The discovery of ancient dinosaurs gives us a fascinating window into life millions of years ago. These early dinosaurs hold clues about evolution and adaptation, showing us how life started and thrived. Each of these dinosaurs lived during unique timeframes, with fossils found in different corners of the globe. The details about their habitats, diets, and origins help us understand their roles in prehistoric ecosystems. Here are some of the oldest known dinosaurs ever discovered, showcasing what early life on Earth might have looked like.
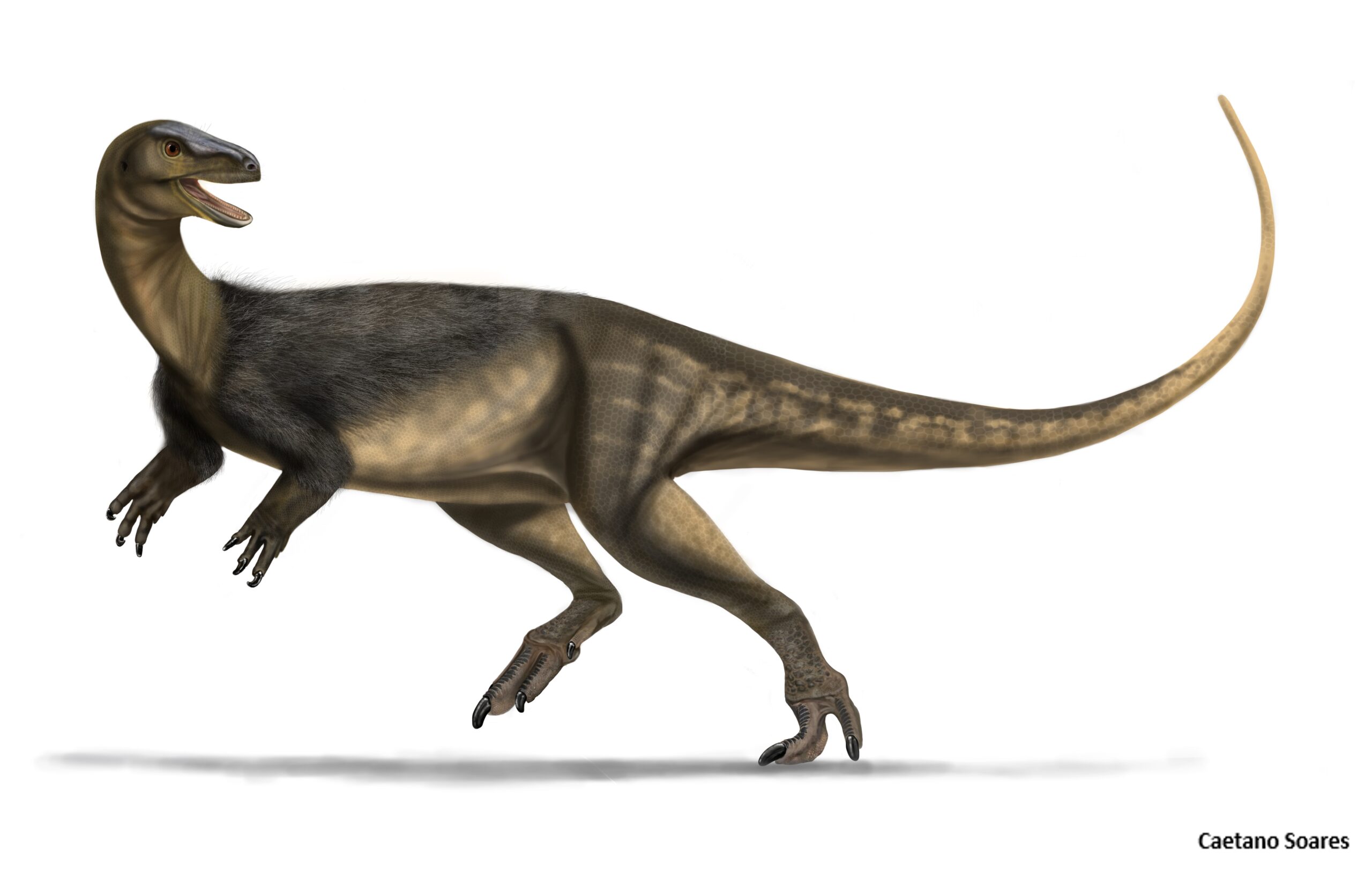
Nyasasaurus
Nyasasaurus is often considered the oldest known dinosaur, dating back around 243 million years. Fossils of this dinosaur were discovered in Tanzania, near Lake Nyasa, which inspired its name. This early dinosaur was small, reaching only about 2-3 meters in length. It likely walked on two legs, making it agile for its size. Its exact diet is unclear, though it is believed to be omnivorous, eating both plants and small animals. Nyasasaurus lived during the Middle Triassic period, indicating dinosaurs existed earlier than previously thought. Its bones display signs of rapid growth, a trait common in later dinosaurs.
