Pollinators play a crucial role in maintaining the health of ecosystems. They are responsible for pollinating many of the plants that provide us with food, fuel, and fiber. However, many pollinator species are facing steep declines, which threatens not only biodiversity but also food security. Understanding which pollinators are most at risk is the first step toward preserving them.
Honeybees
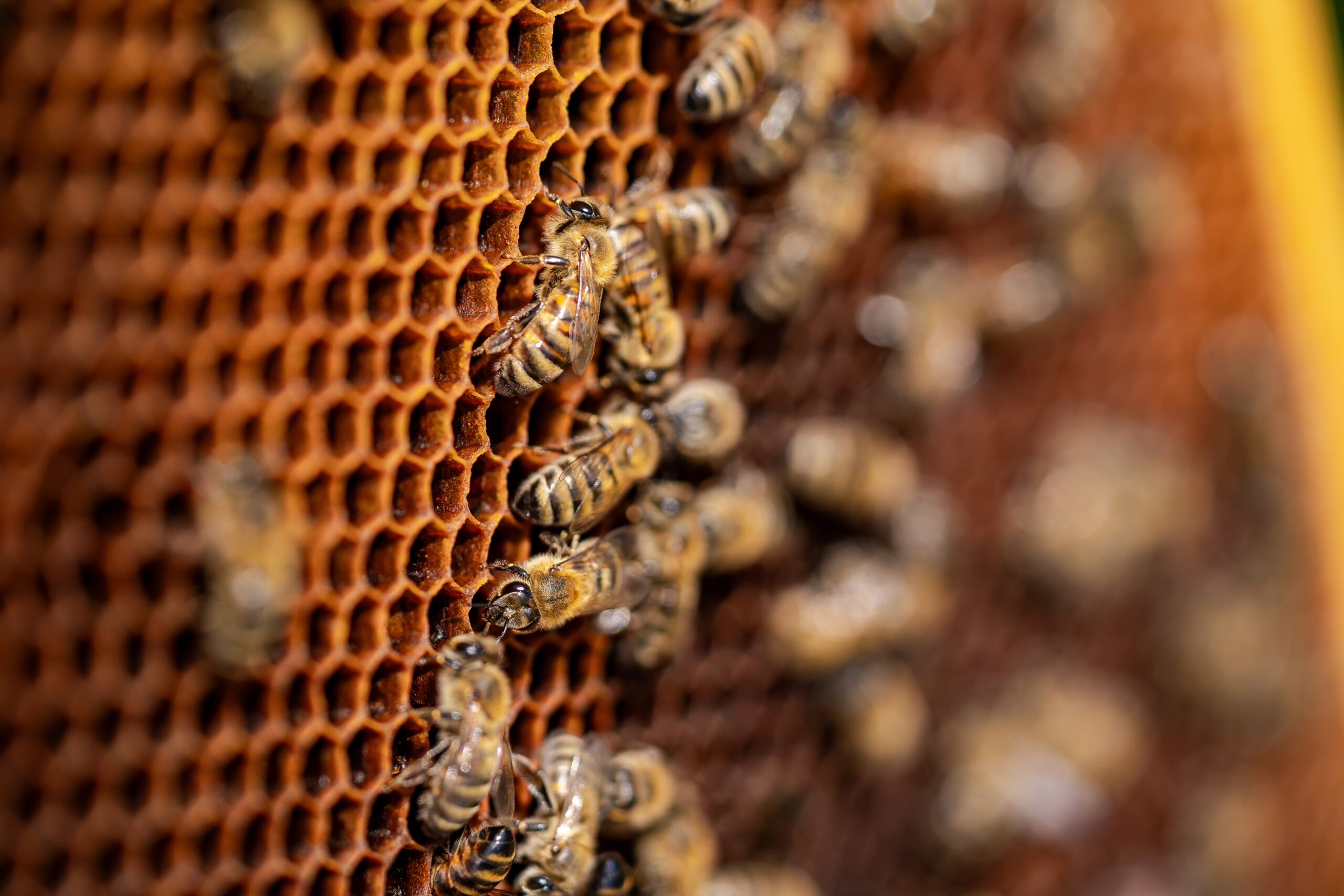

Honeybees are essential for pollinating a wide range of crops. They are social insects that live in colonies and produce honey. Many fruits and vegetables depend on honeybee pollination for growth. However, they face threats from pesticide exposure, habitat loss, and diseases like colony collapse disorder. Their decline could have a significant impact on food production worldwide.
Bumblebees
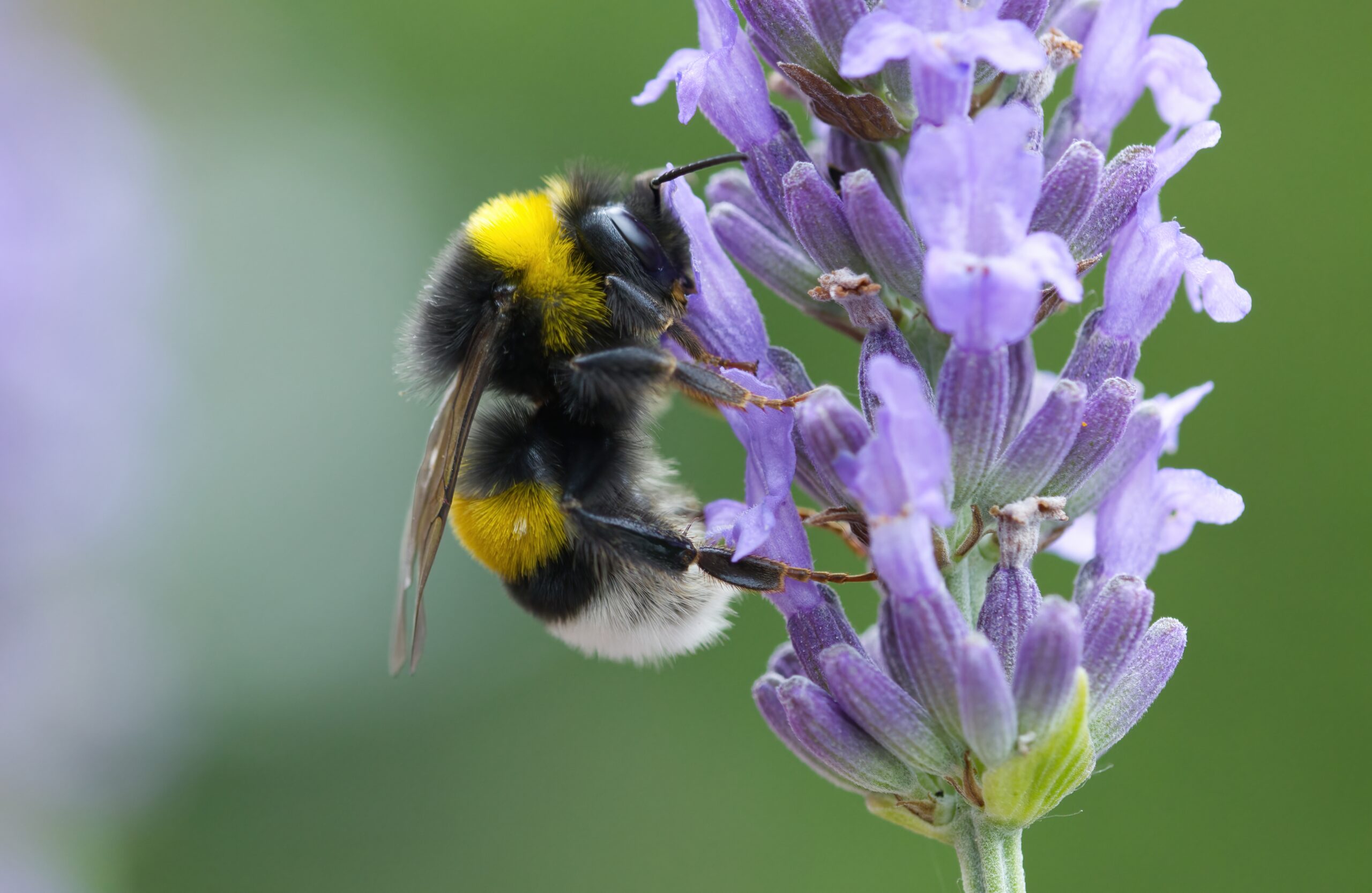

