The 1954 quarter was issued by the US Mint many decades ago. As an old coin made of silver, it is no wonder that a lot of coin enthusiasts would like to add this coin to their collection.
If you wish to learn more, read on. This article will discuss the composition, design, historic milestone, and value of the 1954 quarter.
What Is the 1954 Washington Quarter Made Of?
One of the first things people ask about the 1954 quarter is its composition. A lot of people would be happy to know that this coin is made of 90% silver and 10% copper. Because of this, the coin is more valuable than coins made of base metals.
Coins struck before 1965 are made of silver. The coins today are minted with copper or nickel.
Now, you might wonder, why did the US Mint change the composition of regular coins? There are two primary reasons.
For one, people try to hoard silver coins because of their perceived value. Because of this, the regular coins, including Washington quarters, don’t circulate well, which defeats the purpose of producing them.
The second reason is that the market value of silver was steadily rising. It came to a point when it is more expensive to produce the coins than their face value.
So, through the Coinage Act of 1965, the US Mint removed silver from regular coins.
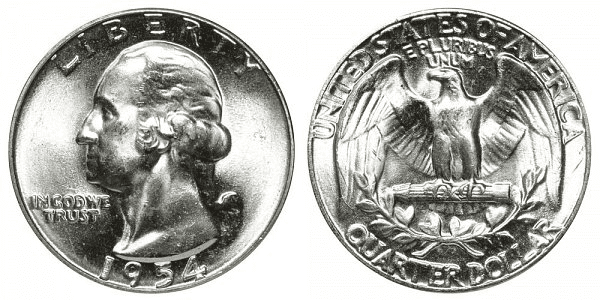
For the 1954 Washington quarter, the obverse features the image of George Washington. Inscriptions include LIBERTY, 1954, and IN GOD WE TRUST.
On the reverse, you will find the heraldic eagle holding a bundle of arrows. Underneath the eagle is an olive branch. Inscriptions include UNITED STATES OF AMERICA, E PLURIBUS UNUM, and QUARTER COIN.
1954 Washington Quarter Varieties
The Washington quarter was in great demand by the early 1950s. Thus, there were three mint centers, namely, the Denver, Philadelphia, and San Francisco mint centers, that worked together to produce more than 88 million quarters. There are four varieties of the 1954 Washington quarter and their main difference is their mint marks.
| Variety | Mint Location | Mintage |
| 1954 D Washington quarter | Denver | 42,305,500 |
| 1954 S Washington quarter | San Francisco | 11,834,722 |
| 1954 P Washington quarter | Philadelphia | 54,412,203 |
| 1954 Proof Washington quarter | Philadelphia | 233,300 |
| Total | 108,785,725 |
After two consecutive years of the Denver Mint producing the most number of quarter coins, the Philadelphia Mint once again took the crown in 1954 and continued to do so until 1956.
Let’s now take a deeper look at each of the 1954 Washington quarter varieties.
1954 D Washington Quarter
Year of minting: 1954
Mint Mark: D
Place of minting: Denver
Quantity produced: 42,305,500
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: starts at around $4.45 and $7 (circulated condition)
Mass: 6.30 grams
Edge: Reeded
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 90% silver and 10% copper
Diameter: 24.3 millimeters
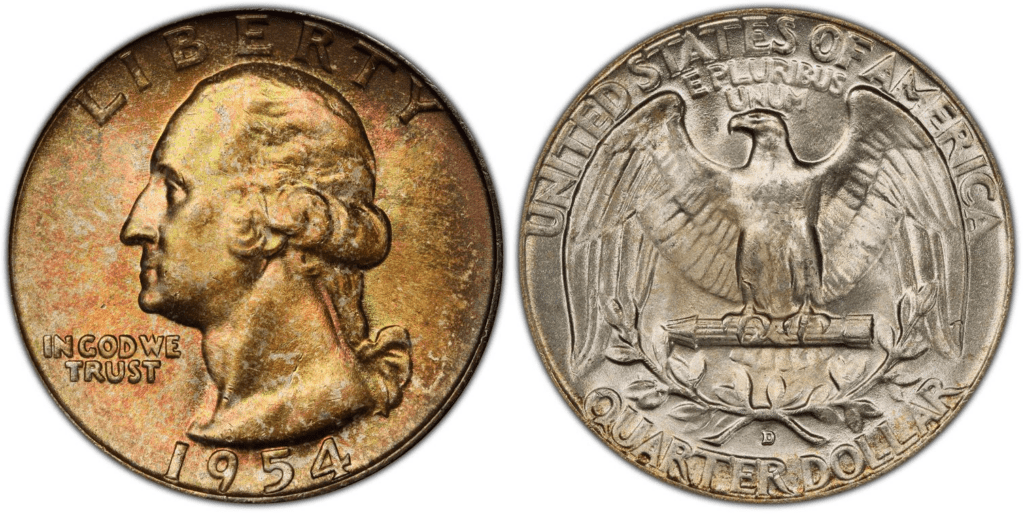

The Denver Mint produced more than 42 million quarter coins in 1954. This is lower than what was produced in 1953, which was more than 56 million. The mintage of the Denver Mint variant continued to slide down in 1955, when only 3 million quarters were produced in the Denver Mint.
