Duck is an umbrella term for numerous species of waterfowl, smaller and shorter than geese and swans, which people sometimes mistake them as. These adorable animals have over 100 species worldwide.
Humans often keep them as pets or domesticated animals, but there are still more ducks in the wild.
Many are considered endangered due to duck hunting, which some perceive as ad sport, habitat loss, predators, and climate changes. They inhabit wetlands, lingering around rivers, ponds, and lakes, loving to dive and hunt for grains, aquatic plants, invertebrates, and grass.
But with many species comes a population problem as ducks do not have it ease.
And while you might not add to their decreasing populations, you can still explore the list of the rarest ducks worldwide that require additional protection.
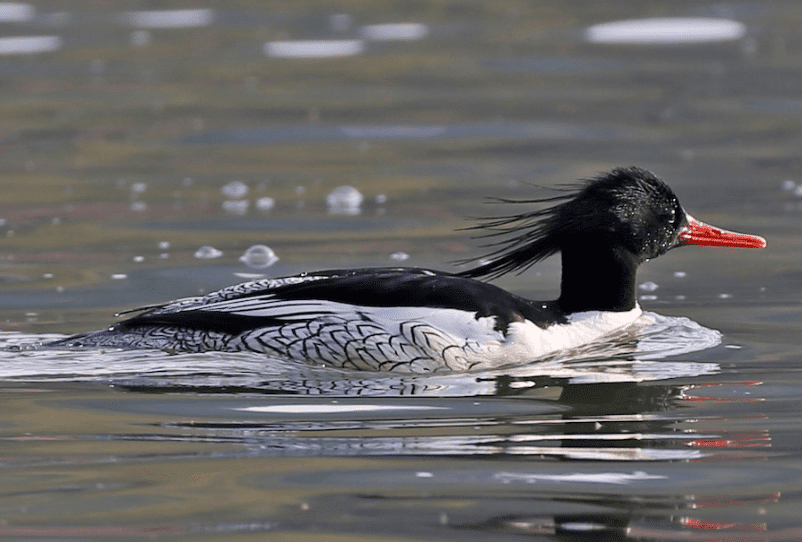
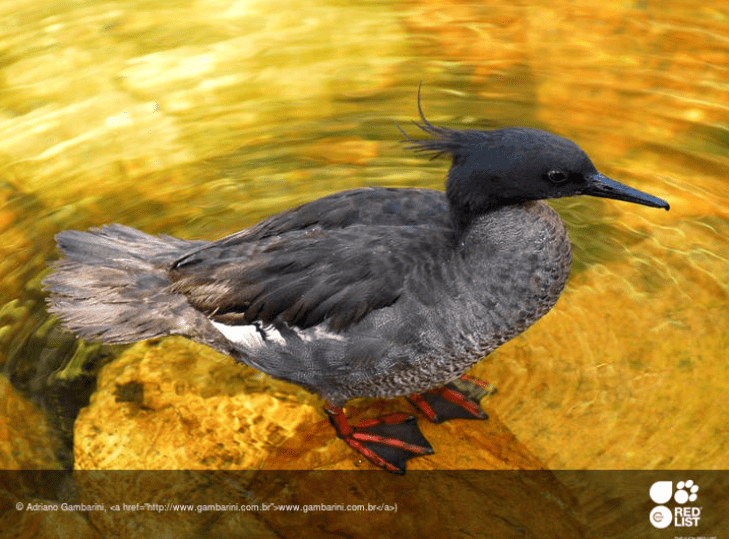
10. Scaly-sided Merganser
Current Conservation Status: Endangered
Location: China, Korea, Russia
Scientific Name: Mergus squamatus

photo source: eBird
Also known as the Chinese Merganser, the Scaly-sided duck is native to China, also living in extreme Southeast Siberia. Males and females have distinctive feathers, as males have dark feathers on their bodies, while females are dressed in dark gray, both carrying white details.
They got their name from underside feathers, which look like fish scales. The species is listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List.
Unlike most ducks, Merganser migrates to the north to breed and spends winter in the south. It breeds in clear flowing rivers and makes nests in tree holes.
Did you know?
Chinese Merganser is challenging to breed as they require clean water and quality protein-rich food to eat, not starting anything before they have this. But when the male duck court females, they mirror each other’s head movements, squawking harshly to attract. Females hatch from 4 to 12 eggs.
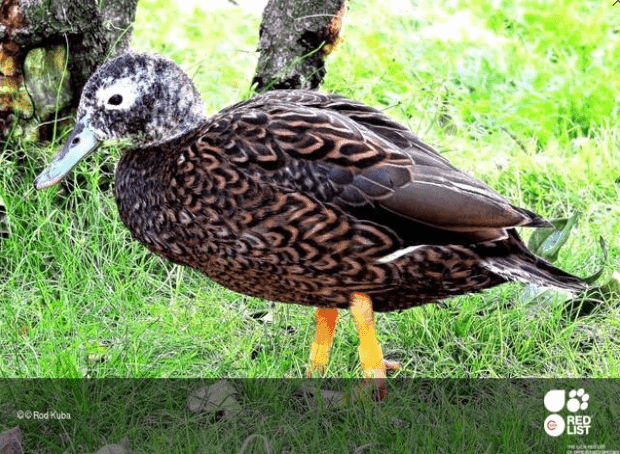
9. Meller’s Duck
Current Conservation Status: Endangered
Location: Madagascar
Scientific Name: Anas melleri