Bumblebees are larger than honeybees and are known for their ability to pollinate in cooler weather. They are key pollinators for crops like tomatoes and blueberries. Unlike honeybees, they don’t produce large amounts of honey but are vital for cross-pollination. Their populations have been shrinking due to climate change, habitat loss, and pesticide exposure. Bumblebee decline could disrupt natural plant reproduction cycles.
Monarch Butterflies
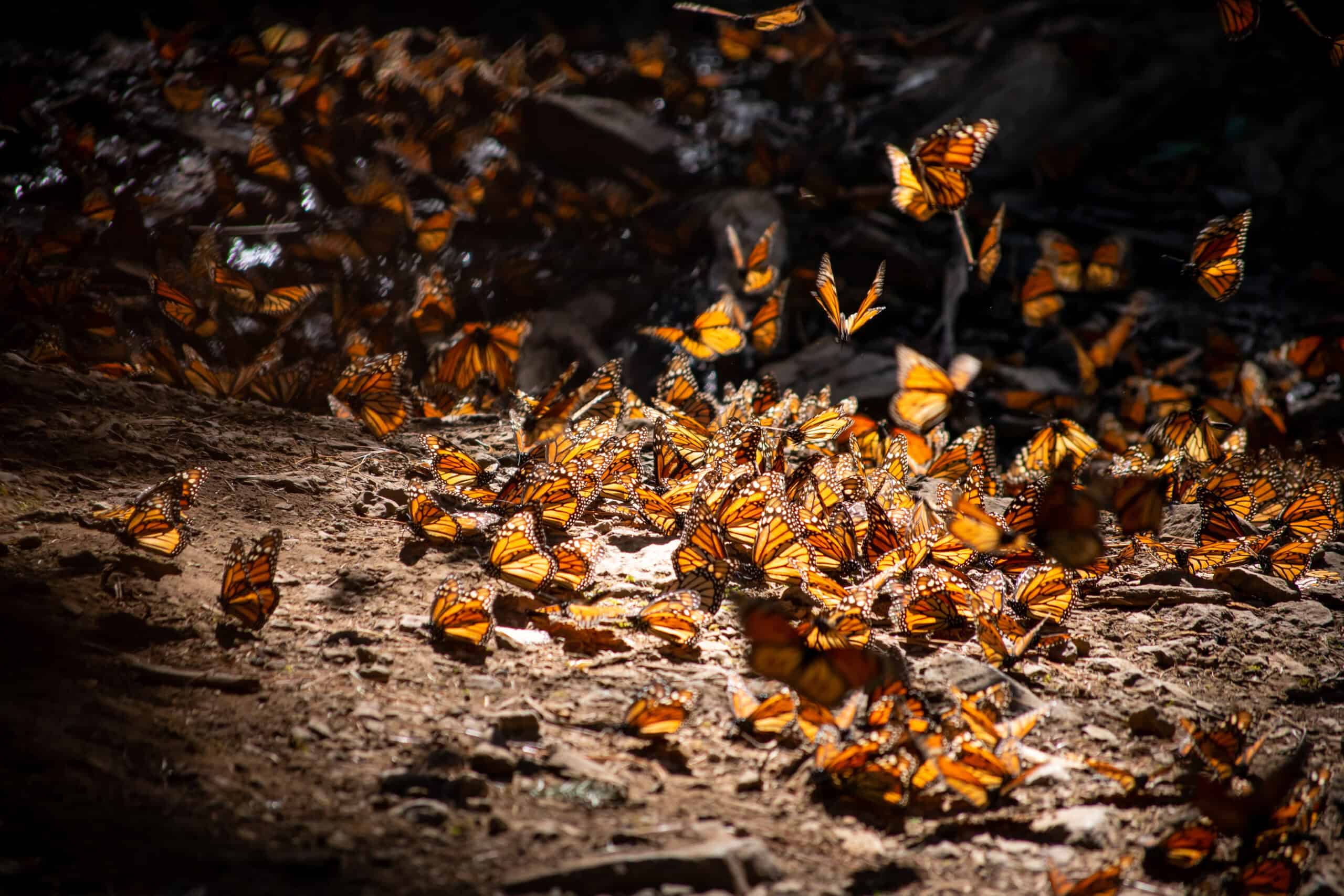

Monarch butterflies are famous for their long migration across North America. They pollinate various wildflowers as they travel, helping maintain biodiversity. Their numbers have been plummeting due to habitat destruction and loss of milkweed, their primary food source. Pesticides also threaten these delicate pollinators. Protecting their habitats could prevent further declines.
Carpenter Bees
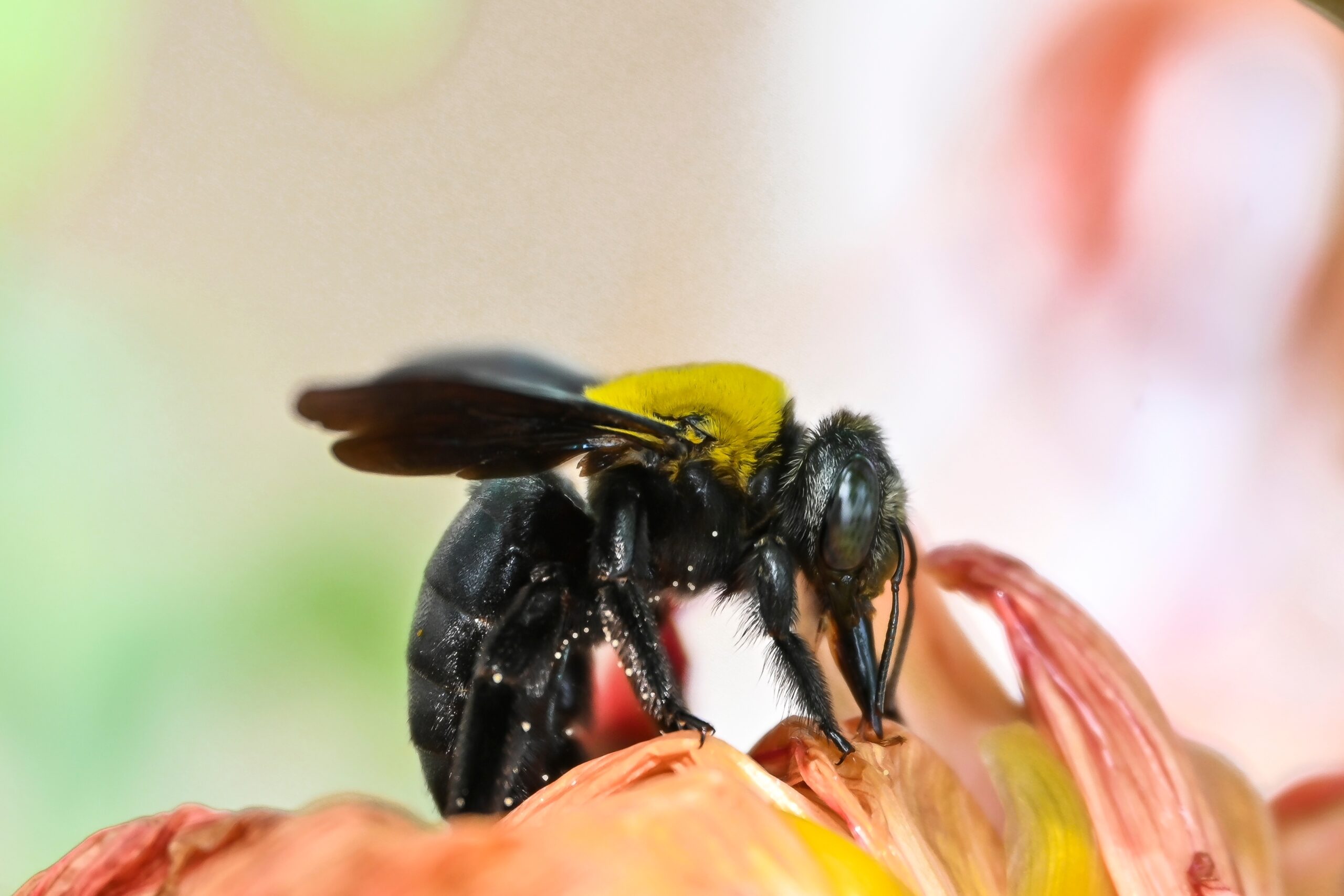

