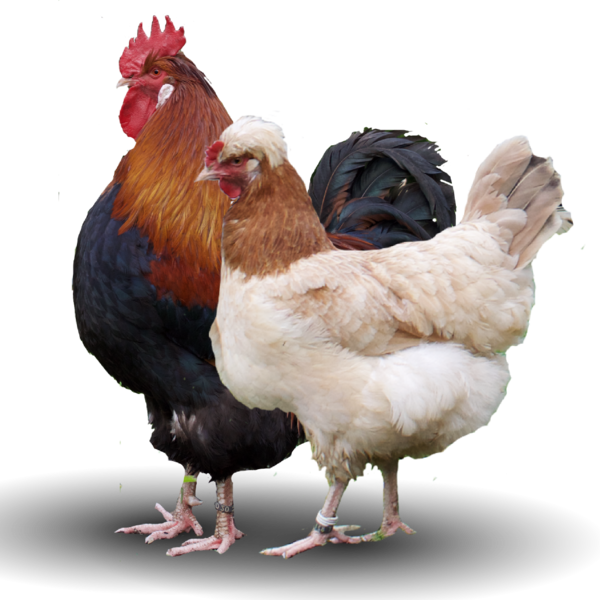

If you’re looking to raise chickens that offer both unique qualities and practical benefits, rare breeds can be an excellent choice. Read More.
16 Historic Landmarks Hidden in Unexpected Urban Locations
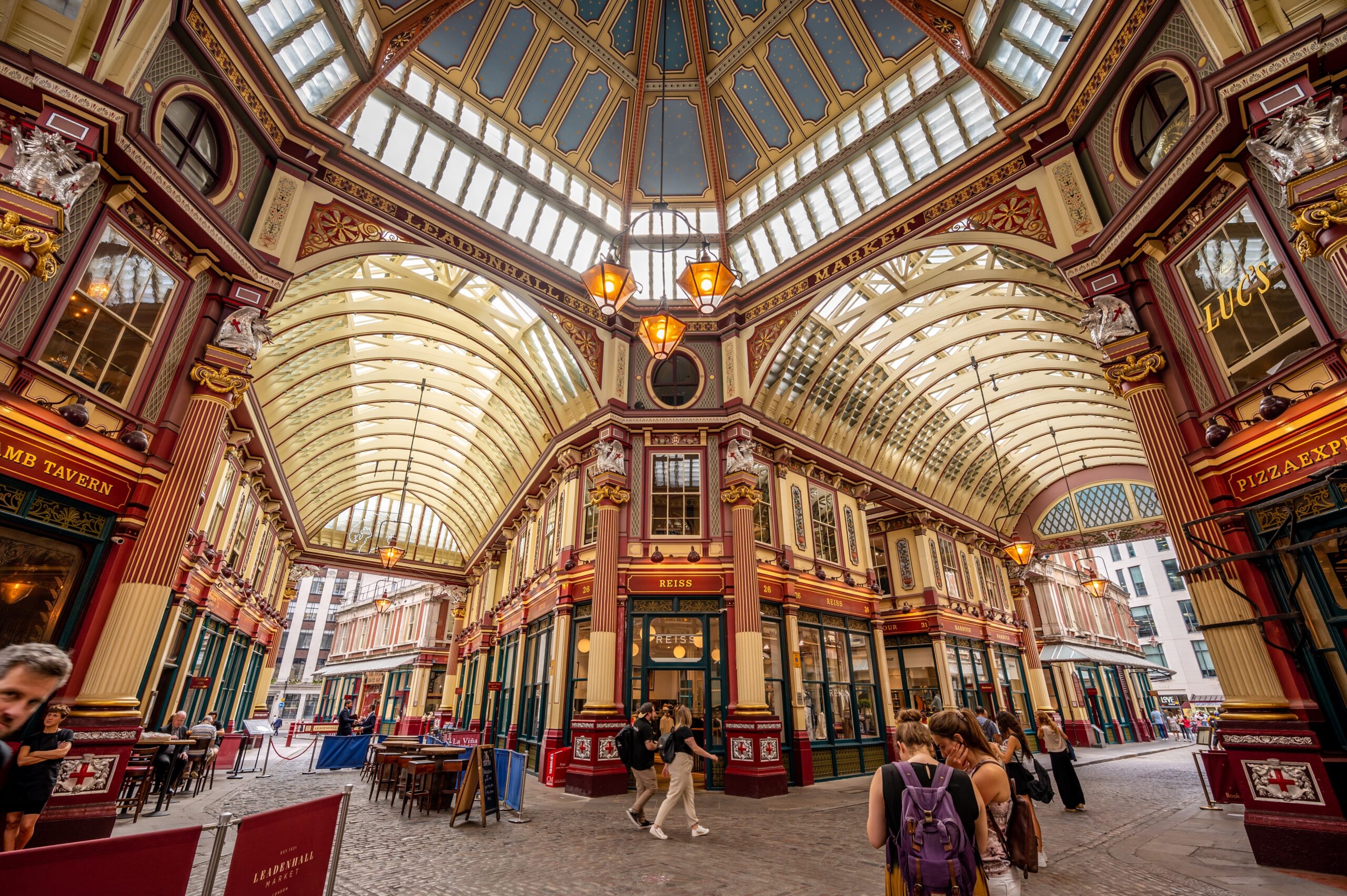

Urban landscapes often hide history in plain sight, blending ancient landmarks with modern settings. Read More.