photo source: eBird
Meller’s Ducks are not critically endangered, but their status might change due to decreasing population. They resemble mallards or wild ducks. This sizeable brown duck is endemic to Madagascar and introduced to Mauritius too, but this population is likely extinct.
Meller’s ducks have some green feathers along their brown bodies, with black and white details on their chest and heads. They inhabit the Lac Alaotra wetlands the most, and the experts have established a conservation program to protect and breed the species. The population is still considered to be small.
Did you know?
This species got its name from the botanist Charles James Meller, who dedicated his life to plant collection, but also to working with ducks’ preservation.
8. Hawaiian Duck
Current Conservation Status: Endangered
Location: Hawaii, United States
Scientific Name: Anas wyvilliana

photo source: eBird
The first Hawaiian bird on the list is the duck with the same name, endemic to the Hawaiian Islands. This species is non-migratory, as the populations live in a limited number of locations. But they’re listed as endangered due to natural predators and hybridization.
Hawaiian duck or Koloa maoli (meaning native duck) has mottled brown feathers, with the males being more prominent than the females.
The species is wary of their environment, often found in pairs rather than in groups, hiding in tall, wetland grass and bushes.
Did you know?
Hawaiian ducks used to be present on almost all Hawaiian Islands, but their population has been declining for some time. They used to reside on the hottest coasts and mountain ponds up to 7,000 feet high. That soon changed as they can be found only on Kaua’i Island.
7. Blue Duck
Current Conservation Status: Endangered
Location: New Zealand
Scientific Name: Hymenolaimus malacorhynchos

photo source: Wikipedia
The next duck on the list is the Blue Duck, a member of the goose, swan, and duck family that is endemic to New Zealand. The blue duck is the only member of the genus Hymenolaimus listed as endangered on the IUCN Red List. The population is decreasing due to predators such as trout and short-tailed weasel.
The blue duck got its name from the interesting-looking feathers, as it downs dark slate-gray, almost blue feathers on the head, with white and chestnut details.
The male call is a high-pitched whistle, while the female has a rattling growl. Females are also smaller in size.
Did you know?
A Blue duck is depicted on the reverse (back) side of the New Zealand $10 banknote, with an image of suffragist Kate Sheppard on the front. New Zealand currency shows the beauty of many of their native birds, as the banknotes are nicknamed kiwi, a name given after the national bird.
6. Laysan Duck
Current Conservation Status: Critically Endangered
Location: Hawaii, United States
Scientific Name: Anas laysanensis