Carpenter bees resemble bumblebees but don’t live in colonies. They drill into wood to create nesting spaces, which makes them important for pollinating plants like passionfruit. These bees play a crucial role in ecosystems, but their habitats are increasingly being destroyed. Chemical exposure and deforestation also contribute to their decline. Their loss could affect plant species that rely on their specific pollination style.
Sweat Bees
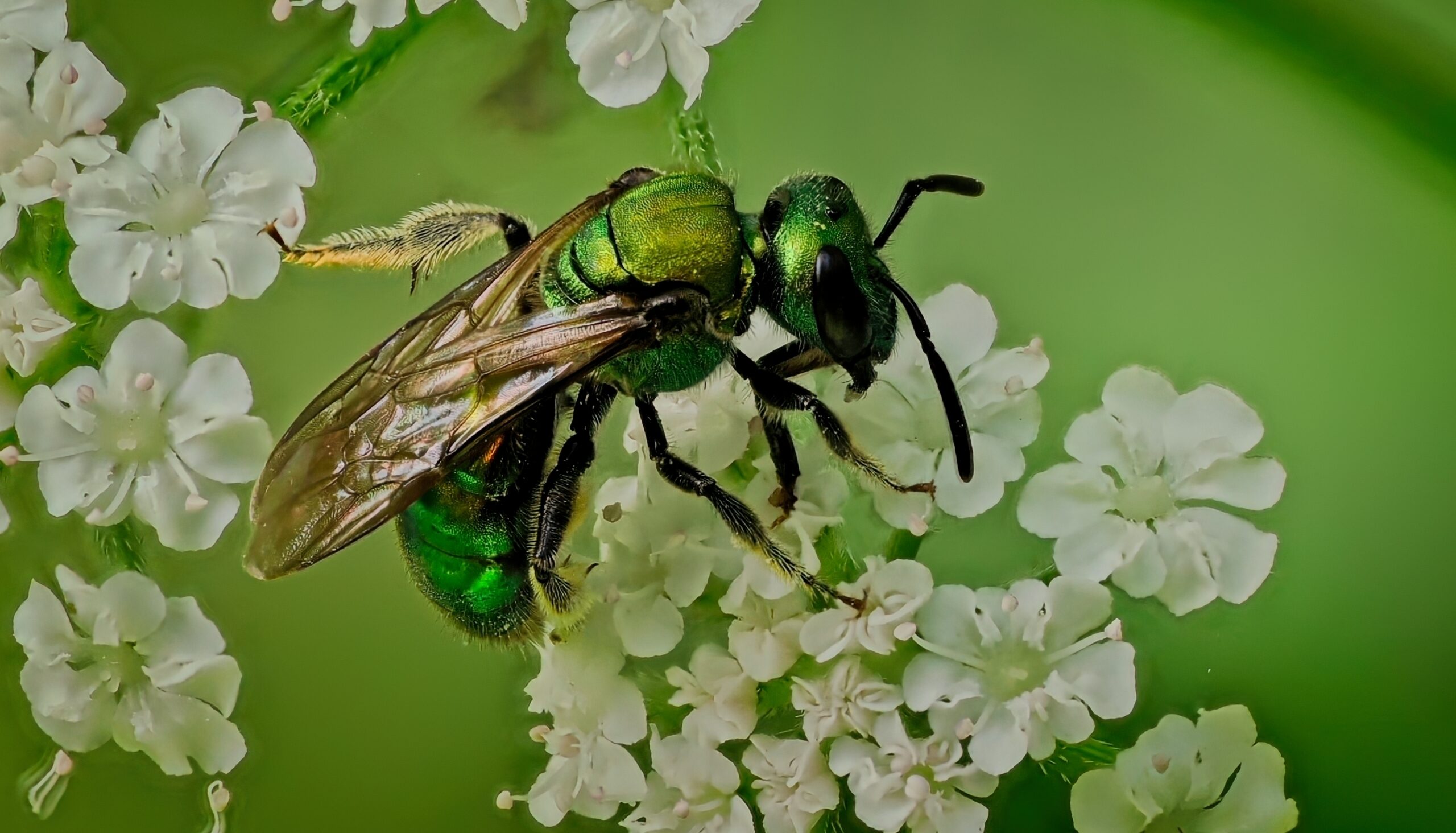

Sweat bees are small, metallic-looking bees that are essential for pollinating wildflowers and crops. They get their name from their attraction to human sweat, which provides them with essential salts. These bees are solitary and nest in the ground. However, urbanization and pesticide use have led to a significant decline in their populations. Their loss could disrupt local ecosystems and plant diversity.
Leafcutter Bees
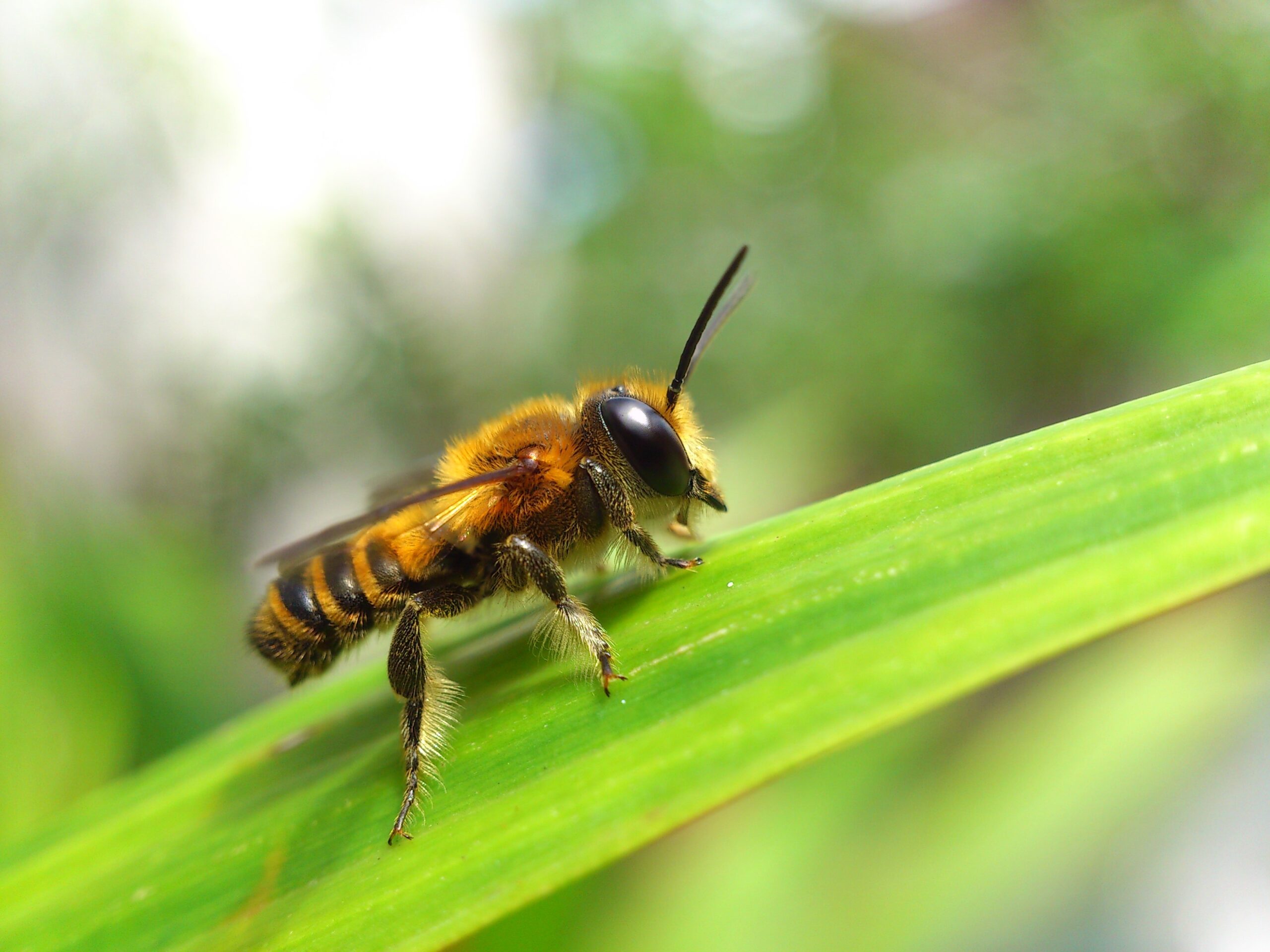

