History often remembers the loudest voices, but many significant thinkers have quietly shaped modern thought. These forgotten literary figures have influenced philosophy, literature, and society in ways that still resonate today. By exploring their ideas, we can uncover the hidden roots of contemporary beliefs. This article sheds light on those who, though less known, have left an indelible mark on the intellectual landscape. Their contributions deserve recognition.
Vico

Giambattista Vico was an Italian philosopher who challenged the prevailing ideas of his time. He believed that history follows a cyclical pattern, a theory he called the “corsi e ricorsi.” His work emphasized the importance of culture and language in shaping human societies. Vico’s ideas laid the groundwork for later developments in the philosophy of history and anthropology. Though not widely recognized during his lifetime, his theories have influenced thinkers like Karl Marx and James Joyce.
Madame de Staël
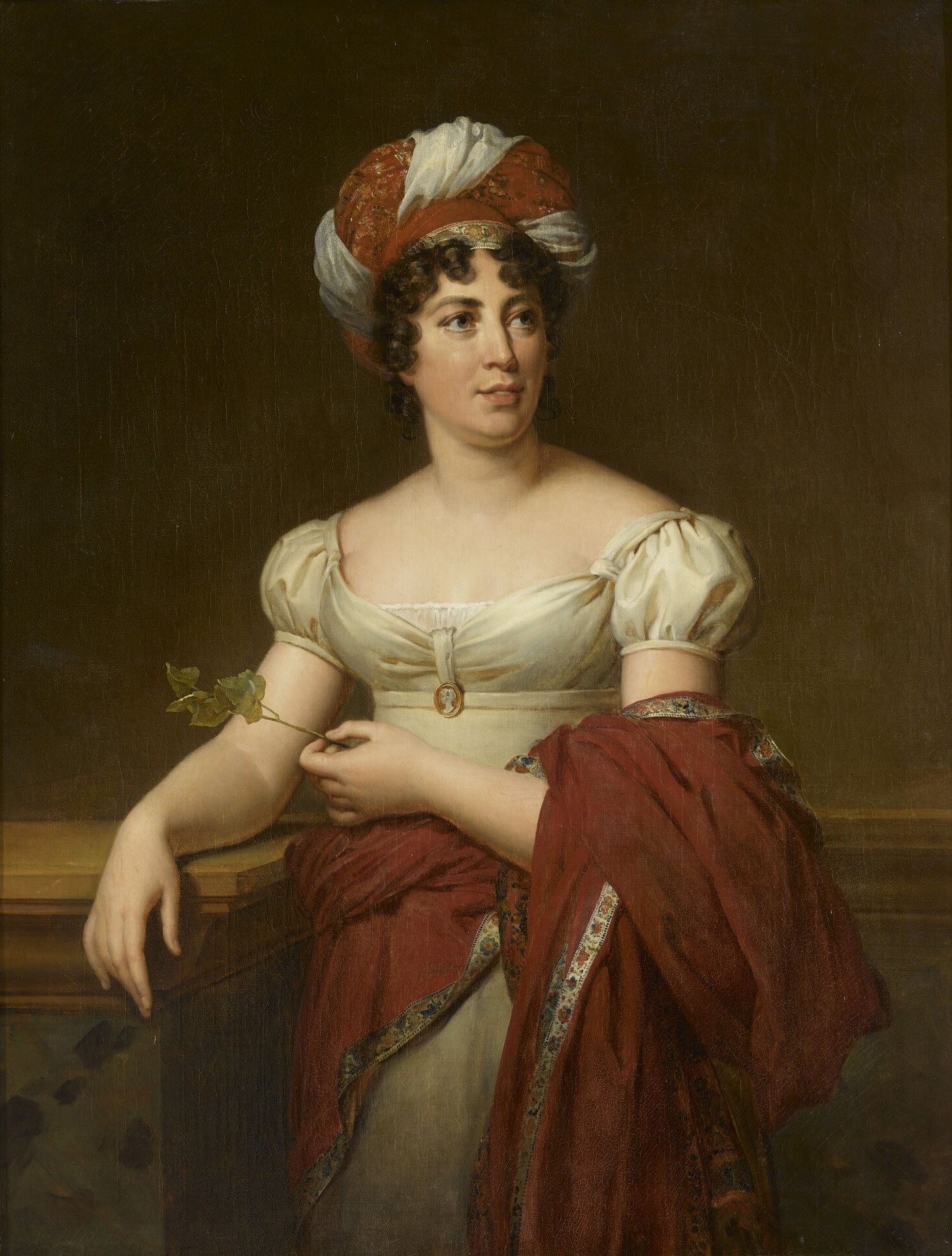

Madame de Staël was a French-Swiss writer who played a crucial role in the development of European Romanticism. Her salons were gathering places for intellectuals, where she advocated for individualism and emotional expression. Her works, such as Delphine and Corinne, explored themes of personal freedom and the struggles of women in society. Despite facing political exile, she continued to influence European thought through her writings and connections. Today, she is remembered as a pioneer of Romantic literature.
Johann Gottfried Herder
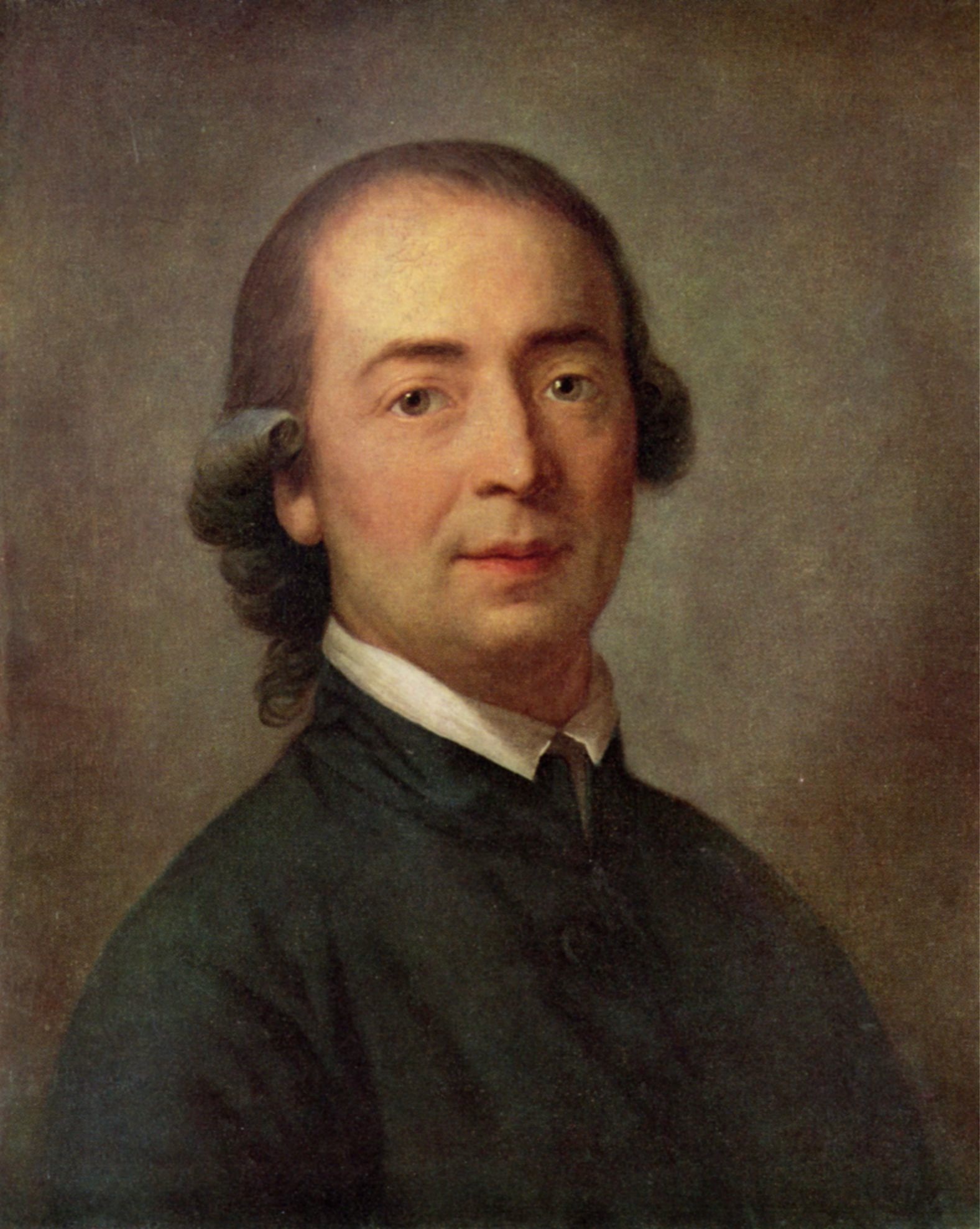

