What Is the 1991 Washington Quarter Made Of?
The first Washington quarter was struck in 1932. At that time, it was first made of silver and copper. However, from 1965, the Washington quarter, along with other US coins, were made into base metals. That’s why the 1991 Washington quarter is made of 91.67% copper and 8.33% nickel.
The 1991 quarter has a mass of 5.67 grams, the diameter of 24.3 mm, and a thickness of 1.75 mm. It also has 119 reeds.
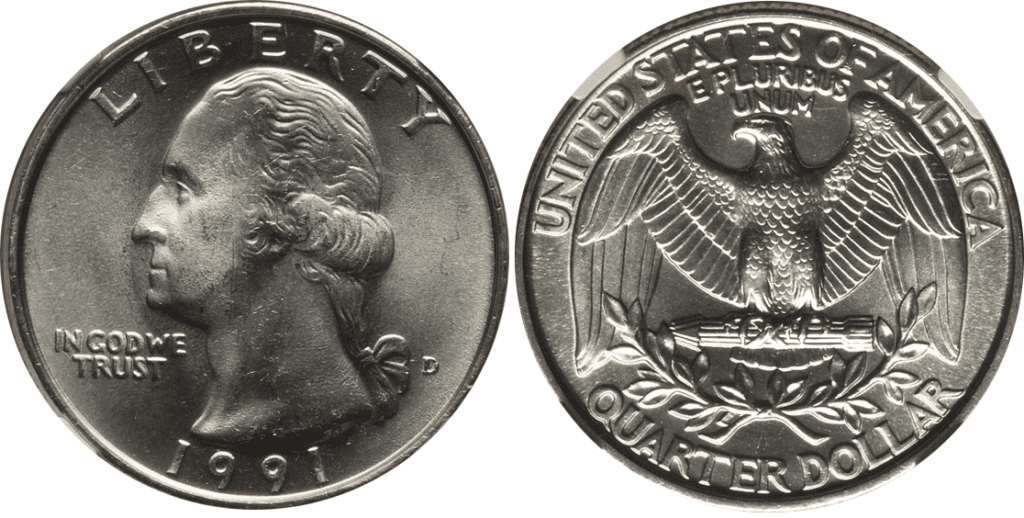

The 1991 quarter was designed by John Flanagan. The obverse side has the image of George Washington, the first American president. His image is facing left and on his front are the words “IN GOD WE TRUST.”
Beneath him is the year of minting, which is 1991. On the right side of his pigtail is the mint mark, if present, can be P, D or S.
On the reverse, you’ll find the following inscriptions:
- E PLURIBUS UNUM
- QUARTER DOLLAR
- UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
The reverse features the eagle with its wings spread out. It’s a symbol of the courage, power, and independence of the United States. The eagle holds a bundle of arrows that signifies the readiness of the country to go to war and defend itself. Underneath the arrows are olive branches that symbolize peace.
1991 is one of the many years that the quarter coin was minted. Although it was only in 1932 that the quarter started to feature Washington, the quarter has long been minted before that.
Years of minting include the following:
- 1796
- 1804–1807
- 1815–1828
- 1831–1930
- 1932
- 1934–present
Before 1932, the quarter had different designs. You have the draped bust, capped bust, seated liberty, barber, Isabella quarter, and Standing Liberty. Finally, in 1932, the same year of Washington’s 200th birthday, the quarter changed its design and now includes the first president’s image.
1991 Washington Quarter Varieties
There are different varieties of the 1991 Washington Quarter. Some of them differ from each other based on their mint mark. Others are different due to the error they received.