Leafcutter bees are solitary bees known for cutting circular pieces from leaves to build their nests. They are vital for pollinating plants like alfalfa and other legumes. Unlike social bees, they don’t live in colonies but work alone. Habitat destruction and pesticide use are primary factors in their population decline. Protecting their nesting sites could aid in their conservation.
Mason Bees
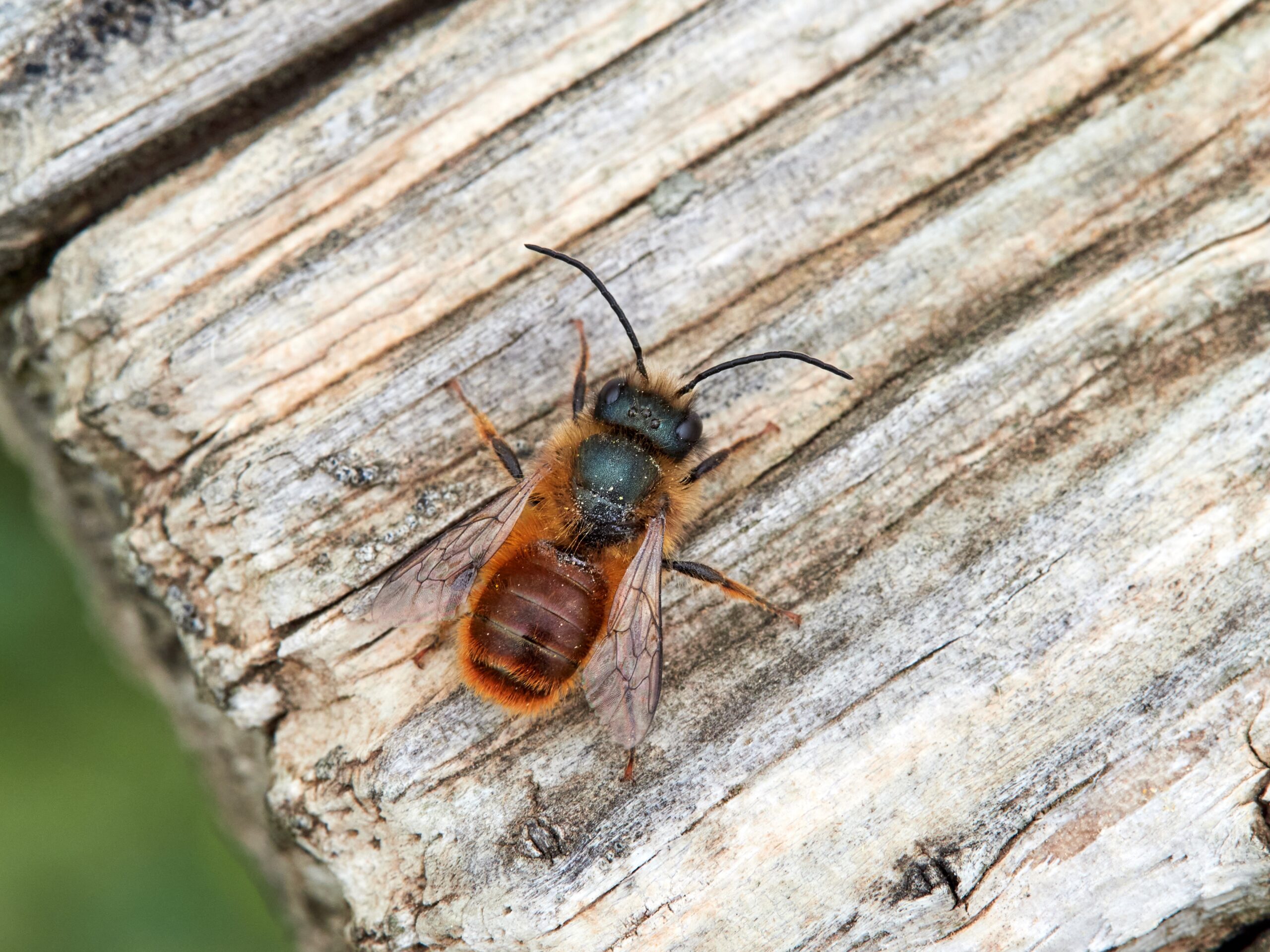

Mason bees are solitary, gentle pollinators that are highly efficient at their job. They pollinate fruit trees like apples and cherries. These bees use mud to build their nests, often in cracks or holes. Habitat loss and pesticide exposure have put them at risk. Mason bees are more effective pollinators than honeybees, making their decline even more alarming for agriculture.
Hummingbirds
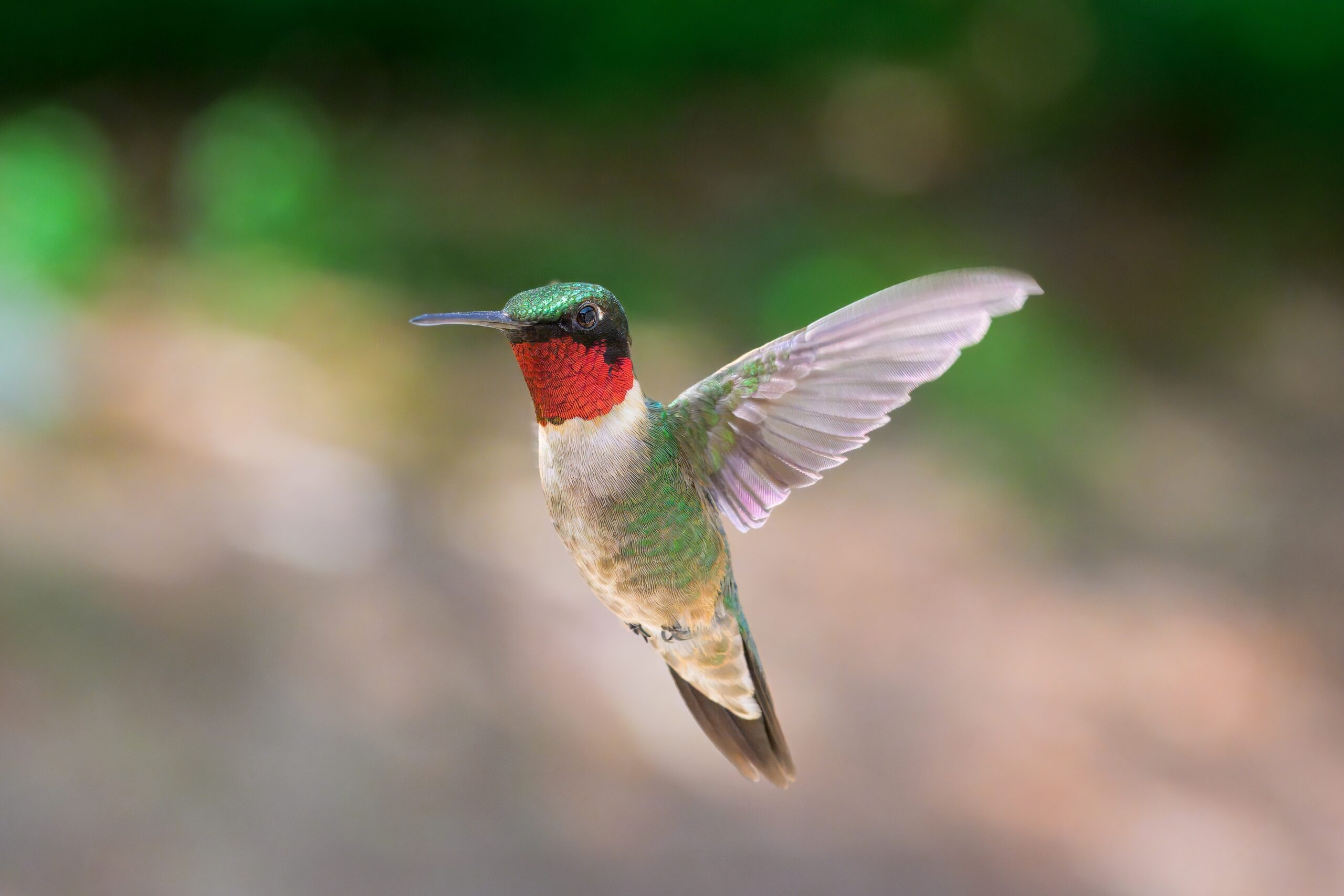