1954 S Washington Quarter
Year of minting: 1954
Mint Mark: S
Place of minting: San Francisco
Quantity produced: 11,834,722
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: starts at around $4.45 and $7 (circulated condition)
Mass: 6.30 grams
Edge: Reeded
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 90% silver and 10% copper
Diameter: 24.30 millimeters
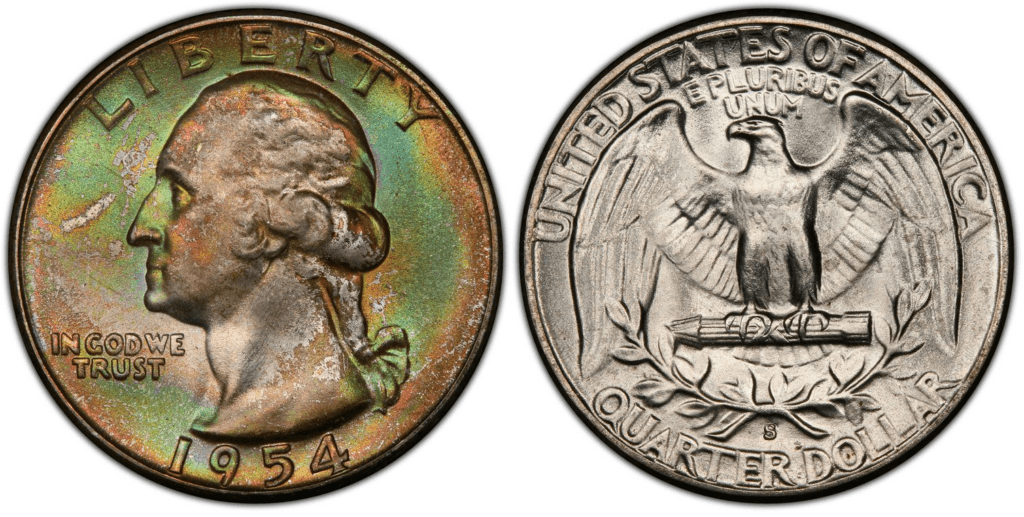

The San Francisco Mint produced more than 11 million quarters in 1954. From 1953 to 1955, the production capabilities of the San Francisco Mint continually dipped down. This trend was something you expect for a mint center that would eventually close in 1955.
Most quarters produced in 1954 were struck with heavily eroded dies. As a result, 1954-S quarters typically show blurry surfaces.
1954 P Washington Quarter
Year of minting: 1954
Mint Mark: none
Place of minting: Philadelphia
Quantity produced: 54,412,203
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: starts at around $4.45 and $7 (circulated condition)
Mass: 6.30 grams
Edge: Reeded
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 90% silver and 10% copper
Diameter: 24.30 millimeters
The Philadelphia Mint produced more than 54 million quarters in 1954. This was a sudden spike in the production of the Philadelphia Mint. You need to realize that in 1953, there were only about 18 million quarter coins from this mint.