Here are some of the most common 1991 Washington Quarter you should know:
1991 D Washington Quarter
Year of minting: 1991
Mint Mark: D
Place of minting: Denver
Quantity produced: 630,966,693
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: 25 cents – $12.00 (or more)
Mass: 5.67 grams
Edge: Reeded
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 91.67% Copper and 8.33% Nickel
Diameter: 24.3 millimeters
Thickness: 1.75 millimeters
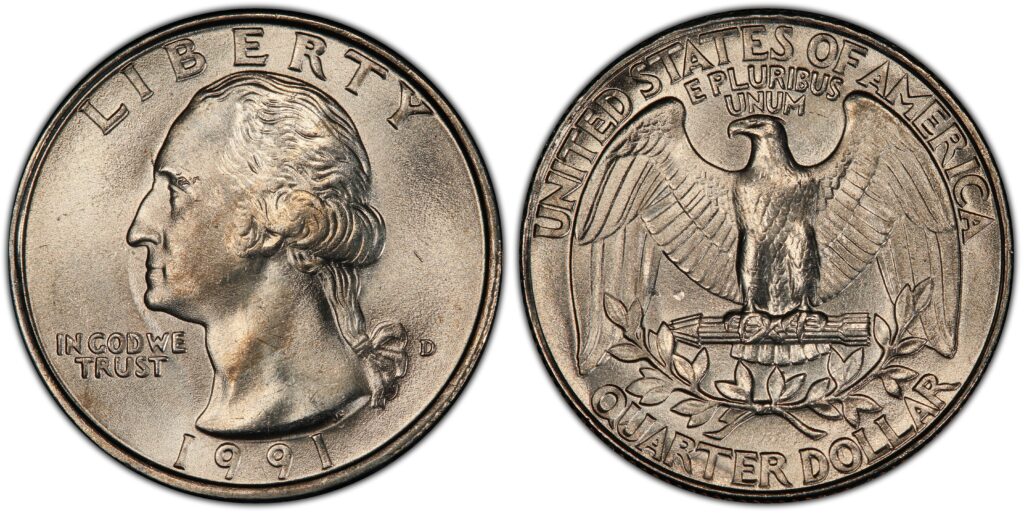

The Denver Mint produced more than 630 million Washington quarter coins in 1991. The quarters they produced bear the D mint mark. The usual price of this coin can be around $0.25 to $12.00.
1991 P Washington Quarter
Year of minting: 1991
Mint Mark: P or no mint mark
Place of minting: Philadelphia
Quantity produced: 570,968,000
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: 25 cents – $12.00 (or more)
Mass: 5.67 grams
Edge: Reeded
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 91.67% Copper and 8.33% Nickel
Diameter: 24.3 millimeters
Thickness: 1.75 millimeters
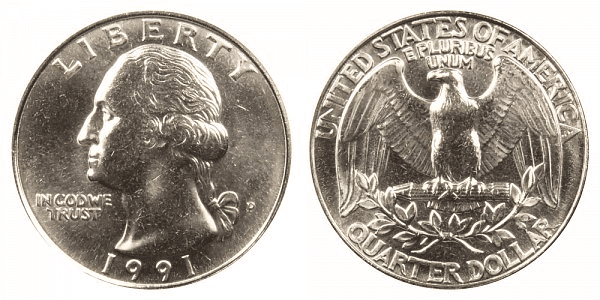
The 1991 Washington quarter made in Philadelphia has no mint mark or if there is, there’s P. The usual price of this coin is 25 cents – $12.00, the same as the D 1991 quarter. The more pristine and well-preserved the condition of your coin is, the more expensive it can be.
The Philadelphia Mint produced almost 571 million Washington quarters.
1991 S Washington Quarter
Year of minting: 1991
Mint Mark: S
Place of minting: San Francisco
Quantity produced: 2,867,787
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: 25 cents – $4.00 (or more)
Mass: 5.67 grams
Edge: Reeded
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 91.67% Copper and 8.33% Nickel
Diameter: 24.3 millimeters
Thickness: 1.75 millimeters
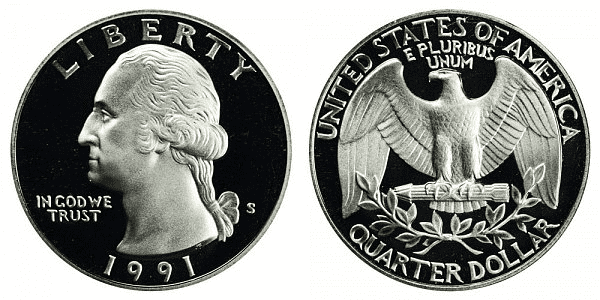
The 1991 S quarter can be sold for $0.25 to $4.00. There were almost three million Washington quarters produced by the San Francisco Mint.