Hummingbirds are small, vibrant birds that feed on nectar, inadvertently pollinating flowers. They are crucial for pollinating tubular flowers that other pollinators cannot access. Habitat destruction, climate change, and pesticides have led to a decline in their populations. Their loss could affect not only flowers but the animals that depend on those plants for food.
Bats
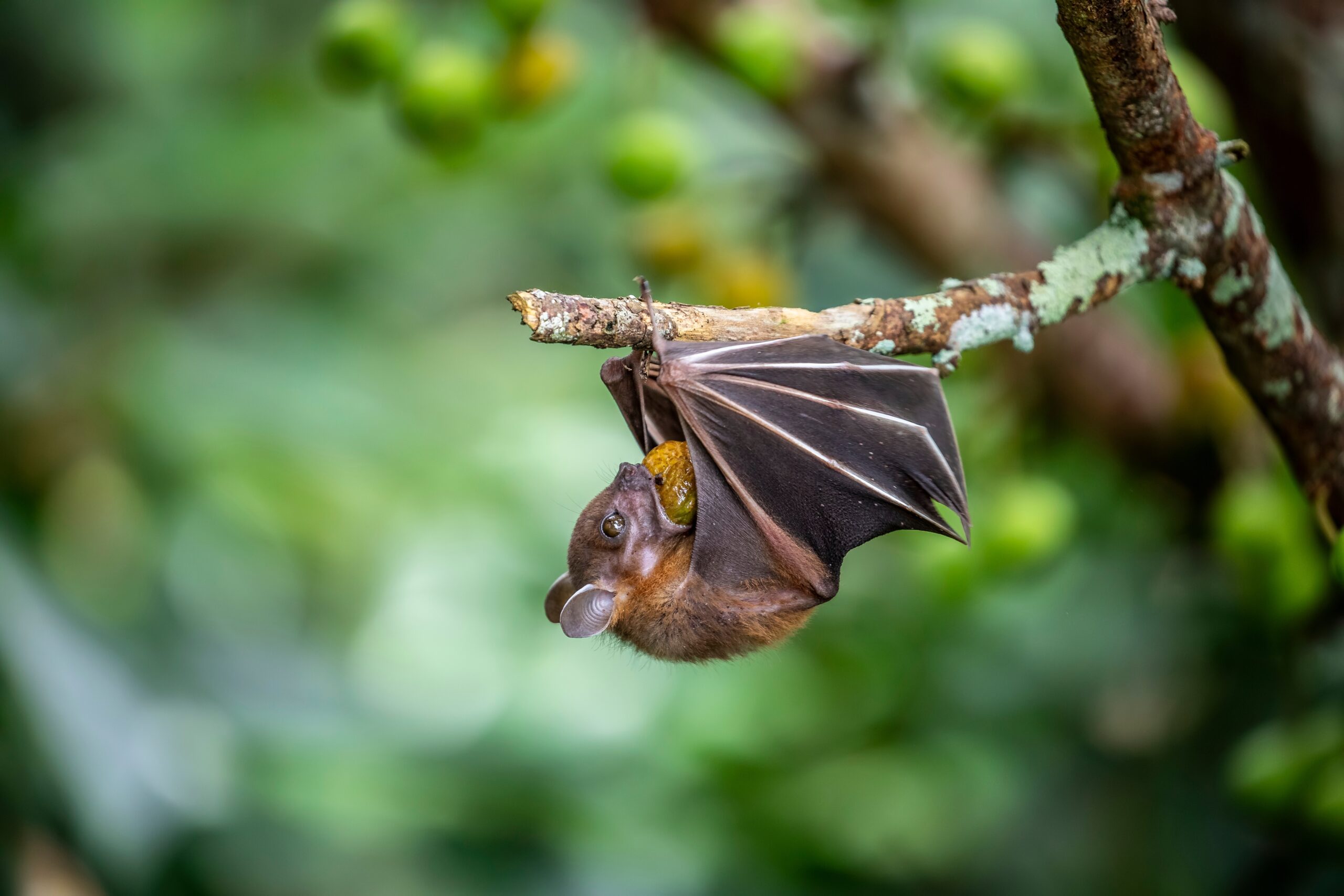