With a massive mintage, the Philadelphia Mint surpassed the Denver Mint in terms of production. What’s great about the 1954-P quarter is that there are plenty of examples up to MS 66.
1954 Proof Washington Quarter
Year of minting: 1954
Mint Mark: none
Place of minting: Philadelphia
Quantity produced: 233,300
Face Value: $0.25 (twenty-five cent)
Price: starts at around $17 (uncirculated condition)
Mass: 6.30 grams
Edge: Reeded
Designer: John Flanagan
Composition: 90% silver and 10% copper
Diameter: 24.30 millimeters
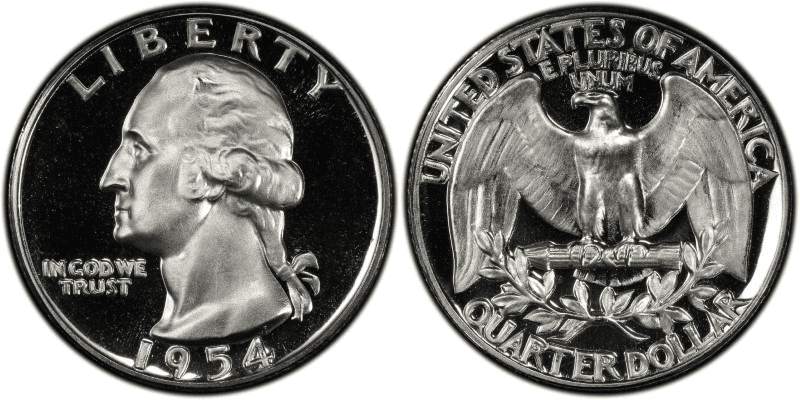

The demand for proof coins increased in 1954. In 1953, there were only 128,800 proof coins but in 1954, that number increased to 233,300. This trend continued up until the 1960s, when mintage reached up to a million.
List Of 1954 Washington Quarter Errors
Why should you be interested in error coins? After all, these coins aren’t perfectly struck coins, right? That might sound plausible logical thinking, but the truth is that some error coins are even more valuable than regular coins.
Because of the uniqueness and interesting appearance of error coins, they may attract higher value from collectors.
Here are some examples of 1954 Washington quarter errors:
Repunched mint marks
The repunched mint marks (RPMs) are among the most common errors in coins. Here’s an example of a 1954 Washington quarter with RPM error:
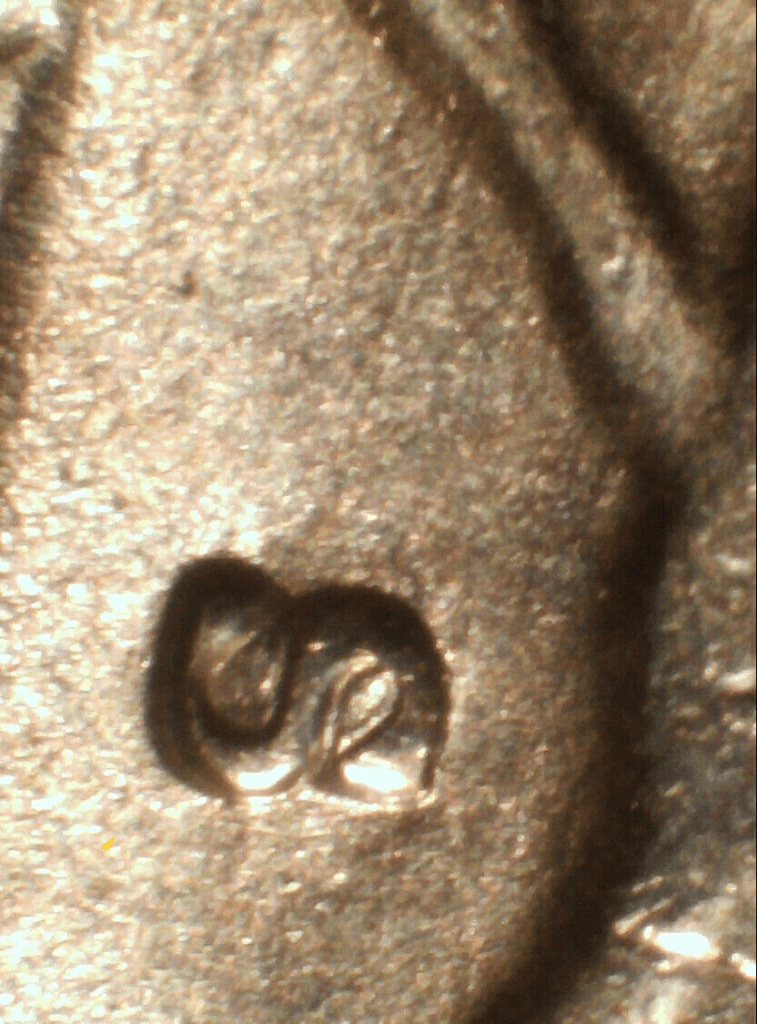
RPMs happen when the mint mark is punched on the coin twice. In this example, it’s an S over S mintmark error.
