The 1950 Jefferson nickel is among the most loved and popular coins in the United States. The Jefferson nickel has already been around for more than 70 years now. Thus, an old 1950 Jefferson nickel would improve your coin collection.
When discussing the 1950 Jefferson nickel, the first question that comes to mind is, “What is it made of?” This is a good question because the material used to produce the nickel can increase or decrease its value.
So, the 1950 nickel is made of 75% copper and 25% nickel. Only during World War II did the US Mint need to change the composition of nickel since copper and nickel were important raw materials in winning the war. Thus, from mid-1942 to 1945, nickel was made in 56% copper, 35% silver, and 9% manganese.

The artist Felix Schlag prepared the original design of the Jefferson nickel. He was chosen after winning the competition held by the US Mint. Aside from having his design featured on the US coin, he was also given $1,000 as prize money.
Schlag designed both the obverse and reverse sides of the coin. His design would remain essentially the same from 1938 until 2004 when the obverse was replaced by a design by Joe Fitzgerald in 2005. After that, in 2006, the Jefferson nickel was redesigned by Jamie Franki.
The obverse features the portrait of the founding father Thomas Jefferson, the third president of the United States. Inscriptions include the following:
- IN GOD WE TRUST
- LIBERTY
- 1950
On the reverse, you’ll find the Monticello mansion, owned and even designed by Jefferson himself. The mansion is located in Charlottesville, Virginia. The inscriptions include the following:
- E PLURIBUS UNUM (which means “out of many, one”)
- MONTICELLO
- FIVE CENTS
- UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
1950 Jefferson Nickel Varieties
The 1950 Jefferson nickel comes in three standard varieties. These are the 1950-D, 1950-P, and 1950-P proof nickels. In 1950, only the Philadelphia and Denver mints were operational. The San Francisco Mint stopped producing nickels.
So, the expectation was for the Philadelphia and Denver Mint to step up. However, this expectation wasn’t met as both Mints produced even lower mintage than the previous year. This led to low production of nickels in 1950.
What’s more interesting here is that the number of 1950 nickels was already too low and got worse since many people hoarded the coin, believing the low mintage would add to the value of the coin in the future.
Now, you might wonder why only a few nickels were produced in 1950. The main reason is that the United States went through a severe recession in 1948, and its effects were felt even in the early 1950s.
So, with that said, take a look at the three varieties of the 1950 Jefferson nickel below:
1950 P Jefferson nickel
Edge: Smooth
Mint Mark: No mint mark
Place of minting: Philadelphia
Year of minting: 1950
Face Value: $0.05 (fifty cents)
Price: $0.05 to $86 (or more)
Quantity produced: 9,796,000
Designer: Felix Schlag
Composition: 75% copper and 25% nickel
Mass: 5 grams
Diameter: 21.21 mm
Thickness: 1.95 mm
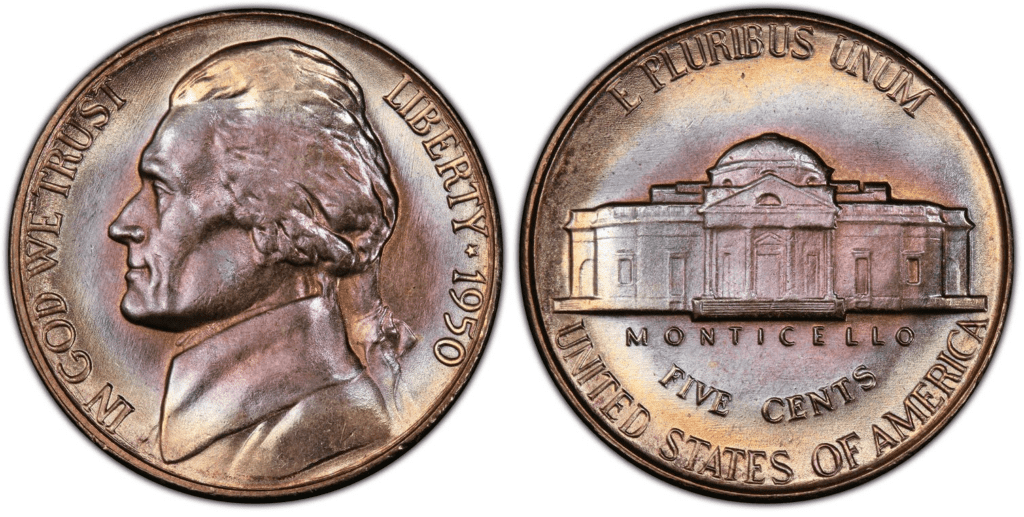

The 1950-P Jefferson nickel was struck in the Philadelphia Mint, and 9,796,000 of these coins were produced. The price starts at around $0.05 to $86. As always, circulated coins are less valuable compared to uncirculated ones.