Johann Gottfried Herder was a German philosopher who championed the idea of cultural nationalism. He believed that each nation had its own unique “Volksgeist,” or spirit of the people, which was expressed through language, folklore, and traditions. Herder’s ideas were foundational for the development of modern cultural anthropology and influenced the rise of nationalism in Europe. His work laid the groundwork for understanding the diversity of human cultures. Despite being overshadowed by his contemporaries, Herder’s impact on modern thought is profound.
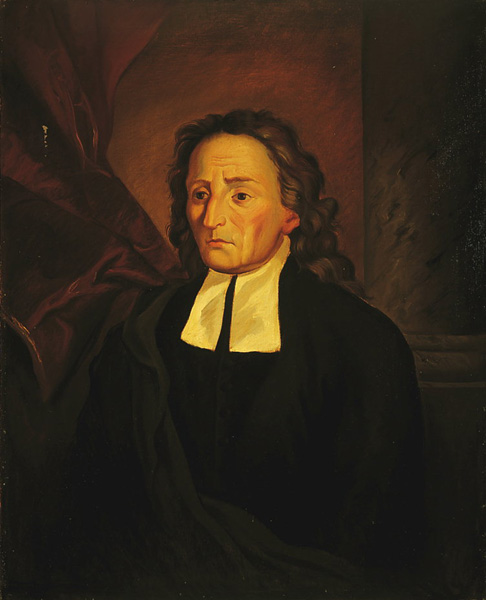
Alcuin of York
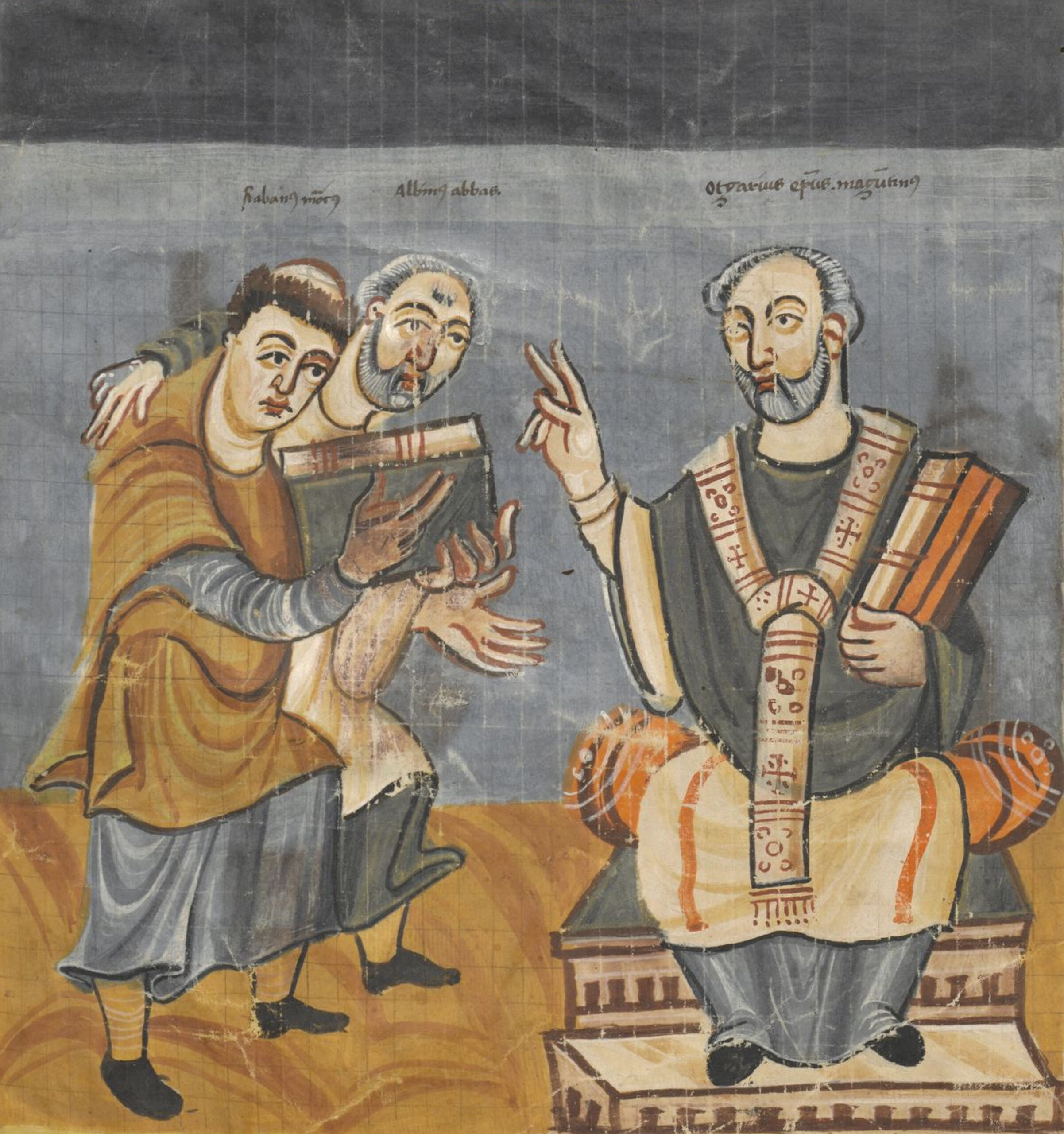