Looking at the mintage of the 1991 S quarter, you might ask, “Why is it that the San Francisco Mint produced significantly less than the other minting centers?”
Well, the answer is that they produce proof coins, which are more time-consuming to produce. Each coin is manually cleaned and wiped. The proof coins also receive more details. They look shinier and more beautiful than the standard struck coins.
List Of 1991 Washington Quarter Errors
Aside from the three varieties mentioned above, there are also those coins that received errors. Thus, they become a unique type of Washington coin.
Errors may happen due to different reasons. It could be there was a misalignment, the planchet wasn’t positioned correctly or wasn’t cut properly, the coin was struck more than once, and so much more.
Here are some examples of 1991 Washington quarter errors.
Die attrition error
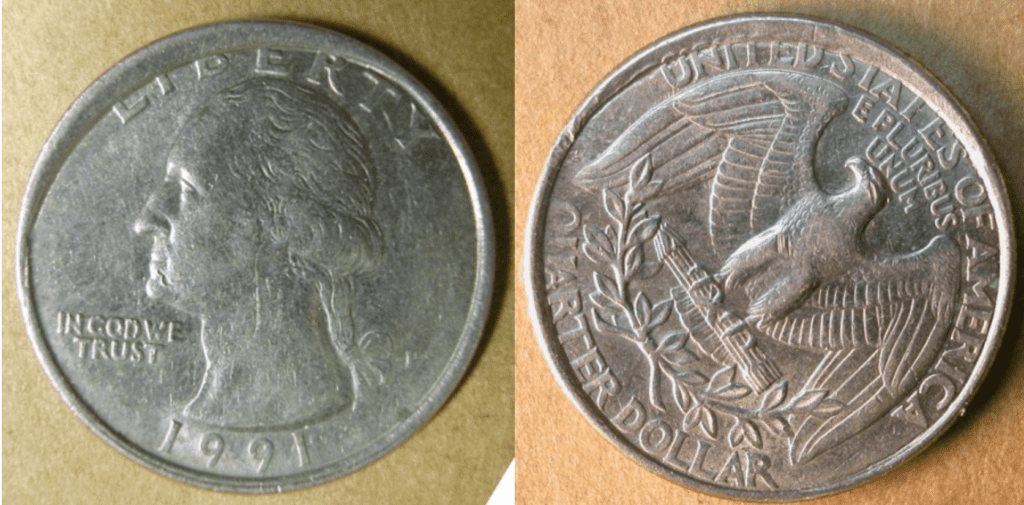

The die attrition error is perhaps among the most common types of error in coin minting. As you can see in the image, there’s peripheral die damage that caused the word “LIBERTY” to be partially covered.
Attrition errors happen when the hammer die temporarily becomes misaligned. This then strikes the beveled entrance of the collar. As a result, the coin has an unstruck portion, just like what you see in the image above.