Strike-through error
The strike-through error happens when a foreign object gets stuck on the die or the planchet. The die would then strike through this foreign object.
The result isn’t always the same. Some strike-through errors would look like an indentation on the coin. Some would look like unnecessary marks or distortion.
Here’s an example of a strike-through error in a 1954 quarter:
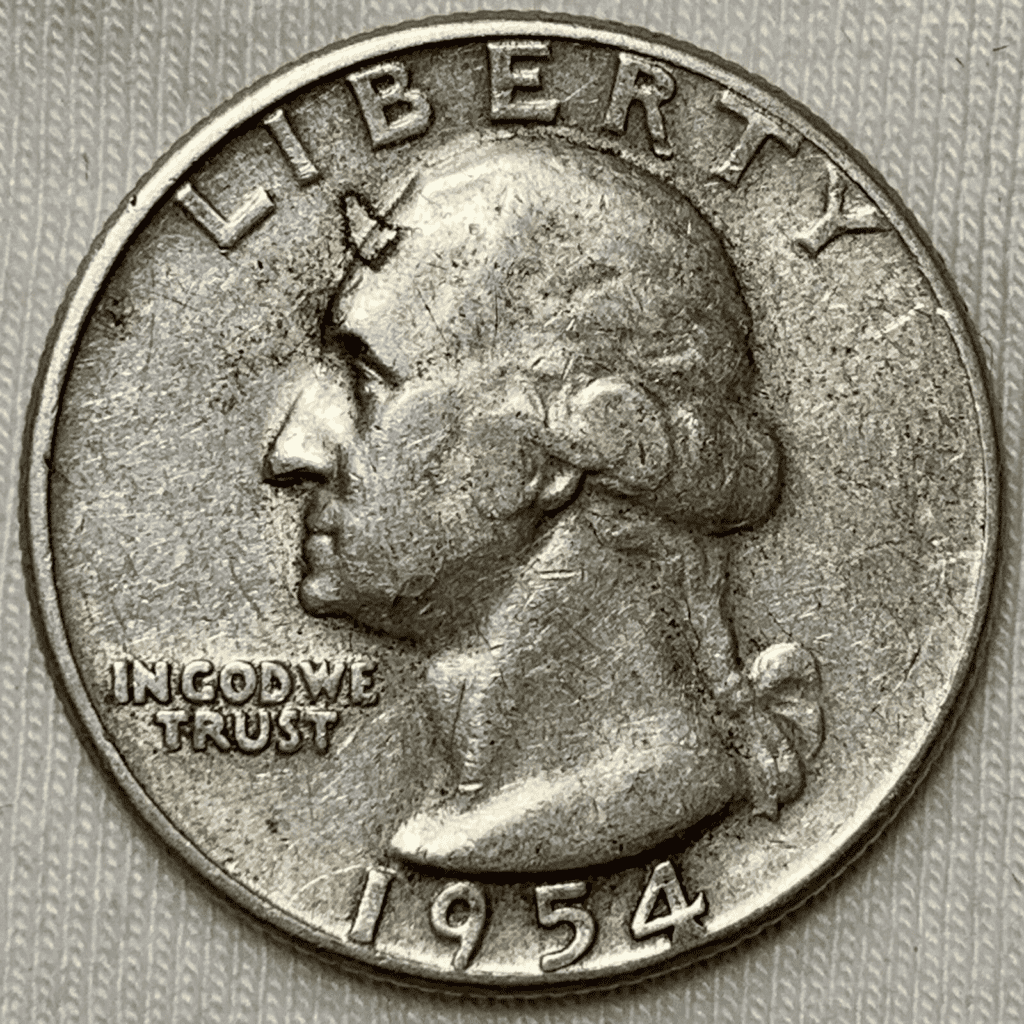
Die break error
Although the die is made of a hard material, it would eventually break due to wear and tear. When a die breaks, it develops a crack on its surface. The crack would then hit the coin’s surface and leave a mark on the coin.