Alcuin of York was an English scholar and clergyman who played a pivotal role in the Carolingian Renaissance. He revitalized education in medieval Europe by establishing schools and promoting the study of classical texts. Alcuin’s efforts helped preserve many ancient works that might have otherwise been lost. His influence extended to theology, philosophy, and the arts, making him one of the key intellectual figures of his time. Although not widely known today, Alcuin’s contributions were critical to the preservation and transmission of knowledge in the West.
Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz
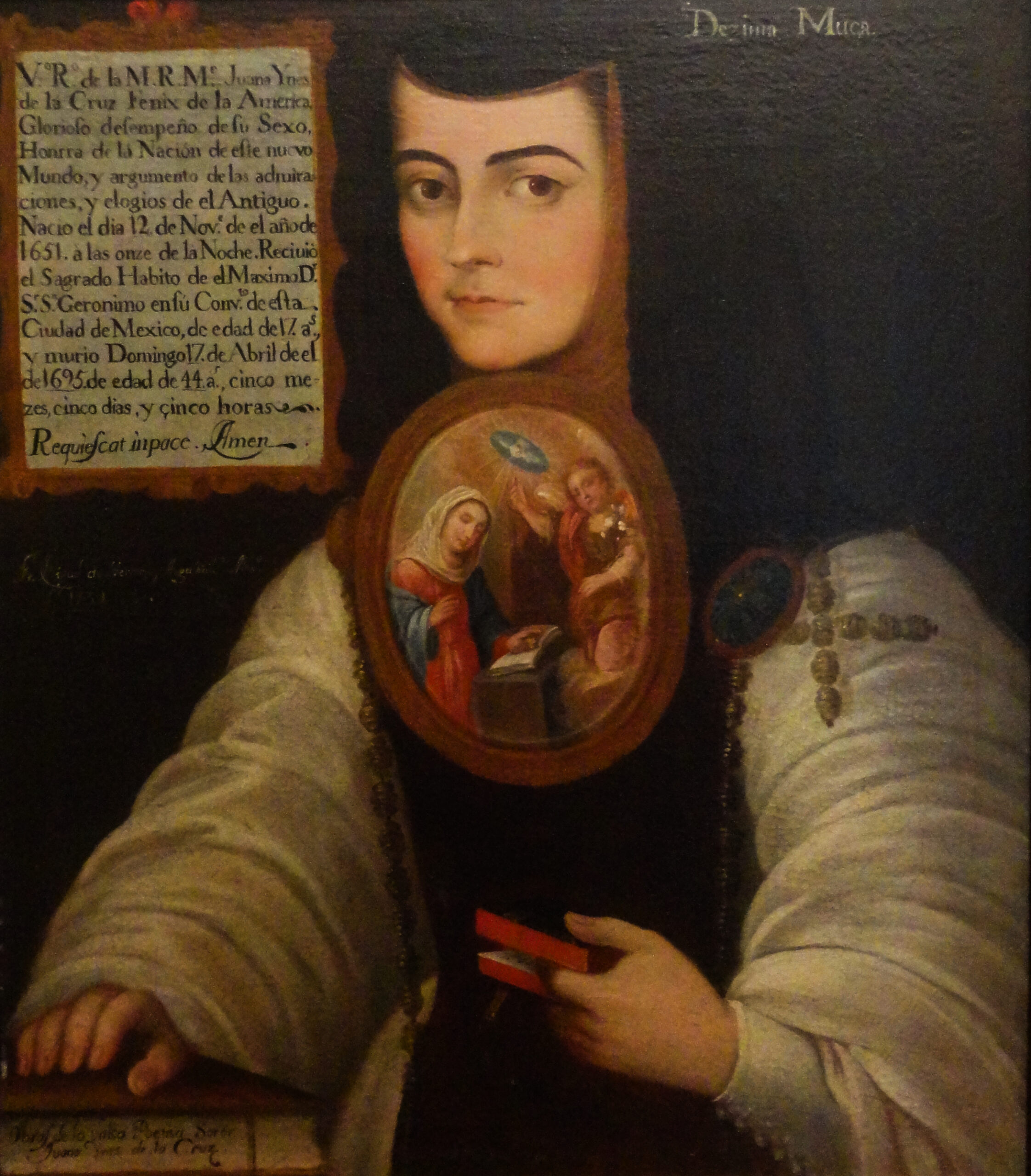

Sor Juana Inés de la Cruz was a Mexican nun, scholar, and writer who defied the conventions of her time. She wrote extensively on topics ranging from theology to poetry, challenging the societal norms that restricted women’s intellectual pursuits. Her most famous work, Respuesta a Sor Filotea, defends women’s right to education and intellectual freedom. Sor Juana’s writings continue to inspire feminists and scholars today. Her legacy as a trailblazer for women’s rights in the Americas is undeniable.
Paul Valéry
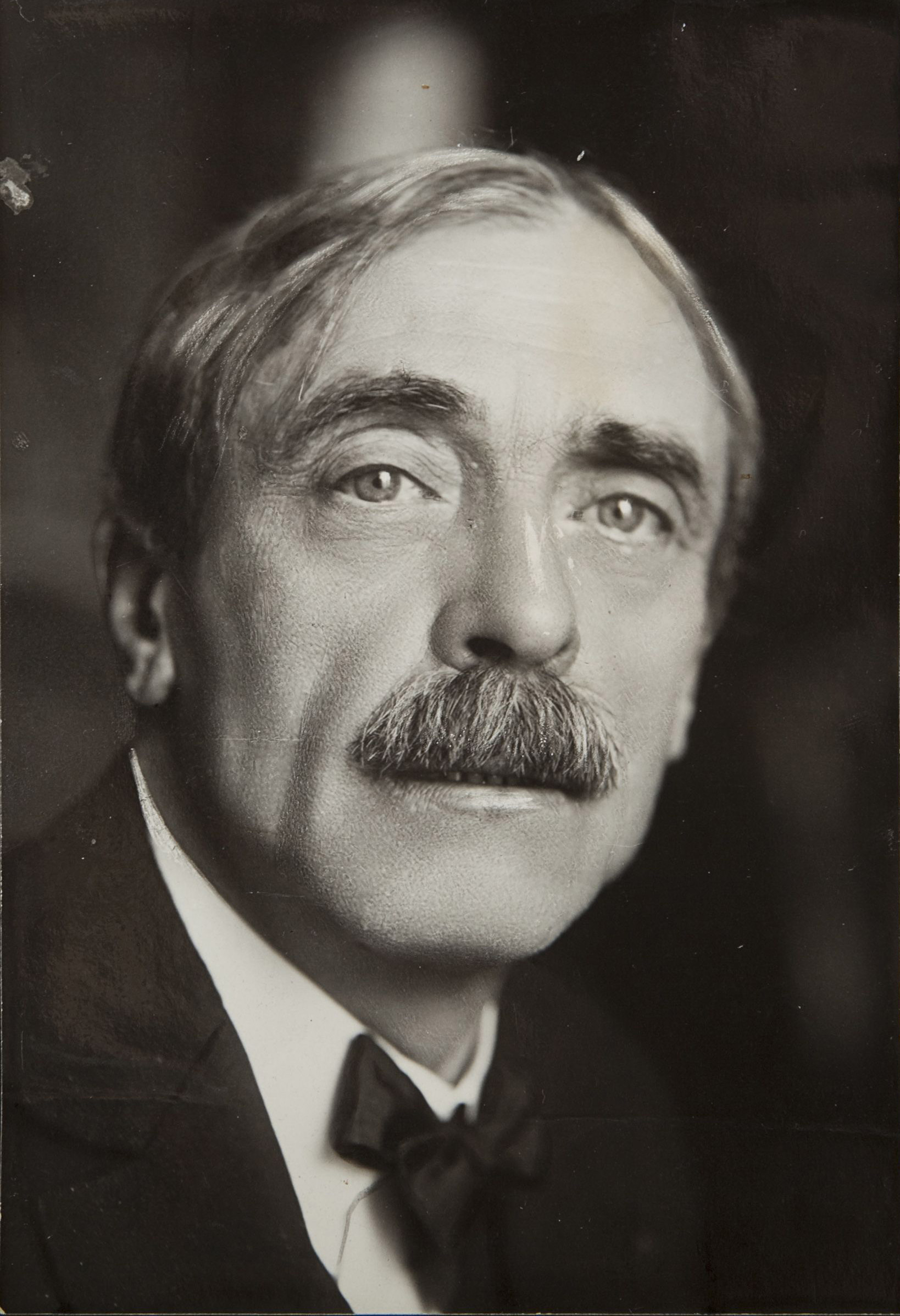