1950 P Jefferson nickel (Proof)
Edge: Smooth
Mint Mark: No mint mark
Place of minting: Philadelphia
Year of minting: 1950
Face Value: $0.05 (fifty cents)
Price: $7 to $83.00 (or more)
Quantity produced: 51,386
Designer: Felix Schlag
Composition: 75% copper and 25% nickel
Mass: 5 grams
Diameter: 21.21 mm
Thickness: 1.95 mm
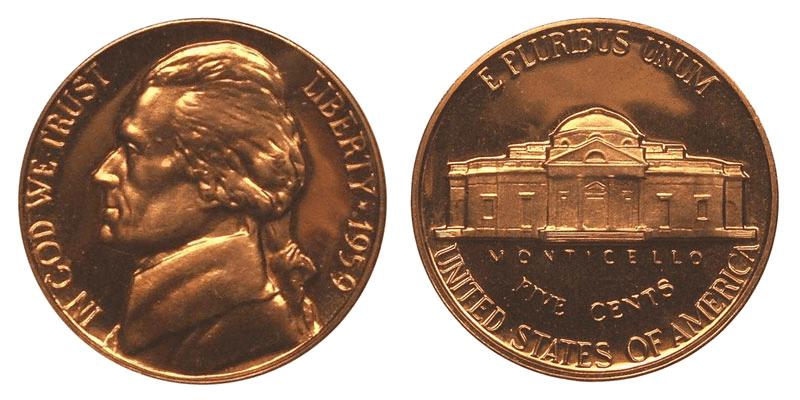
The Philadelphia Mint also produced special proof coins in 1950. They produced more than 51 thousand for that year. The mintage figure of the 1950-proof coin seemed too low at that time, but this number was small compared to the mintage of the subsequent years to come.
As you may already know, proof coins are more difficult to produce and time-consuming. Initially, the Philadelphia Mint produced semi-brilliant proof coins. However, many customers complained, so the Mint thoroughly polished the dies and planchets.
As a result, the coins became more brilliant and beautiful. However, the overly polishing of the dies caused the strike to be less prominent. This means that 1950 nickels with Ultra or Deep Cameo ratings would be very elusive.
Price may start at around $7 to $83.00.
1950 D Jefferson nickel
Edge: Smooth
Mint Mark: D
Place of minting: Denver
Year of minting: 1950
Face Value: $0.05 (fifty cents)
Price: $0.05 to $79.00 (or more)
Quantity produced: 2,630,030
Designer: Felix Schlag
Composition: 75% copper and 25% nickel
Mass: 5 grams
Diameter: 21.21 mm
Thickness: 1.95 mm
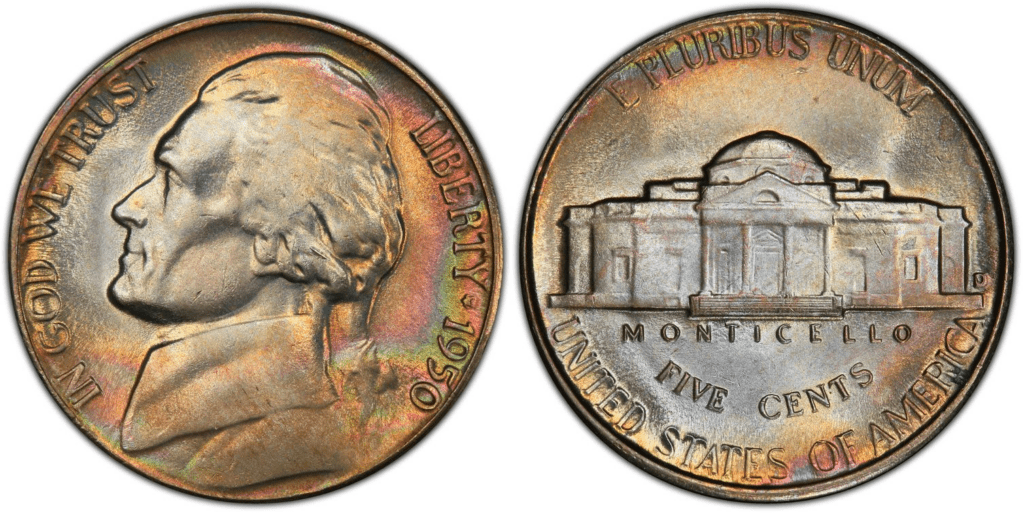

The 1950-D proof Jefferson nickel was struck in the Denver Mint. The Denver Mint produced the second-highest number of 1950 nickels reaching more than 2 million. However, that mintage figure is far less than the previous years.