Bats are nocturnal pollinators, essential for pollinating night-blooming plants like agave and cactus. They play a critical role in the ecosystem by helping plants reproduce and disperse seeds. However, habitat loss, disease, and pesticide exposure have contributed to their decline. A decrease in bat populations could impact the plants that rely on them for pollination.
Hoverflies
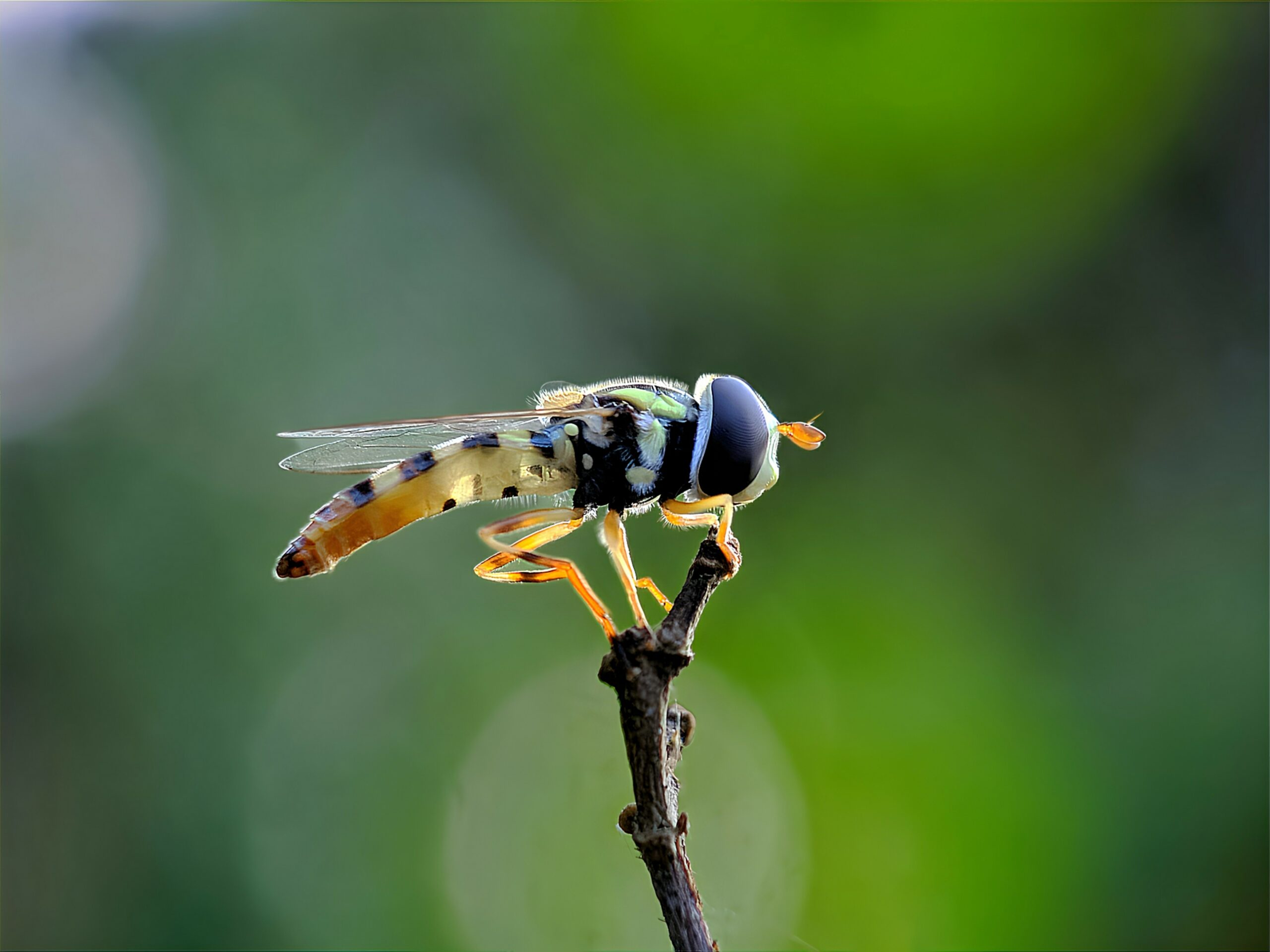

Hoverflies are small, bee-like insects known for their ability to hover in place. They feed on nectar and help pollinate a wide range of plants. These insects are important for crops like carrots and onions. Unfortunately, habitat loss and pesticide use have caused a drop in their numbers. Their decline could affect both wild and cultivated plants.
Moths
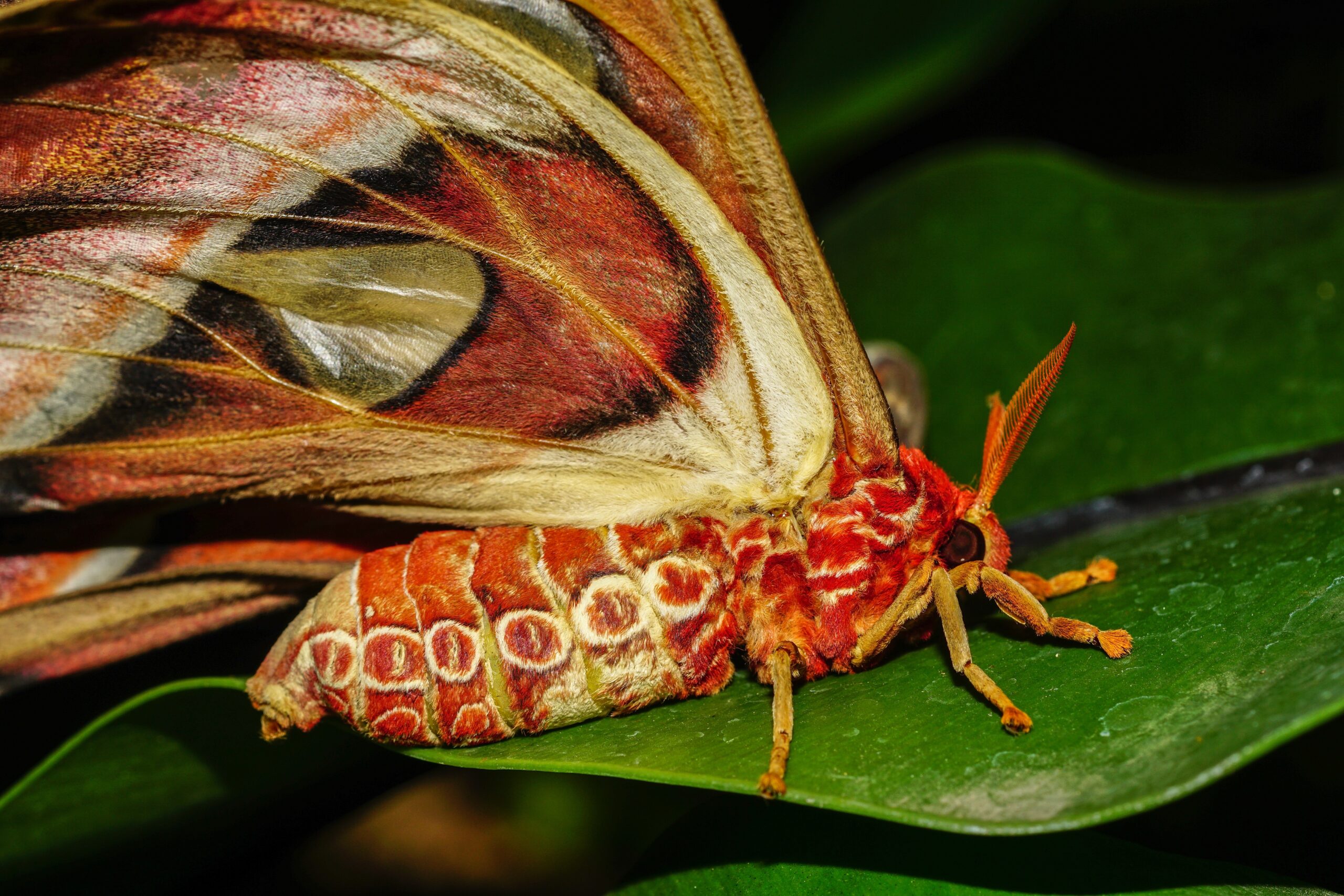