1991-D Washington quarter finger strike error coin
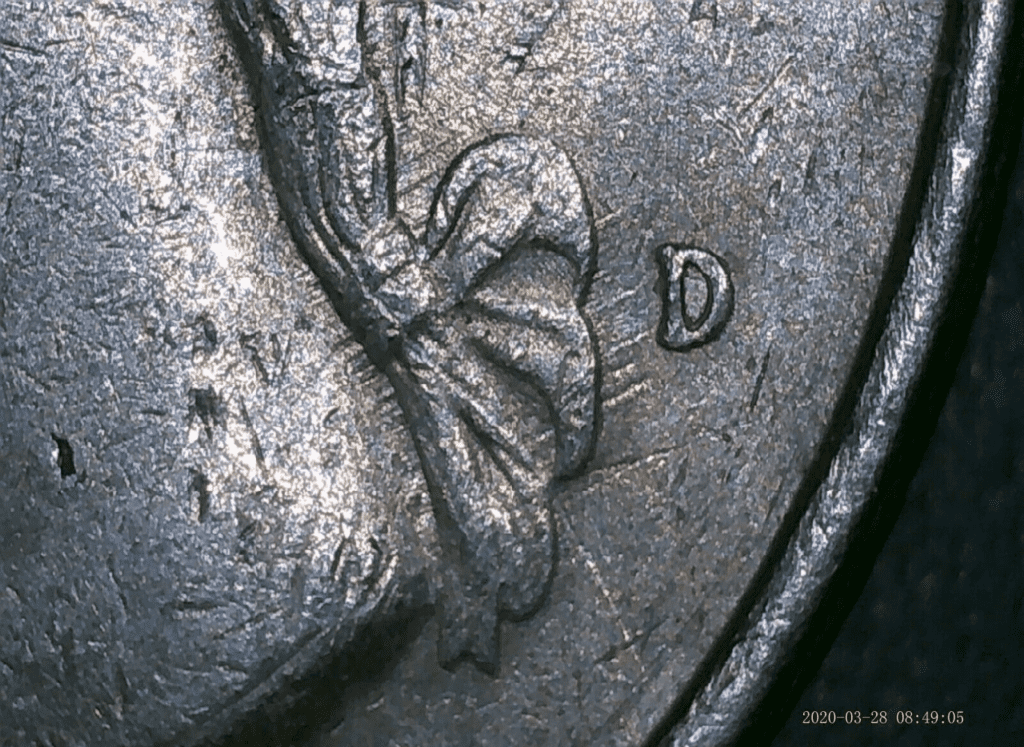

In this error, the coin was struck through a feeder finger. Because of this, there’s a deep impression on some parts of the coins. This impression is often accompanied with vertical walls. The impression’s margins can be straight, angular, or concave.
1991-D Washington quarter DDR error coin
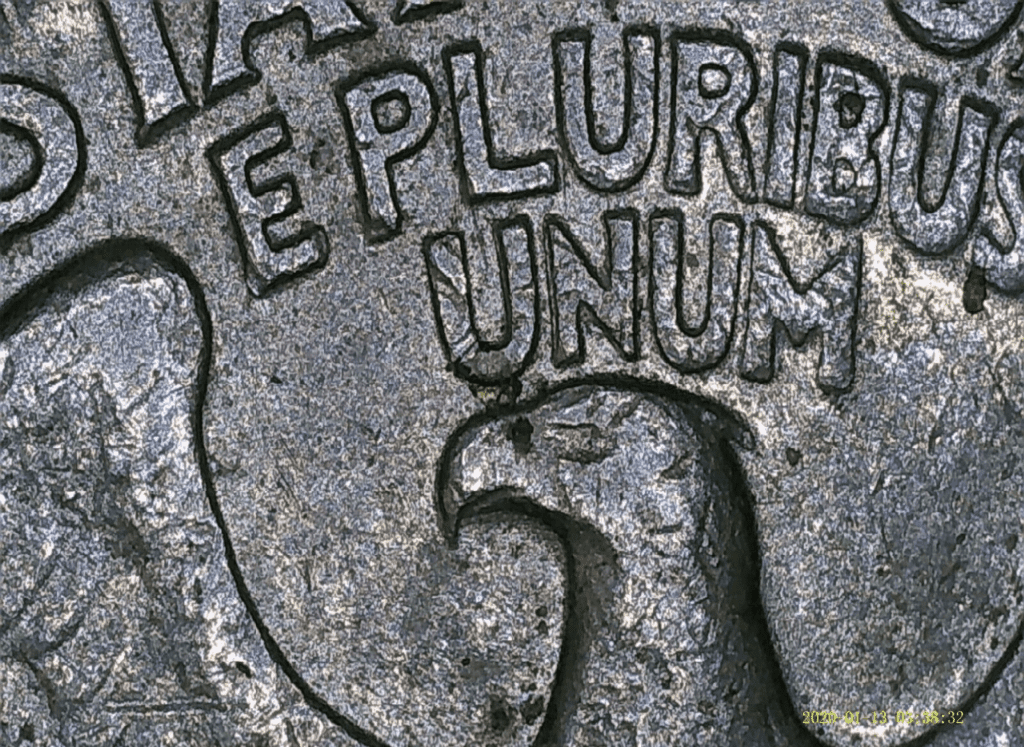
The doubled die coins like the one you’re seeing above happen when the coin die strikes the coin twice. As a result, there’s a doubling of some portion of the coin. For most collectors, the more obvious the doubling of the image or other elements, the higher the price of the coin.