Paul Valéry was a French poet, essayist, and philosopher who bridged the gap between Symbolism and modernist literature. His works explored themes of consciousness, art, and the limitations of human knowledge. Valéry’s most famous poem, La Jeune Parque, reflects his intricate use of language and deep philosophical insights. He also wrote essays on diverse subjects, including architecture, dance, and aesthetics. Although not as widely known as some of his contemporaries, Valéry’s influence on 20th-century literature and philosophy is significant.
Julien Benda
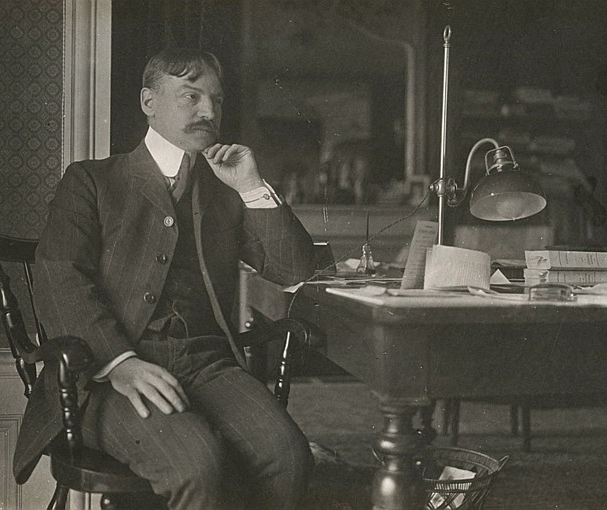

Julien Benda was a French philosopher and writer known for his critique of the intellectual climate of his time. In his influential work, La Trahison des Clercs (The Treason of the Intellectuals), Benda argued that intellectuals had abandoned their duty to truth in favor of political and nationalist causes. He advocated for a return to universal values and reason. Benda’s ideas were controversial, yet they sparked important debates about the role of intellectuals in society. His work remains relevant in discussions on ethics and intellectual integrity.
Emil Cioran
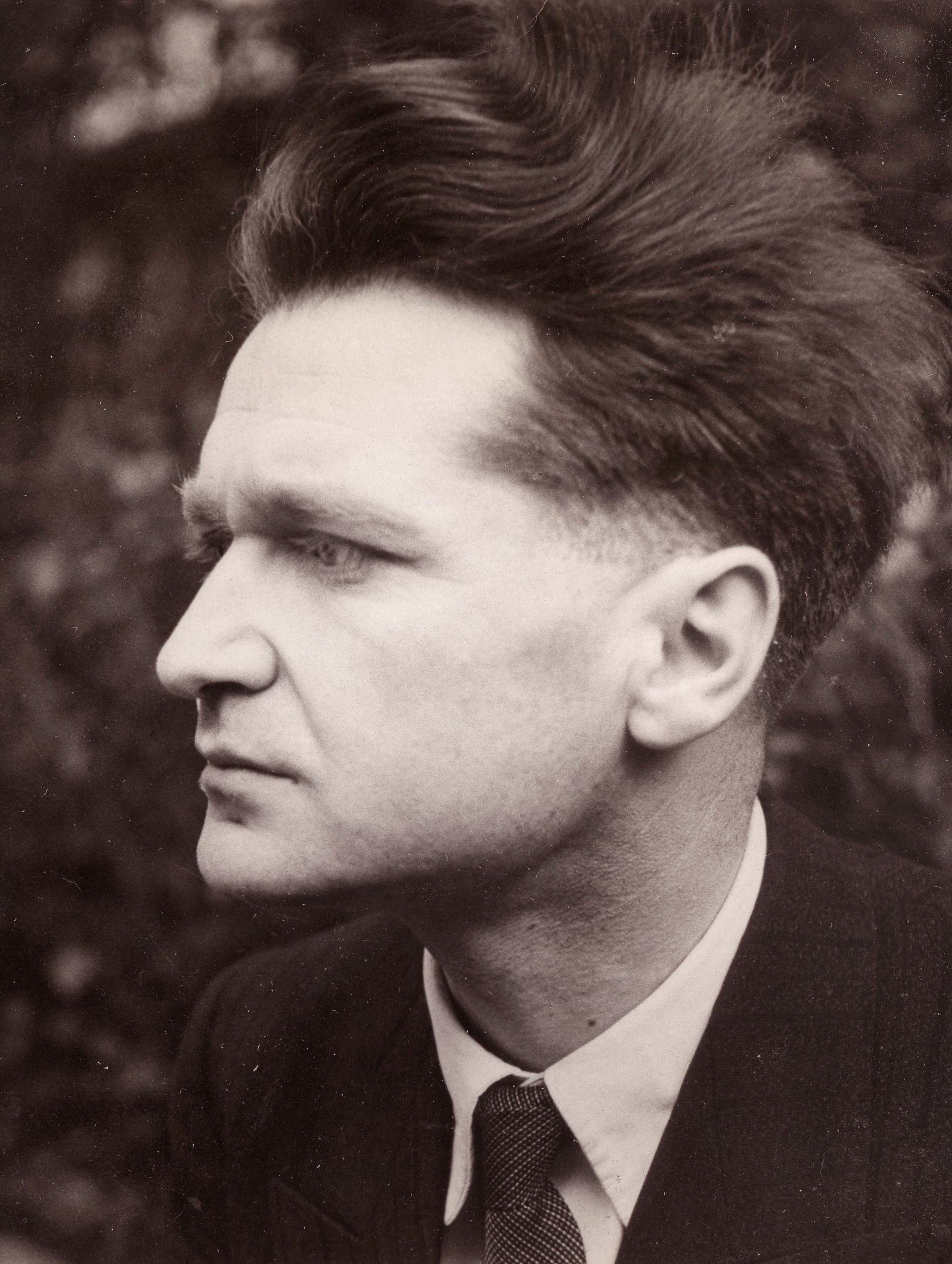