Here’s an example of a die break error:
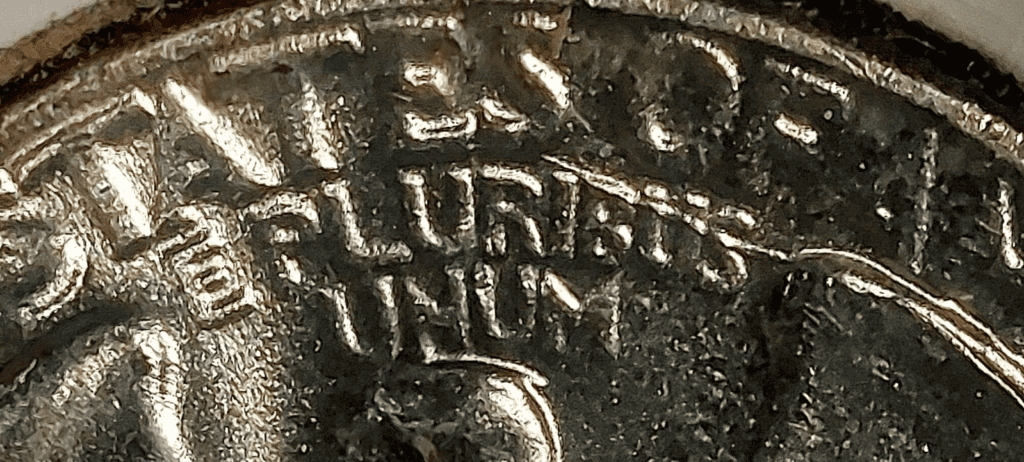
How Much Is The 1954 Washington Quarter Worth Today?
One of the most important questions to answer when it comes to the 1954 Washington 50-cent coin is its value. So, is this coin really valuable? Is it worth your time and money?
The answer really depends on the condition and rarity of your coin. If you’re just going to base the value of the coin on its denomination, then it would only be just 25 cents. Circulated 1954 quarter coins can be more expensive, which can be around $5 to $10.
The melt value of the 1954 50-cent coin is around $3.9750. It may increase further as the value of silver increases.
To help you know the real value of the 1954 Washington quarter, here’s a table of their auction records:
| Coin | Condition | Grade | Sold date | Sold by | Value |
| 1954 P Washington quarter | Superb Gem Uncirculated | MS 68 | January 8, 2003 | eBay | $17,250 |
| 1954 Proof Washington quarter | Superb Gem Uncirculated | PR 69 (Deep Cameo) | November 6, 2014 | Heritage Auctions | $12,925 |
| 1954 S Washington quarter | Superb Gem Uncirculated | MS 68 | March 31, 2021 | Stack’s Bowers | $12,000 |
| 1954 D Washington quarter | Superb Gem Uncirculated | MS 67+ | February 23, 2020 | Heritage Auctions | $9,000 |
How Does The Grading System Work?
In terms of coins, a grade measures the coin’s look and condition. For a 1954 quarter, an appraiser would use a magnifying glass or a microscope to fully know the level of preservation, luster, attractiveness, and strike of your coin.
Based on the appraiser’s findings, he will then give a grade from 1 to 70 based on the Sheldon Scale. A perfect score is MS 70 for coins made for circulation and PR 70 for proof coins. If your coin receives a grade of 70, it means that it has a flawless surface and if there’s any scratch on it, you can only see it under a microscope.