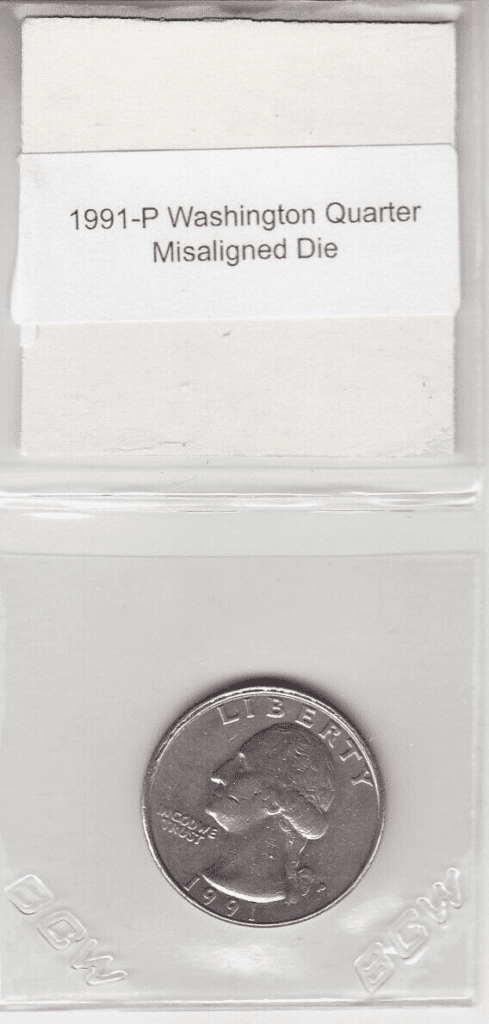
1991-P Philadelphia Washington Quarter Misaligned Die Error
This type of error happens when the die is misaligned, tilted, offset, or rotated. As you can see in the image above, the strike didn’t hit the center. You’ll see a wider margin at the “LIBERTY” portion of the coin.
How Much Is 1991 Washington Quarter Worth Today?
The 1991 Washington quarter with a standard struck and in circulated condition can be just around $0.25 to $2.00. Its selling value is almost the same as its face value. Melt value isn’t that far as well, standing at $0.0510.
While the value of a 1991 Washington quarter isn’t that much, you can still find a valuable coin if it is still in great condition. Price can also go up when it is highly graded and deemed as a rare coin.
To give you an idea, here’s a table of the different varieties of 1991 Washington quarter coins and their estimated value:
| Coin | Condition | Grade | Mintage | Value |
| 1991 D Washington Quarter | Circulated/mint | Not graded | 630,966,693 | $0.25 to $2.00 |
| 1990 D Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-65 | 630,966,693 | $10 |
| 1990 D Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-66 | 630,966,693 | $60 |
| 1990 D Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-67 | 630,966,693 | $665 |
| 1990 P Washington Quarter | Circulated/mint | Not graded | 570,968,000 | $0.25 to $2.00
|
| 1990 P Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-65 | 570,968,000
|
$10 |
| 1990 P Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-66 | 570,968,000
|
$17.50 |
| 1990 P Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/mint | MS-67 | 570,968,000
|
$115 |
| 1990 S Washington Quarter | Circulated/proof | Not graded | 2,867,787 | $0.30 to $2 |
| 1990 S Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/proof | PR-68 | 2,867,787 | $5.54 |
| 1990 S Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/proof | PR-69 | 2,867,787 | $7.43 |
| 1990 S Washington Quarter | Uncirculated/proof | PR-70 | 2,867,787 | $20.25 |
How Does The Grading System Work?
The Sheldon Scale is used by numismatists to provide a numerical value to coins. The Sheldon Scale goes from poor (P-1) to perfect mint state (P-1) (MS-70). Coins were originally evaluated using words to reflect their condition (Good, Fair, Excellent, Etc.). Unfortunately, coin collectors and dealers had different ideas about what each of these terms represent.