Price may start at $0.05 to $79.00.
List Of 1950 Jefferson Nickel Errors
Due to the recession, the Mints needed to do some cost-cutting. Unfortunately, this led to the poor strike quality of the coin.
For this reason, the overall quality of the 1950 nickels is quite disappointing, and if you want to collect a premium and beautiful 1950 nickel, you might need to pay a larger amount.
Some of the most common 1950 Jefferson nickel errors include planchet errors. This happened when the planchet wasn’t properly cut. Sometimes, a planchet gets clipped or folded.
Another error is the strike error. As was already mentioned, the dies of the 1950 Jefferson nickel weren’t in good condition anymore. They are worn out and need to be replaced. Yet, despite their condition, the Mint still used them.
This then led to a lot of nickels with shallow contrast. Some can easily lose their details. In addition, some nickels came out with DDO or DDR errors, which means doubled die obverse or reverse, depending on which side the error happened.
Doubled die errors happen when the die hits the planchet twice, doubling some engraved elements.
Although the US Mint didn’t like to have any 1950 nickel error coins, these coins are of great interest to coin collectors. If the coin is still in good condition, the coin might even be worth hundreds and thousands of dollars.
How Much Is The 1950 Jefferson Nickel Worth Today?
The 1950 Jefferson nickel has a face value of five cents. But, unfortunately, its melt value isn’t that big, around $0.0667.
Nevertheless, you might be shocked that a coin with a face value and melt value lower than one dollar can be sold for a lot of money.
To give you an idea, check out this 1950 Jefferson Nickel values chart:
| Coin | Condition | Grade | Mintage | Value |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel | Circulated/mint | Not graded | 9,796,000 | $0.25 to $0.75 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel | Uncirculated/mint | MS-64 | 9,796,000 | $7 to $60 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel | Uncirculated/mint | MS-65 | 9,796,000 | $11 to $86 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel | Uncirculated/mint | MS-66 | 9,796,000 | $64 to $447 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel | Full Steps | MS-67 | 9,796,000 | $1,080 to $4,560 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel (Proof) | Uncirculated/Proof | Not graded | 51,386 | $7 to $81.00 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel (Proof) | Uncirculated/Proof | PR-66 | 51,386 | $56 to $90 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel (Proof) | Uncirculated/Proof | PR-67 | 51,386 | $46 to $228 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel (Proof) | Uncirculated/Proof | PR-68 | 51,386 | $91 to $494 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel (Proof) | Cameo | PR-68 | 51,386 | $840 to $9,988 |
| 1950 P Jefferson Nickel (Proof) | Deep Cameo or Ultra Cameo | PR-67+ | 51,386 | $900 to $6,463 |
| 1950 D Jefferson Nickel | Circulated/mint | Not graded | 2,630,030 | $0.25 to $0.75
|
| 1950 D Jefferson Nickel | Uncirculated/mint | MS-65 | 2,630,030 | $20 to $79 |
| 1950 D Jefferson Nickel | Uncirculated/mint | MS-66 | 2,630,030 | $22 to $45 |
| 1950 D Jefferson Nickel | Uncirculated/mint | MS-67 | 2,630,030 | $101 to $336 |
| 1950 D Jefferson Nickel | Full Step | MS-67+ | 2,630,030 | $1,110 to $1,645 |
The 1950 nickel is no doubt an interesting coin for collectors. What’s more interesting about it is its auction records. Take a look at the following auction records for each variety to learn its potential value:
- $17,250 – 1950-D 5C, FS (Regular Strike) coin with a grade of MS67 sold in 09-13-2006 by Heritage Auctions
- $11,500 – 1950 5C, FS (Regular Strike) coin with a grade of MS67 sold in March 2007 by Bowers & Merena
- $7,475 – 1950 5C, DCAM (Proof) coin with a grade of PR67 sold in January 2010 by Heritage Auctions
How Does The Grading System Work?
The Sheldon Scale is used by numismatists to provide a numerical value to coins. The Sheldon Scale goes from poor (P-1) to perfect mint state (P-1) (MS-70). Coins were originally evaluated using words to reflect their condition (Good, Fair, Excellent, Etc.). Unfortunately, coin collectors and dealers had different ideas about what each of these terms represent.