photo source: IUCN Red List
Laysan Duck, also known as Laysan teal, is endemic to the Hawaiian Laysan Island. They feed without diving, grabbing at the seeds, and other aquatic animals on the water surface. Laysan ducks have a small living range that adds to their critically endangered status on the IUCN Red List.
This species is smaller in size with teal and dark-brown details. They also have a prominent white eye-ring, only adding to their charm. Laysan ducks usually have a fat ring around their necks, but the purpose is unknown.
Did you know?
Laysan ducks are bad fliers but great runners, which is unusual for ducks. They do not have natural enemies but still prefer to hide in bushes and grass where they can hide from potential predators. Laysan ducks love to live in pairs and mate in spring.
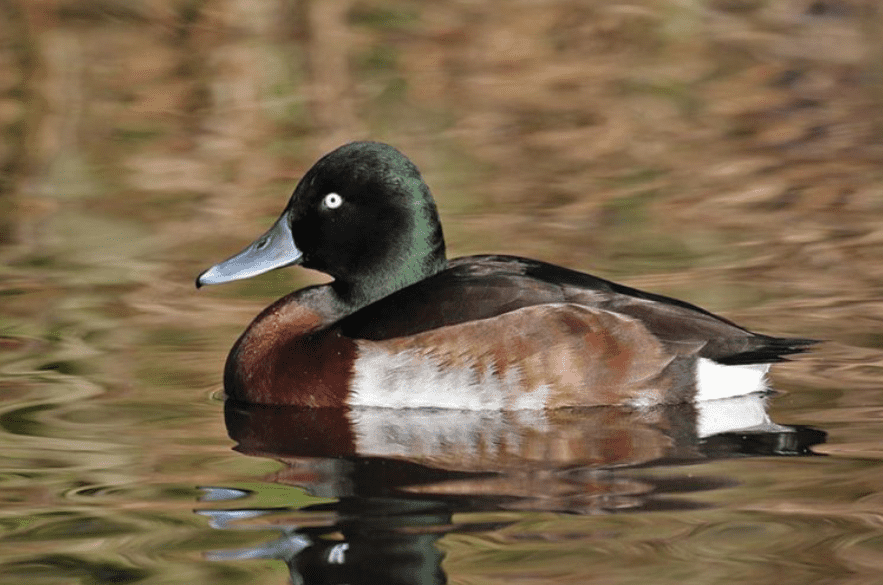
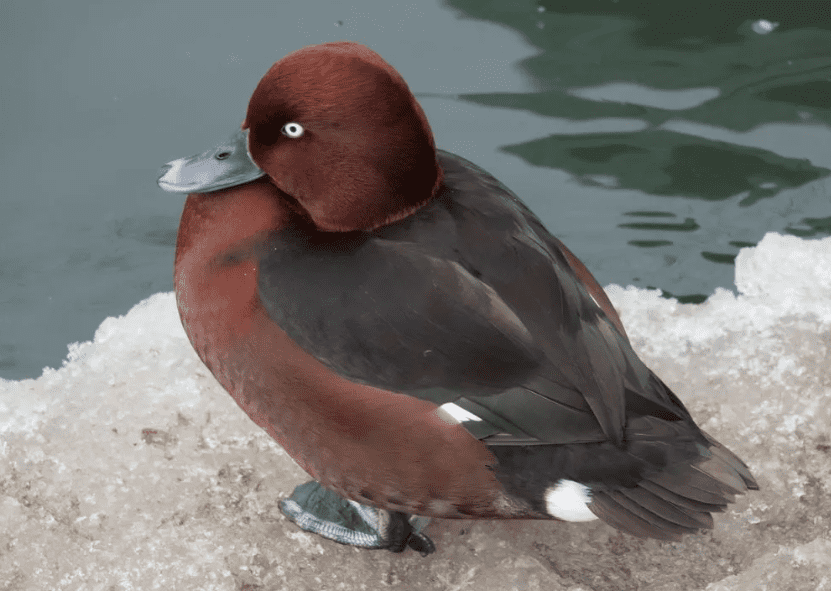
5. Baer’s Pochard
Current Conservation Status: Critically Endangered
Location: China, Mongolia, Russia
Scientific Name: Aythya baeri

photo source: EAAFP
Listed as critically endangered since 2019, Baer’s Pochard is a resident of China and Russia, but they were seen in India, Bangladesh, Japan, Korea, and Myanmar. Pochard ducks are diving ducks who love to feed on plant seeds, waterweed, and other aquatic invertebrates.
This duck species used to be more common, but its population is in decline due to hunting and habitat loss. Baer’s Pochard males have black heads with green gloss over their feathers, while females have lighter shades on their heads that blend into their chestnut-brown chests.
Did you know?
Baer’s Pochard is a first-class protected animal in China, along with all kinds of monkeys, pandas, bears, tigers, and rhinoceros. The animals are protected by the Convention of International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) and the IUCN.
4. Brazilian Merganser
Current Conservation Status: Critically Endangered
Location: Brazil, Argentina, Paraguay
Scientific Name: Mergus octosetaceus

photo source: IUCN Red List
One of the six most threatened waterfowl birds worldwide, the Brazilian Merganser had an estimated 250 mature individuals in 1992, but the population has declined. The main reason for their habitat loss is soybean cultivation, mining, and hydroelectric power schemes.
This sharp-edged beak duck has shiny dark-green feathers with dark-gray details. They are generally silent birds but can bark in certain situations. Merganser duck has been considered critically endangered since 2019, even though they have no one saw it in the past few years.
Did you know?
This species is under legal protection in all three countries, recognized as critically endangered. They are monitored regularly in national parks in Brazil, with the help of special breeding programs to help with saving their population.
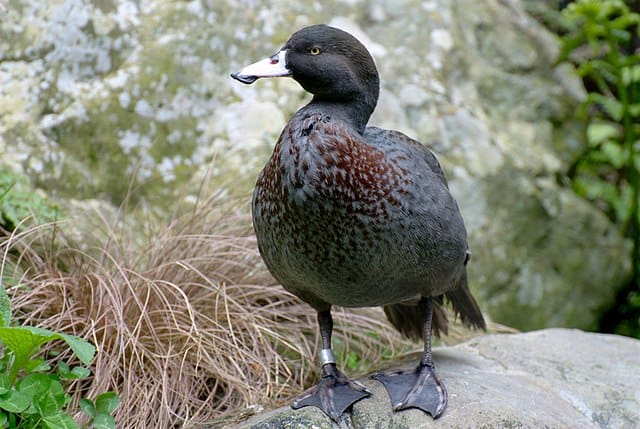
3. Madagascar Pochard
Current Conservation Status: Critically Endangered
Location: Madagascar
Scientific Name: Aythya innotata