Professional numismatists joined together in the 1970s and established CoinGrading standards. These numismatists now assign grades at key places on the seventy-point scale, using the most regularly utilized numeric points in conjunction with the original adjective grade. The following are the most common coin grades:
-
-
- (P-1) Poor – Indistinguishable and probably damaged; if used, must have a date and mintmark; otherwise, rather battered.
- (FR-2) Fair – Nearly smooth, but without the damage that a coin graded Poor often possesses. The coin must have enough detail to be identified.
- (G-4) Fair – Inscriptions have merged into the rims in some areas, and important elements have been mostly erased.
- (VG-8) Very Good- A little weathered, but all of the primary design elements are visible, albeit faintly. There is little if any, central detail left.
- (F-12) Good – The item is very worn, yet the wear is even, and the overall design details stand out clearly. Rims are almost completely isolated from the field.
- (VF-20) Very Fine – Moderately weathered, with some finer features still visible. The motto or all letters of LIBERTY are readable. Both sides of the coin have entire rims that are separated from the field.
- (EF-40) Extremely Fine – Gently used; all gadgets are visible, and the most important ones are bold. The finer details are bold and clear, however, light wear may be seen.
- (AU-50) Uncirculated – Slight evidence of wear on the coin’s design’s high points; may have contact marks; eye appeal should be adequate.
- (AU-58) Uncirculated Choice – Slight traces of wear, no severe contact marks, almost full mint shine, and great eye appeal.
- (MS-60) Mint State Basal – Strictly uncirculated; no indication of wear on the coin’s highest points, but an unsightly coin with reduced luster, visible contact marks, hairlines, and other flaws.
- (MS-63) Mint State Acceptable – Uncirculated, but with contact scratches and nicks, little reduced shine, but otherwise appealing appearance. The strike is weak to average.
- (MS-65) Mint State Choice – Uncirculated with great mint shine, very little contact blemishes, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is unusually severe.
- (MS-68) Mint State Premium Quality – Uncirculated with superb luster, no obvious contact marks to the naked eye, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is quick and appealing.
- (MS-69) Almost Perfect Mint State – Uncirculated with perfect brilliance, a sharp and appealing strike, and extremely good eye appeal. A near-perfect coin with minor imperfections in the planchet, strike, and contact markings (seen only under 8x magnification).
- (MS-70) Mint State Perfect – Under 8x magnification, there are no tiny imperfections discernible; the strike is crisp, and the coin is perfectly centered on a beautiful planchet. Rarely seen on a coin, this coin is bright and whole, with original luster and exceptional eye appeal.
-
Where To Buy Or Sell 1991 Washington Quarter?
There are different places for you to buy or sell 1991 Washington Quarter. You can first try and go to the Internet. A simple search on Google with keyphrase, “Where to buy or sell 1991 Washington quarter,” should give you hundreds of useful links.
There are a lot of websites that specialize in buying and selling coins. You may have heard about CoinTrackers, USA Coin Book, and Grey Sheet. Aside from that, you can go to online selling platforms such as eBay, Amazon, Etsy, and Facebook marketplace, to name a few.
Aside from that, you can go to reputable coin grading service providers such as NGC and PCGS. They can tell you where to buy and sell 1991 Washington quarters.
Aside from those, you can visit coin shops, auction houses, and antique shops. Look for collectors in your area as well. Perhaps, you can also join groups or clubs of coin enthusiasts. The more people you know, the more your network will grow.
FAQs
Are P mint quarters worth anything?
Yes, P mint quarters are worth a lot of money — all of them, but the rare ones. For example, 1983-P Washington quarter coins are rare. It can be worth more than $20.
Is there a 1991 quarter worth $1300?
Yes, there is a 1991 quarter worth $1,300. It was sold in 2019 in the United States.
What is the 1991 P Quarter Error “Cud or Die Chip / Double at eye”?
The 1991 P quarter with a cud or die chip error, sometimes called double at eye error, is improperly struck due to a gouge or dent in the die. Because of this, there’s a “bump” on the coin.