Emil Cioran was a Romanian philosopher known for his dark, existential reflections. He wrote extensively on the futility of existence, exploring themes of despair, death, and the absurdity of life. Cioran’s aphoristic style and bleak worldview resonated with readers disillusioned by the atrocities of the 20th century. His works, such as The Trouble with Being Born and A Short History of Decay, challenged traditional notions of progress and meaning. Though often overlooked, Cioran’s influence on existentialist and postmodern thought remains significant.
Ibn Khaldun
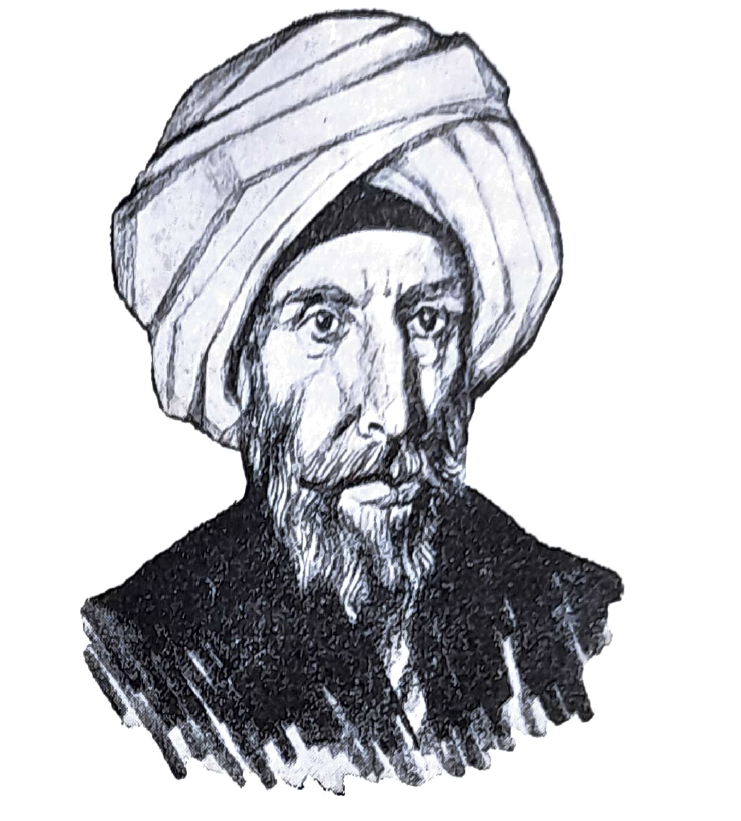

Ibn Khaldun was a 14th-century North African historian and philosopher who pioneered the field of sociology. He is best known for his work Muqaddimah, in which he introduced the concept of “asabiyyah,” or social cohesion, as a driving force in the rise and fall of civilizations. Khaldun’s analysis of history emphasized economic, social, and environmental factors, making him a precursor to modern social science. His ideas about the cyclical nature of history and the dynamics of power continue to be relevant. Khaldun’s contributions are foundational, though often underappreciated.
Giordano Bruno
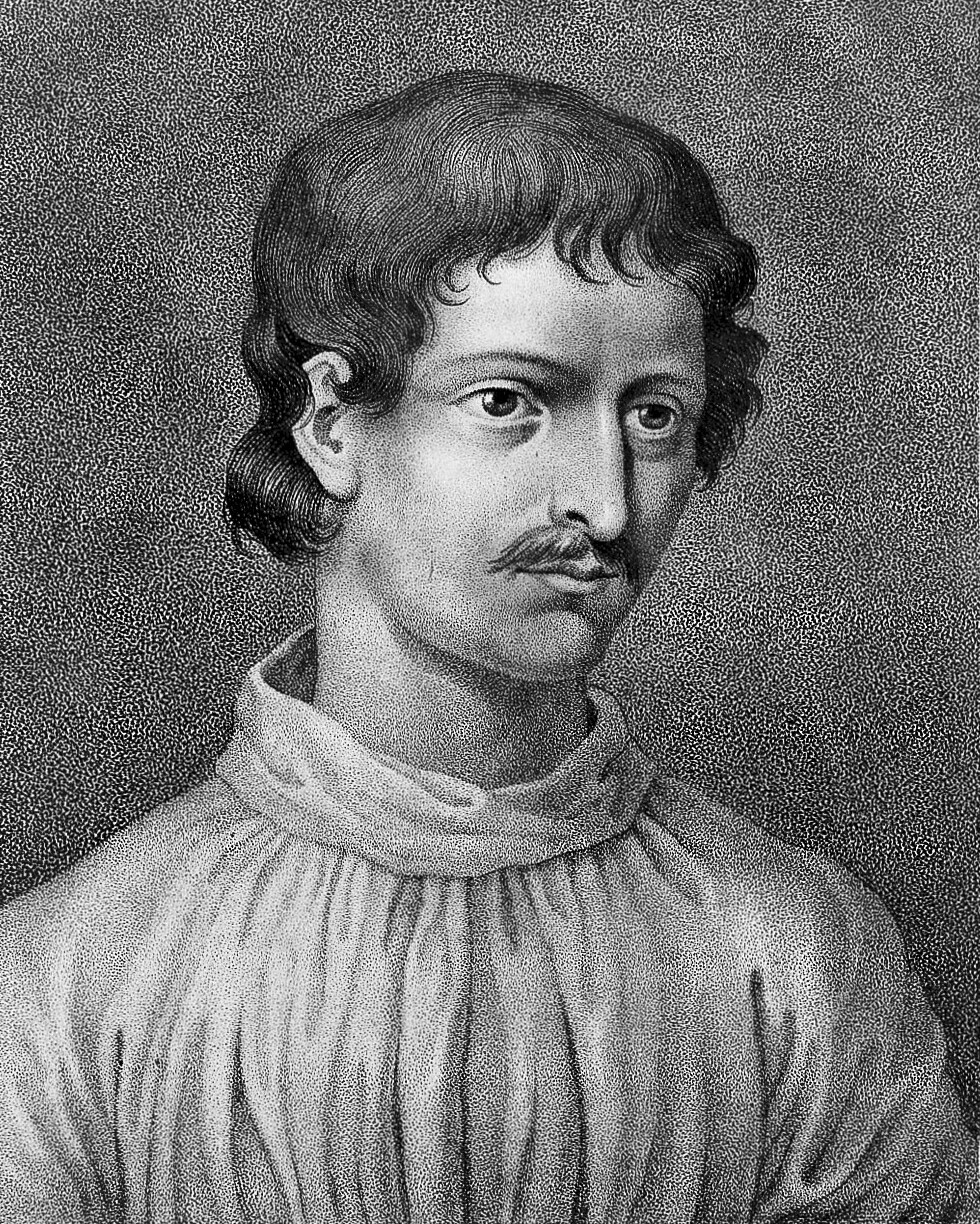