photo source: Kidadl
Madagascar Pochard is among the rarest birds in the world, and scientists believed they were extinct until explorers rediscovered the species in Madagascar in 2006. They found 22 Pochards nesting in a small lake in the north, but only six females were left by 2009.
The Malagasy government started a captive breeding problem to help with their endangered status, successfully hatching 24 ducklings. Unfortunately, the IUCN estimate of the mature individuals left is around 30 at the time of this writing, as they have been critically endangered since 2016.
Did you know?
Madagascar Pochards are medium-sized, chestnut ducks with dark brown and white wings. These ducks do not migrate and move in pairs. They live exclusively in wetlands in Madagascar, as the only wild populations are at Lake Matsaborimena and Lake Sofia.
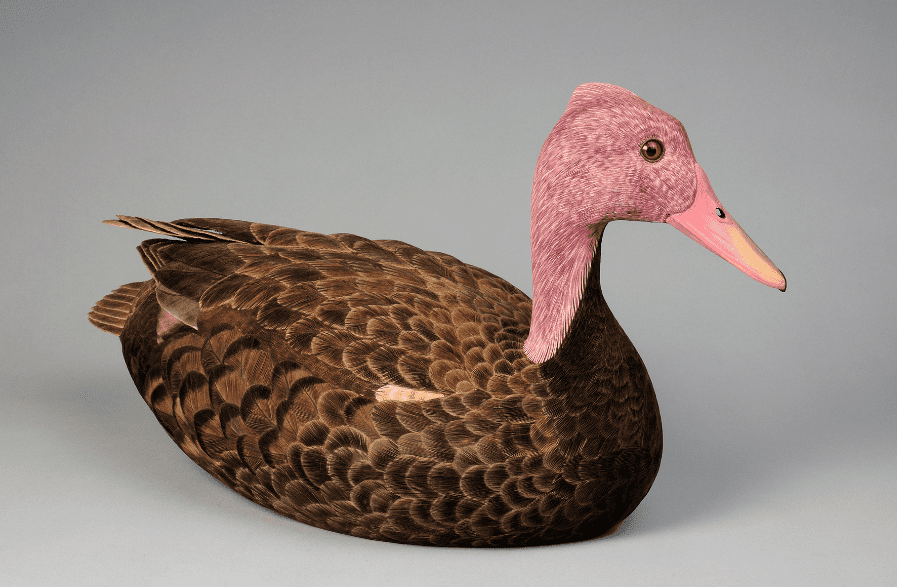
2. Pink-headed Duck
Current Conservation Status: Critically Endangered
Location: Bangladesh, India, Myanmar
Scientific Name: Rhodonessa caryophyllacea

photo source: The Sixth Extinction
Tied for the first place of the rarest ducks is the so-called Pink-headed Duck, which is considered extinct. Native to Bangladesh, Myanmar, and India, no one had seen this duck in years. The greatest threat to their population is habitat destruction, as they live in forests and wetlands.
This diving duck has a brown body, a pink head, hence the name, and unusual spherically shaped eggs. It has been critically endangered on the IUCN Red List since 2016. The remaining population of Pink-headed Ducks accounts for only 0.4 square miles, as they are not migrating birds.
Did you know?
Pink-headed duck found its place on the top 25 most wanted lost species in Global Wildlife Conservation’s “Search for Lost Species” initiative. Conservation has found eight presumably lost species – Jackson’s Climbing Salamander, Velvet Pitcher Plant, and Wallace’s Giant Bee.
1. Crested Shelduck
Current Conservation Status: Critically Endangered
Location: Korea, Russia
Scientific Name: Tadorna cristata

photo source: Wikipedia
Crested Shelduck is the rarest duck in the world, with an estimated number of up to 49 mature individuals remaining.
This species, also known as the Korean crested shelduck, is found in Russia and China. It is listed as extinct in Japan and added as critically endangered on the IUCN Red List in 2018.
A lot is unknown about the species due to their rarity. The male and female have a different appearance as the males have a greenish-black body while the upper wings and the rest of its face, throat, and beak are grayish. The females have more white details, including a white eye ring.
Did you know?
This duck is a relic species belonging to prehistoric times. Crested Shelduck is considered to be extinct by a lot of experts as the species has not been seen properly since 1964. There were various reports about the occasional sightings from 1985 to 1991 in China, but without any solid proof.