Moths are nocturnal pollinators, often overlooked compared to butterflies. They help pollinate night-blooming flowers, making them essential for certain plants. Many species of moths are declining due to light pollution, habitat loss, and pesticides. Their disappearance could lead to a reduction in plant diversity, especially in night-blooming species.
Leaf-footed Bugs
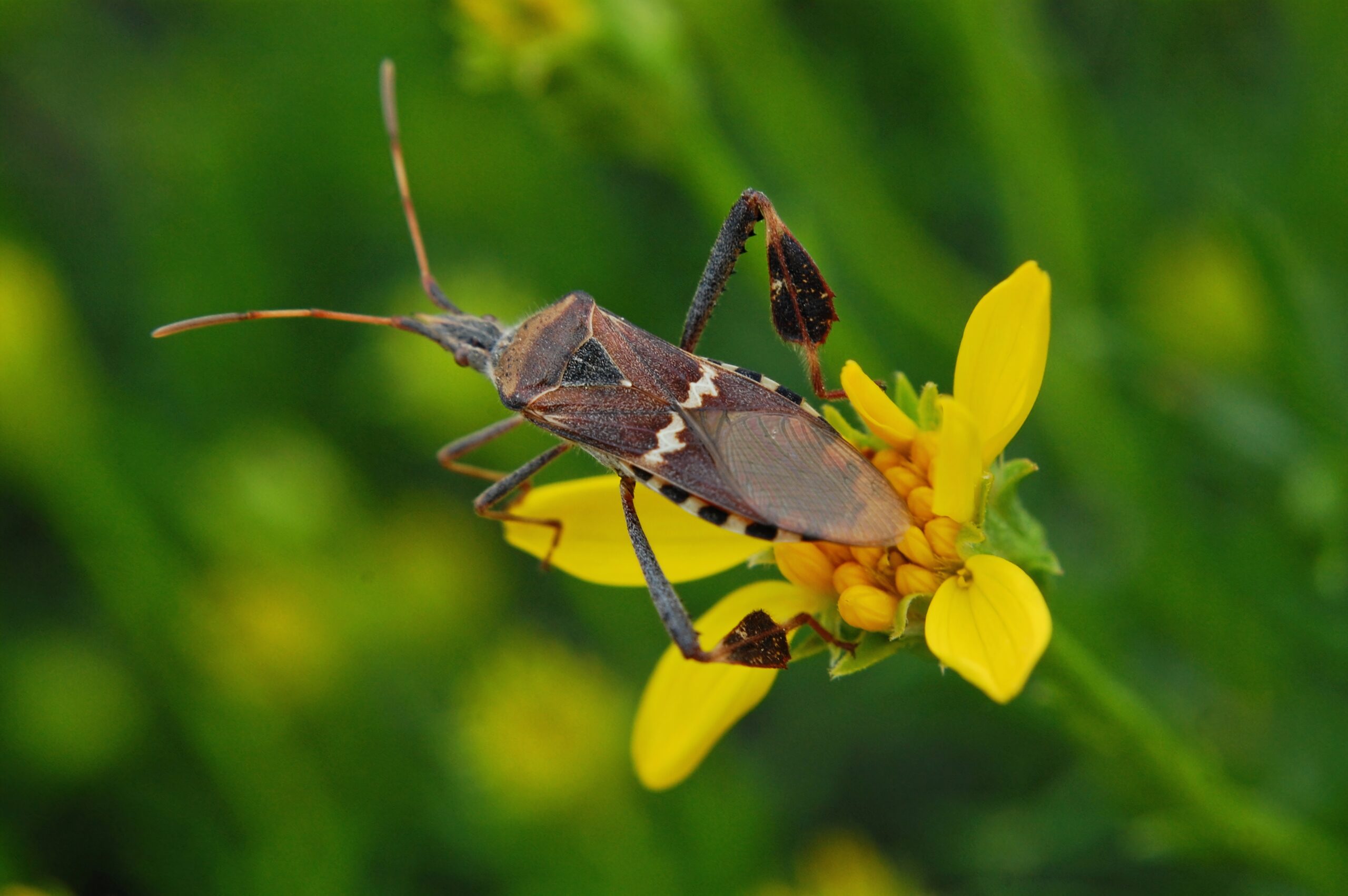

Leaf-footed bugs are medium-sized insects recognizable by the flattened, leaf-like expansions on their hind legs. They primarily feed on plant juices but also assist in pollination by transferring pollen between flowers. These bugs are important for certain plants that have limited pollinators. Unfortunately, habitat destruction and pesticide use have caused their populations to decline. Protecting their habitats could help maintain the plant species that rely on their pollination efforts.
Wasps
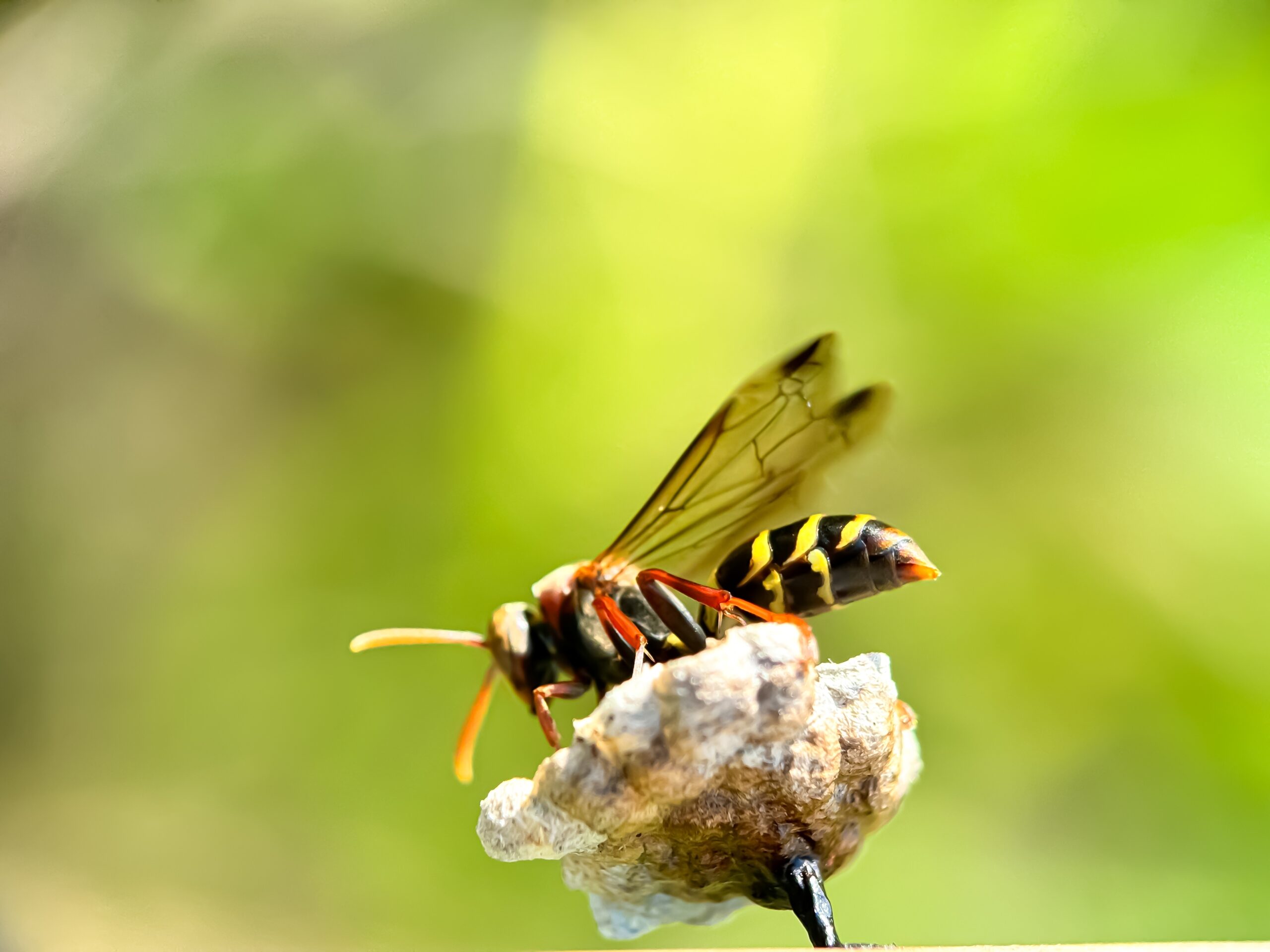