Giordano Bruno was an Italian philosopher and cosmologist who challenged the dominant worldview of his time. He advocated for the concept of an infinite universe, filled with countless worlds, a radical idea that went against the geocentric model. Bruno’s beliefs in the plurality of worlds and the infinite nature of the cosmos influenced later scientific thought. His defiance of religious orthodoxy led to his execution, yet his ideas endured, shaping the course of modern cosmology. Bruno’s legacy as a martyr for free thought remains powerful.
Leopardi
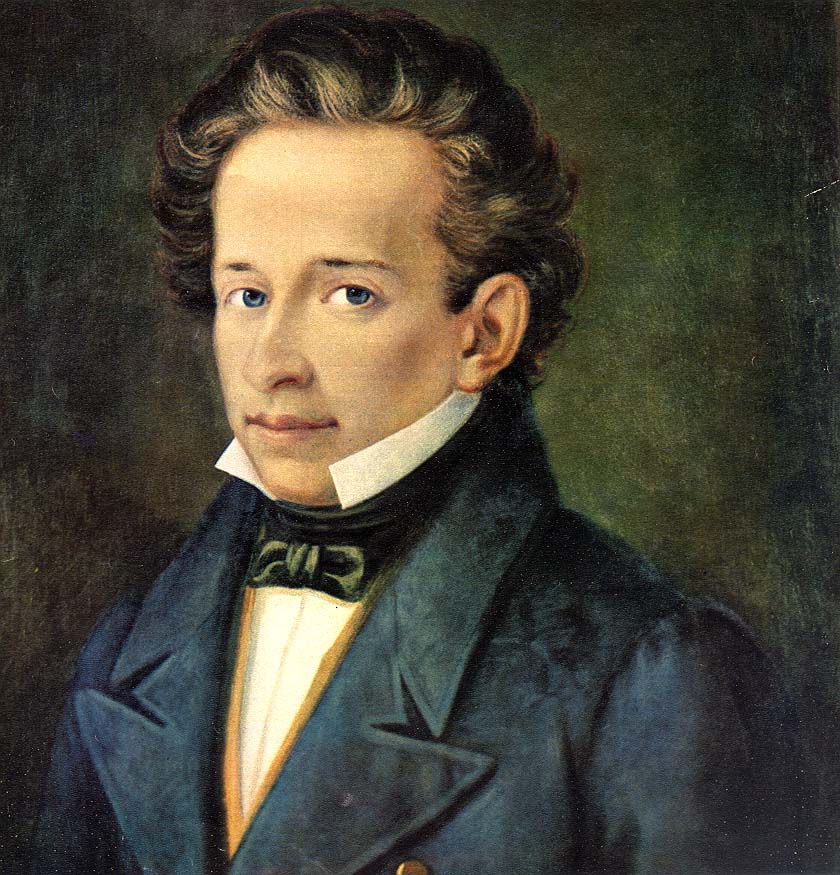
Giacomo Leopardi was an Italian poet and philosopher whose works delve deeply into human suffering and the pursuit of happiness. His pessimistic outlook, captured in works like Canti and Zibaldone, reflects his belief that life is inherently painful and that illusions of happiness are ultimately destructive. Leopardi’s exploration of existential themes prefigured later existentialist and nihilist movements. His influence on modern literature and philosophy, particularly in Italy, is profound, though he remains less known outside his homeland.
José Ortega y Gasset
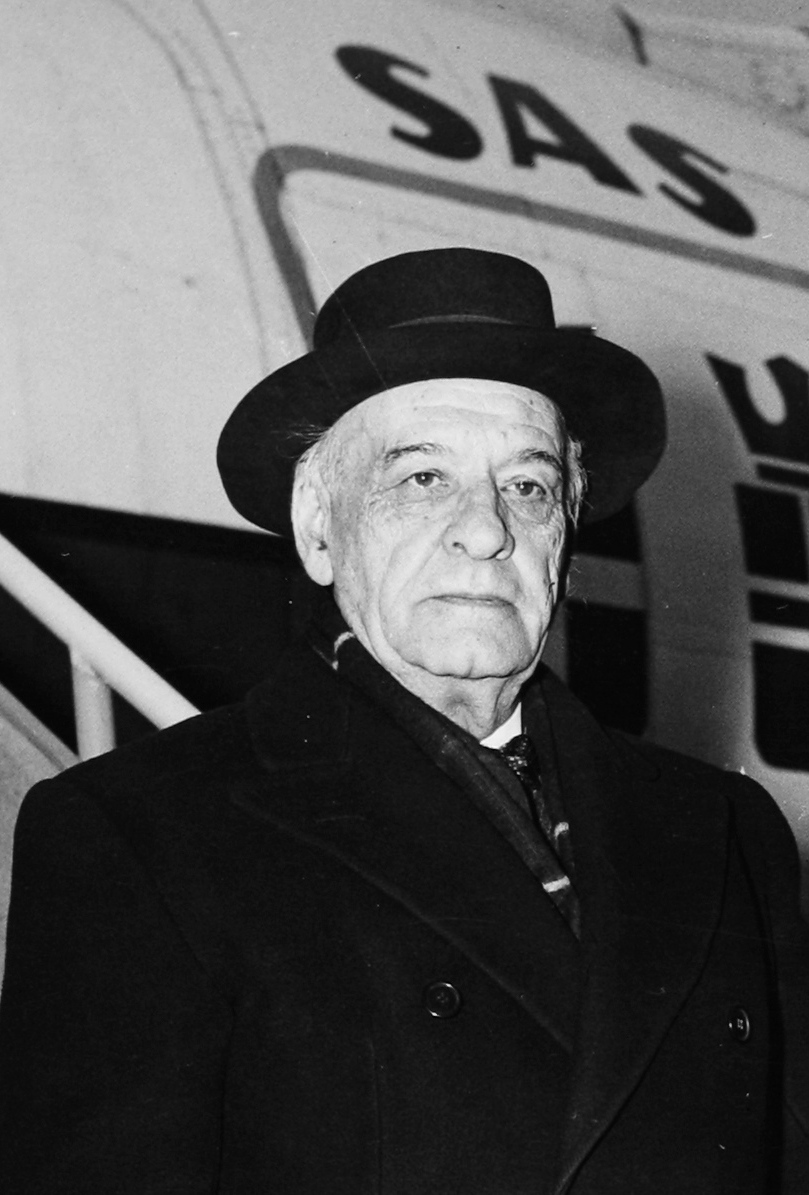