Professional numismatists joined together in the 1970s and established CoinGrading standards. These numismatists now assign grades at key places on the seventy-point scale, using the most regularly utilized numeric points in conjunction with the original adjective grade. The following are the most common coin grades:
-
-
- (P-1) Poor – Indistinguishable and probably damaged; if used, must have a date and mintmark; otherwise, rather battered.
- (FR-2) Fair – Nearly smooth, but without the damage that a coin graded Poor often possesses. The coin must have enough detail to be identified.
- (G-4) Fair – Inscriptions have merged into the rims in some areas, and important elements have been mostly erased.
- (VG-8) Very Good- A little weathered, but all of the primary design elements are visible, albeit faintly. There is little if any, central detail left.
- (F-12) Good – The item is very worn, yet the wear is even, and the overall design details stand out clearly. Rims are almost completely isolated from the field.
- (VF-20) Very Fine – Moderately weathered, with some finer features still visible. The motto or all letters of LIBERTY are readable. Both sides of the coin have entire rims that are separated from the field.
- (EF-40) Extremely Fine – Gently used; all gadgets are visible, and the most important ones are bold. The finer details are bold and clear, however, light wear may be seen.
- (AU-50) Uncirculated – Slight evidence of wear on the coin’s design’s high points; may have contact marks; eye appeal should be adequate.
- (AU-58) Uncirculated Choice – Slight traces of wear, no severe contact marks, almost full mint shine, and great eye appeal.
- (MS-60) Mint State Basal – Strictly uncirculated; no indication of wear on the coin’s highest points, but an unsightly coin with reduced luster, visible contact marks, hairlines, and other flaws.
- (MS-63) Mint State Acceptable – Uncirculated, but with contact scratches and nicks, little reduced shine, but otherwise appealing appearance. The strike is weak to average.
- (MS-65) Mint State Choice – Uncirculated with great mint shine, very little contact blemishes, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is unusually severe.
- (MS-68) Mint State Premium Quality – Uncirculated with superb luster, no obvious contact marks to the naked eye, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is quick and appealing.
- (MS-69) Almost Perfect Mint State – Uncirculated with perfect brilliance, a sharp and appealing strike, and extremely good eye appeal. A near-perfect coin with minor imperfections in the planchet, strike, and contact markings (seen only under 8x magnification).
- (MS-70) Mint State Perfect – Under 8x magnification, there are no tiny imperfections discernible; the strike is crisp, and the coin is perfectly centered on a beautiful planchet. Rarely seen on a coin, this coin is bright and whole, with original luster and exceptional eye appeal.
-
Where To Buy Or Sell 1950 Jefferson Nickel?
There are a lot of places where you can buy or sell 1950 Jefferson nickels. But, of course, remember that the mintage is too low for this year. So, the supply might be scarce.
The first place you can go would be the Internet. With just a few clicks or a push of a button, you can instantly search and find the right five-cent coin you need.
If you can’t find your coin, you can try brick-and-mortar stores. These include coin shops, pawnshops, and antique stores. Aside from that, you can also try auction houses. They are known to offer some of the best US coins.
Be sure to join local or national clubs of coin collectors. Joining these groups could increase your network. People with like minds could point you in the right direction when buying and selling 1950 Jefferson nickels.
FAQs
How much is a 1950 D uncirculated nickel worth?
The 1950 D uncirculated nickel can be worth a few bucks to thousands of dollars. Uncirculated nickels are known for their excellent preservation. The value of your uncirculated nickel would greatly depend on the coin’s overall condition. However, you can be sure that it will be more valuable than circulated nickels.
Where is the mint mark on a 1950 nickel?
The mint mark on a 1950 nickel can be found on the coin’s reverse side. Look between the right side of the Monticello and the coin’s rim. You should see a D mint mark. The mint mark for coins struck in Philadelphia is absent.
Is the 1950-D nickel rare?
Some 1950-D nickels are rare. These coins are usually graded with MS68 and above. So, for example, a super rare 1950-D nickel would be a coin with MS70 grade.
What is the value of a 1950 Jefferson nickel?
The value of the 1950 Jefferson nickel depends on its overall condition. Its face value is 5 cents. Its melt value is slightly higher but would not exceed $1. 1950 Jefferson nickels still in good condition possessing a rare feature, would be valued more. Some 1950 nickels were sold for more than $1,000.