Professional numismatists joined together in the 1970s and established CoinGrading standards. These numismatists now assign grades at key places on the seventy-point scale, using the most regularly utilized numeric points in conjunction with the original adjective grade. The following are the most common coin grades:
-
-
- (P-1) Poor – Indistinguishable and probably damaged; if used, must have a date and mintmark; otherwise, rather battered.
- (FR-2) Fair – Nearly smooth, but without the damage that a coin graded Poor often possesses. The coin must have enough detail to be identified.
- (G-4) Fair – Inscriptions have merged into the rims in some areas, and important elements have been mostly erased.
- (VG-8) Very Good- A little weathered, but all of the primary design elements are visible, albeit faintly. There is little if any, central detail left.
- (F-12) Good – The item is very worn, yet the wear is even, and the overall design details stand out clearly. Rims are almost completely isolated from the field.
- (VF-20) Very Fine – Moderately weathered, with some finer features still visible. The motto or all letters of LIBERTY are readable. Both sides of the coin have entire rims that are separated from the field.
- (EF-40) Extremely Fine – Gently used; all gadgets are visible, and the most important ones are bold. The finer details are bold and clear, however, light wear may be seen.
- (AU-50) Uncirculated – Slight evidence of wear on the coin’s design’s high points; may have contact marks; eye appeal should be adequate.
- (AU-58) Uncirculated Choice – Slight traces of wear, no severe contact marks, almost full mint shine, and great eye appeal.
- (MS-60) Mint State Basal – Strictly uncirculated; no indication of wear on the coin’s highest points, but an unsightly coin with reduced luster, visible contact marks, hairlines, and other flaws.
- (MS-63) Mint State Acceptable – Uncirculated, but with contact scratches and nicks, little reduced shine, but otherwise appealing appearance. The strike is weak to average.
- (MS-65) Mint State Choice – Uncirculated with great mint shine, very little contact blemishes, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is unusually severe.
- (MS-68) Mint State Premium Quality – Uncirculated with superb luster, no obvious contact marks to the naked eye, and exceptional eye appeal. The strike is quick and appealing.
- (MS-69) Almost Perfect Mint State – Uncirculated with perfect brilliance, a sharp and appealing strike, and extremely good eye appeal. A near-perfect coin with minor imperfections in the planchet, strike, and contact markings (seen only under 8x magnification).
- (MS-70) Mint State Perfect – Under 8x magnification, there are no tiny imperfections discernible; the strike is crisp, and the coin is perfectly centered on a beautiful planchet. Rarely seen on a coin, this coin is bright and whole, with original luster and exceptional eye appeal.
-
Where To Buy Or Sell 1954 Washington Quarter?
There are different places where you can buy and sell 1954 Washington quarters. However, these places can be categorized online and offline or both.
Online, you can go to Amazon, eBay, Etsy, Coin Appraiser, USA Coin Book, and Grey Sheets, to name a few. These websites can also allow you to sell your coin.
Offline, you can visit coin shops, antique stores, pawn shops, and auction houses. If available, you can visit their website, too, to see what they offer.
FAQs
What is the melt value of a 1954 quarter?
The melt value for a 1954 quarter at the time of this writing is $3.9859. Since the 1954 quarter is made of silver, it has a higher melt value than coins made with base metals.
Is a 1954 quarter rare?
No, the 1954 quarter isn’t rare. You should be able to easily find one in the market. However, 1954 quarters with higher grades from MS 68 to MS 70 can be considered rare since there are only a few of them today.
How much is a 1954 quarter with no mint mark worth?
The 1954 quarter with no mint mark comes from the Philadelphia Mint. In circulated conditions, the price can be around $4 to $8. However, the price can be higher if the 1954-P quarter is in good and rare condition. To give you an example, a 1954 P Washington quarter was sold for $17,250 on January 8, 2003.
Where is the mint mark on a 1954 quarter?
You can find the mint mark on a 1954 quarter on the reverse side of the coin. Look for it under the central part of the olive branch.