José Ortega y Gasset was a Spanish philosopher who analyzed the cultural and social crises of modern Europe. In his work The Revolt of the Masses, Ortega warned against the rise of mass culture and the decline of individualism. He believed that the masses, if left unchecked, could undermine civilization by rejecting traditional values and intellectual rigor. Ortega’s ideas about the role of elites and the dangers of mass society influenced 20th-century political thought. His work remains a crucial reference for understanding modern cultural dynamics.
Georg Christoph Lichtenberg
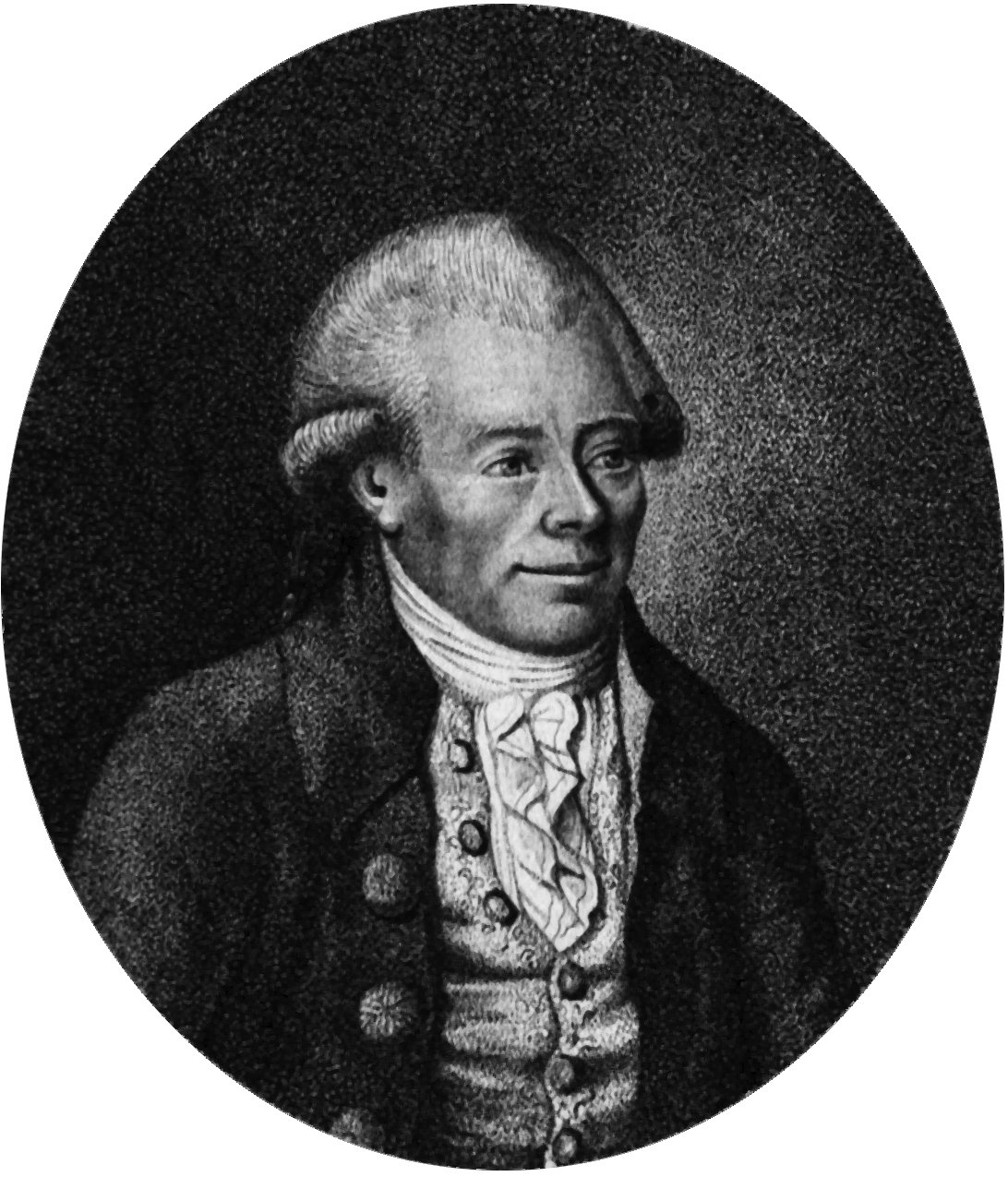

Georg Christoph Lichtenberg was an 18th-century German scientist, satirist, and philosopher known for his sharp wit and keen observations. His Waste Books are filled with aphorisms and reflections on human nature, society, and science. Lichtenberg’s insights often revealed the absurdities of life and the contradictions inherent in human behavior. His work influenced later writers and thinkers, including Nietzsche and Freud. Despite his relative obscurity, Lichtenberg’s contributions to literature and philosophy are deeply valued by those familiar with his work.
Harriet Taylor Mill
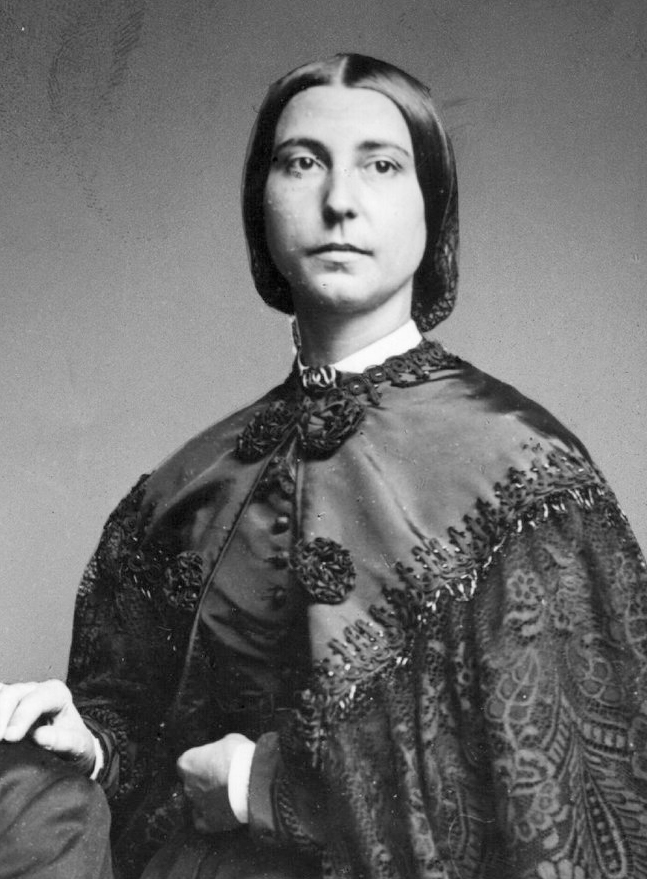

Harriet Taylor Mill was an English philosopher and women’s rights advocate who played a significant role in shaping John Stuart Mill’s ideas. Her influence on his works, particularly The Subjection of Women, was profound, advocating for gender equality and social reform. Taylor Mill’s own writings, though less extensive, articulated a strong vision of women’s rights and social justice. Her collaboration with Mill represents one of the earliest significant contributions to feminist thought. Taylor Mill’s legacy is vital, though often overshadowed by her husband’s fame.
Ernest Renan
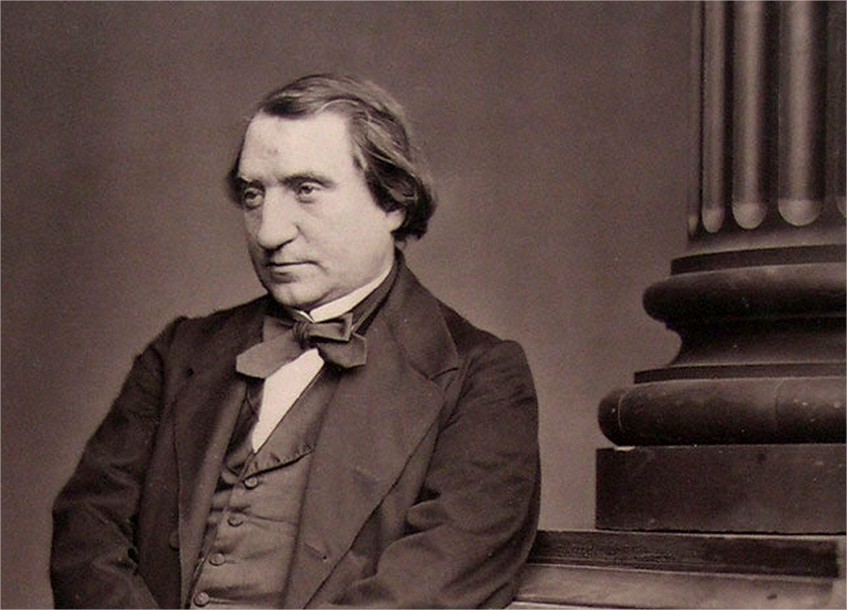