Wasps are often misunderstood but play a vital role in pollination and pest control. Unlike bees, wasps are carnivorous but still feed on nectar, helping to pollinate various plants. They are crucial for crops like figs and other fruits. However, their numbers are declining due to habitat loss and pesticide exposure. The decline in wasp populations could impact both pollination and natural pest management.
Carrion Beetles
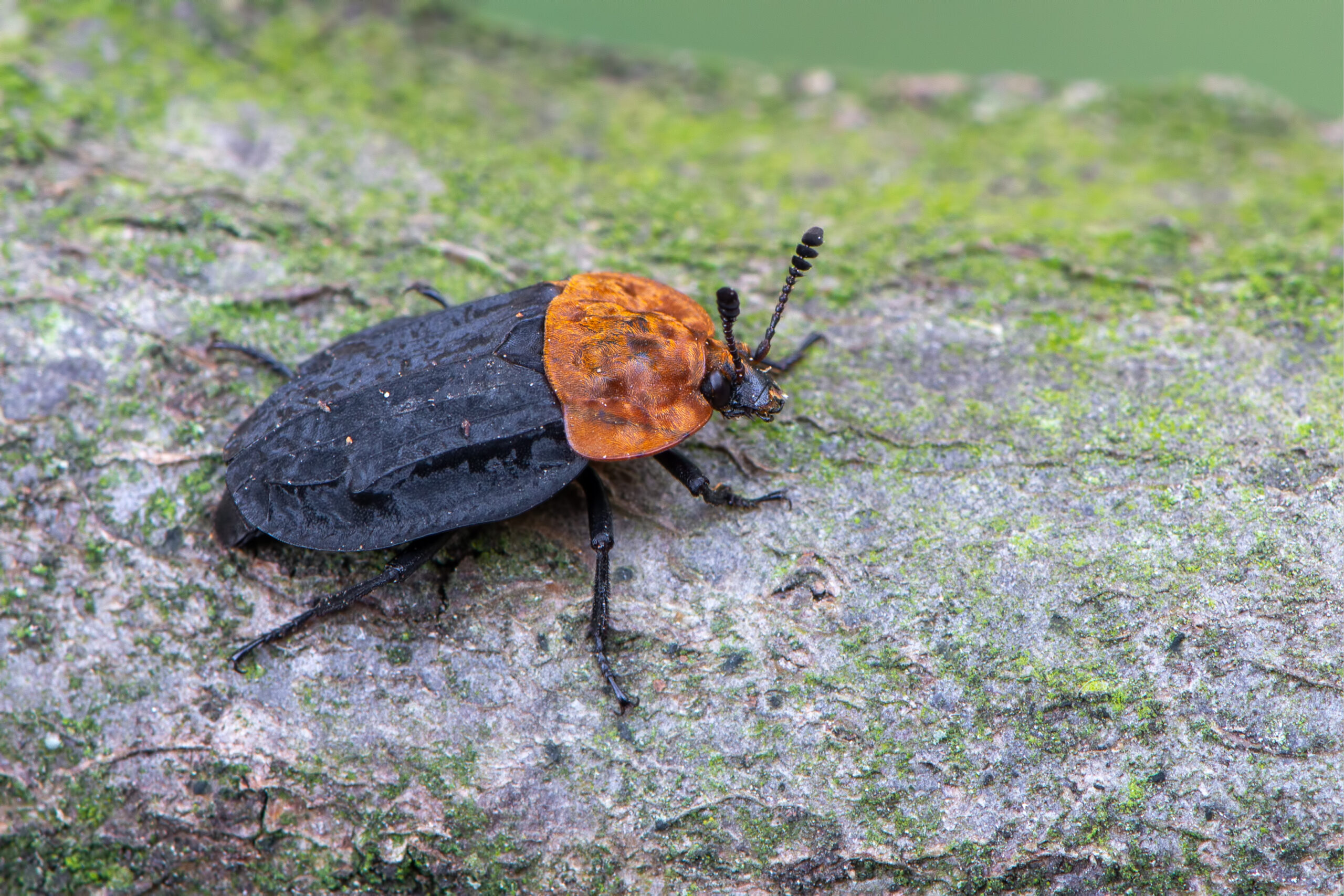

Carrion beetles, known for feeding on decaying organic matter, play a lesser-known but crucial role in pollination. As they move between flowers and decaying material, they inadvertently transfer pollen, helping various plants reproduce. These beetles contribute to maintaining ecosystem health by recycling nutrients. However, habitat loss and pesticide exposure have caused their populations to drop. Protecting their environment is essential for both pollination and the breakdown of organic matter in ecosystems.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More from Rarest.org
22 Plants with Medicinal Properties That Are Endangered

Many plants used in traditional medicine are now endangered due to overharvesting, habitat loss, and environmental changes. Read More.
9 Coveted Antique Swords and Their Auction Prices
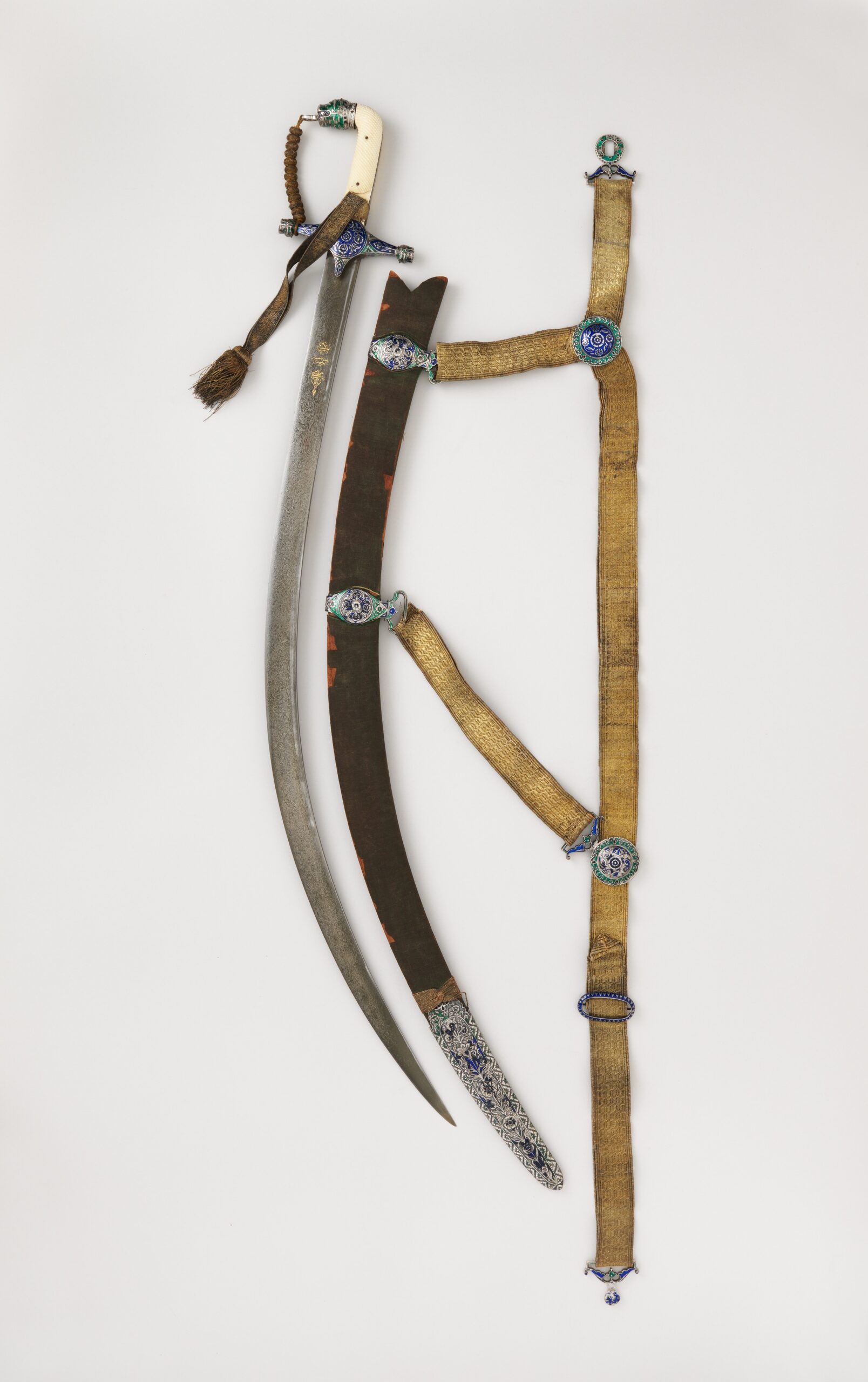

Antique swords have captivated collectors and historians for centuries. These historical weapons tell stories of battles, craftsmanship, and cultural significance. Read More.
13 Sought-After Antique Sewing Machines and Their Collector Value
Antique sewing machines hold a special place in history and in the hearts of collectors. These machines are more than just relics; they are a testament to craftsmanship and engineering. Read More.