Ernest Renan was a French philosopher, historian, and writer known for his critical approach to religion and history. His most famous work, Life of Jesus, presented a historical, rather than theological, view of Jesus, challenging traditional Christian beliefs. Renan’s ideas contributed to the development of modern secularism and historical criticism. His writings sparked controversy and debate, influencing the intellectual landscape of 19th-century Europe. Though controversial, Renan’s work laid the groundwork for modern historical and religious studies.
T. E. Hulme
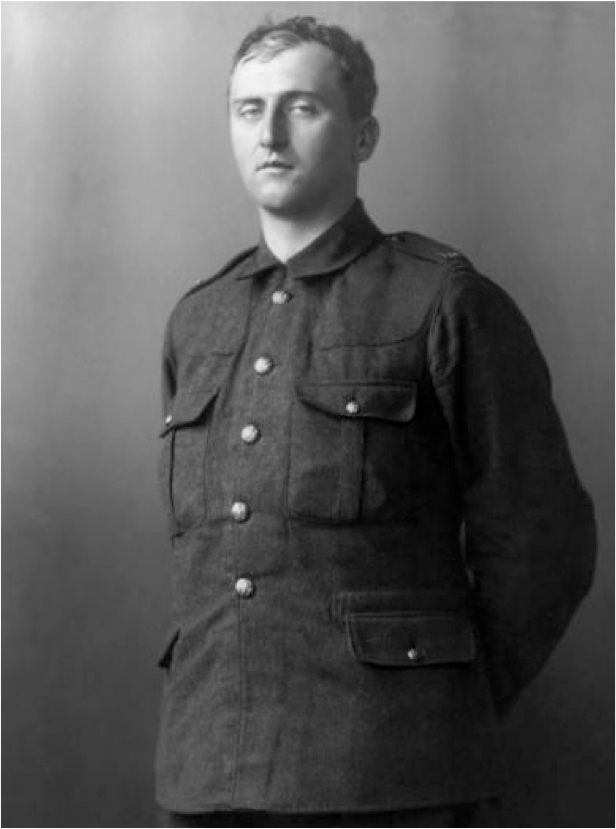

T. E. Hulme was an English critic and poet who played a crucial role in the development of modernist literature. He advocated for a return to classical values of order and discipline in art, opposing the romanticism of his time. Hulme’s ideas influenced poets like T. S. Eliot and Ezra Pound, contributing to the imagist movement. His writings on aesthetics and philosophy, though limited in volume, had a significant impact on 20th-century literature. Hulme’s legacy as a pioneer of modernism is essential, though his name is often overlooked.
Denis Diderot
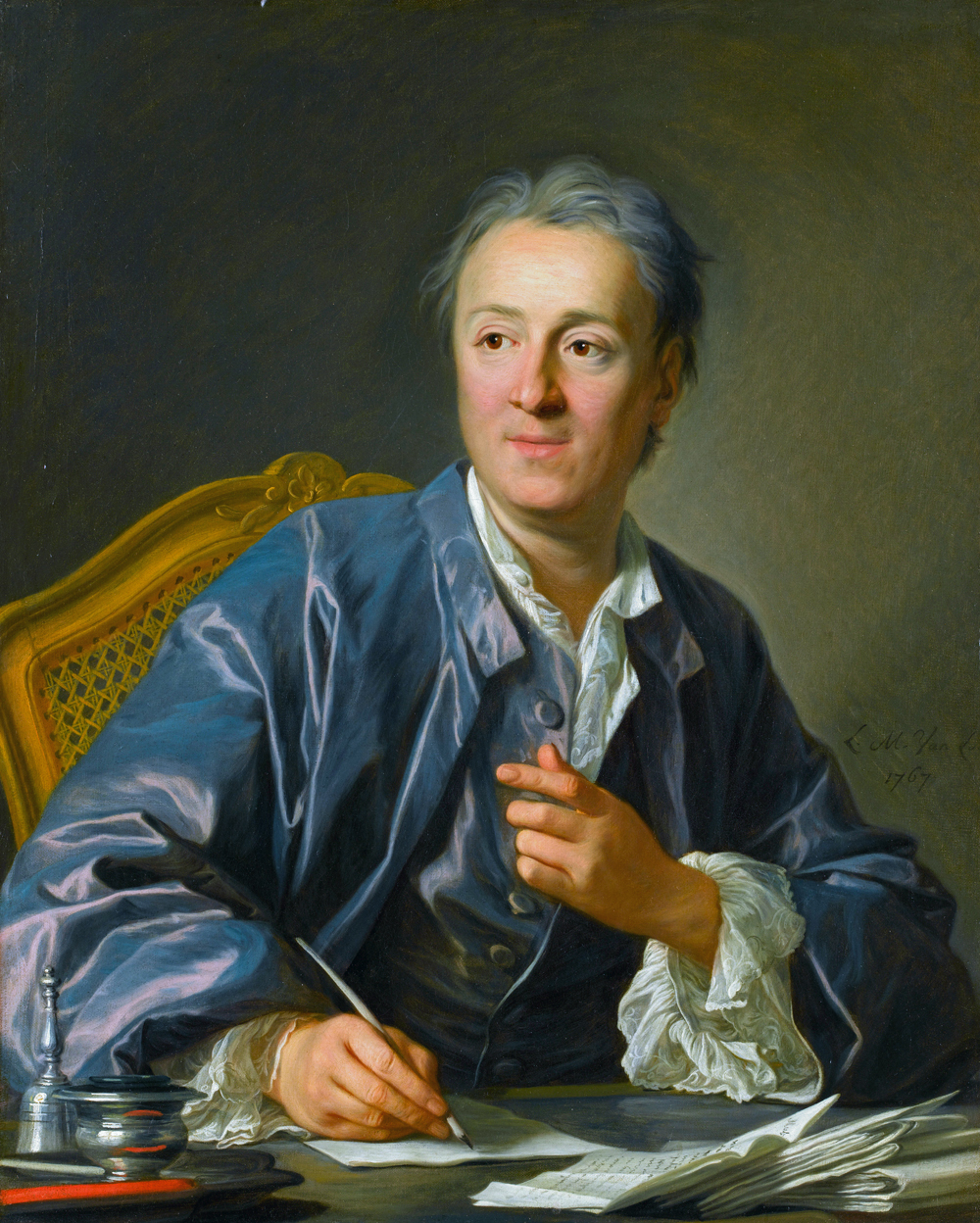

Denis Diderot was a French philosopher, writer, and art critic who played a central role in the Enlightenment. He was the chief editor of Encyclopédie, a monumental work that sought to compile and disseminate knowledge across various fields. Diderot’s writings covered a wide range of topics, including philosophy, science, and art, challenging established norms and promoting rational thought. His ideas influenced the French Revolution and the development of modern democratic principles. Despite his importance, Diderot is often overshadowed by other Enlightenment figures.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More from Rarest.org
14 Mythical Lost Treasures Yet to Be Discovered

The allure of mythical lost treasures has captivated adventurers for centuries. Their stories have endured through generations, inspiring countless quests. Read More.
17 Famous Battlefields with Haunting Stories

Throughout history, battlefields have been places of intense conflict and great sacrifice. Many of these sites have become synonymous with haunting stories that linger long after the battles have ended. Read More.
10 Rare Manuscripts That Every Literary Collector Dreams Of

Rare handwritten manuscripts represent the ultimate treasures in the world of literary collections. Each one carries an irreplaceable connection to history, offering a glimpse into the thoughts and artistry of legendary minds. Read More.