Herrerasaurus
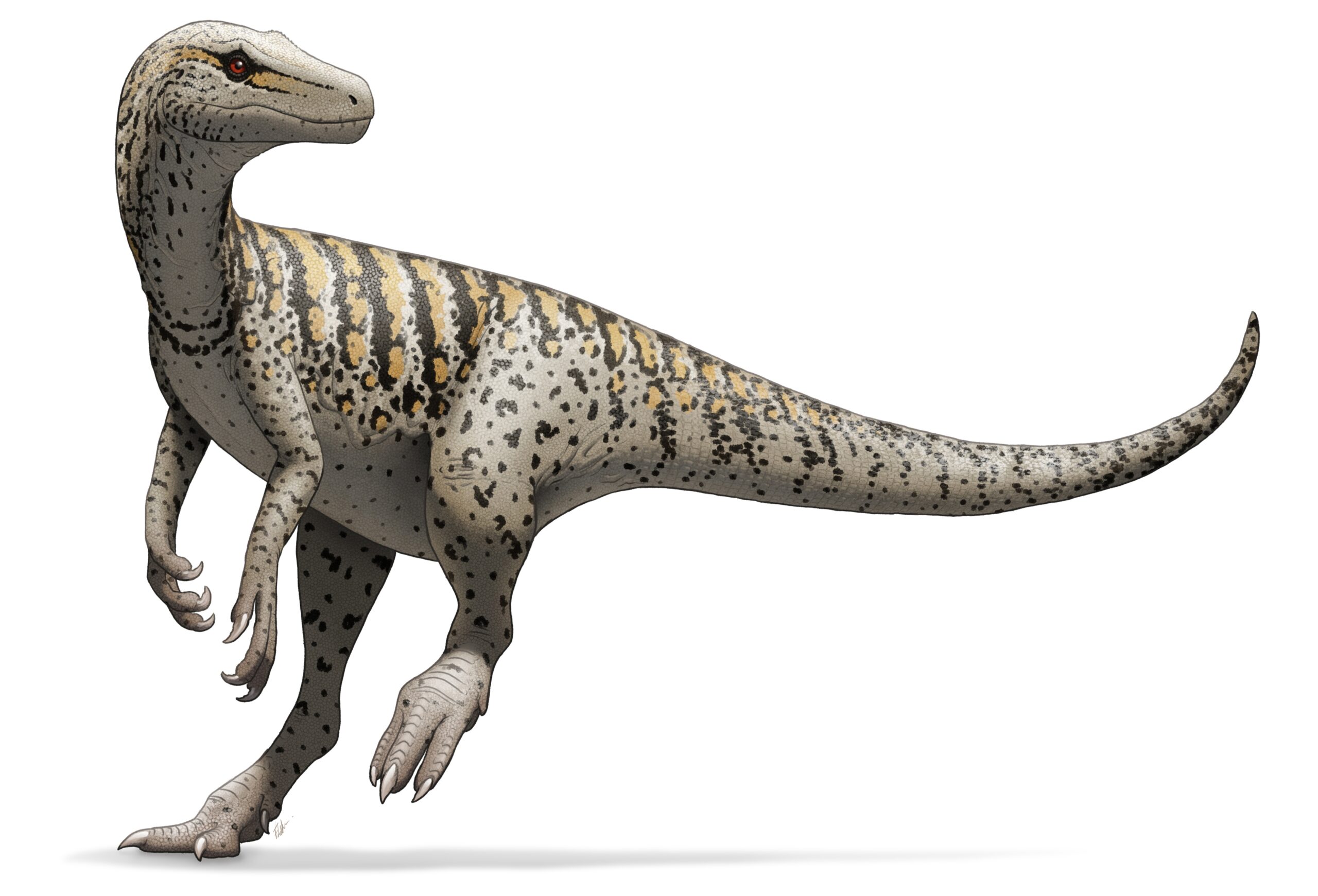

Herrerasaurus roamed what is now Argentina around 231 million years ago. It was named after the rancher who discovered its fossils, Victorino Herrera. This carnivorous dinosaur was about 3-6 meters long, with sharp teeth and claws for hunting. Herrerasaurus lived in the Late Triassic period and is one of the earliest known theropods. Its agile body and strong hind legs made it an efficient predator. Fossils show it had a flexible jaw, allowing it to tear into prey with ease. Herrerasaurus likely preyed on smaller animals, establishing it as a top predator of its time.
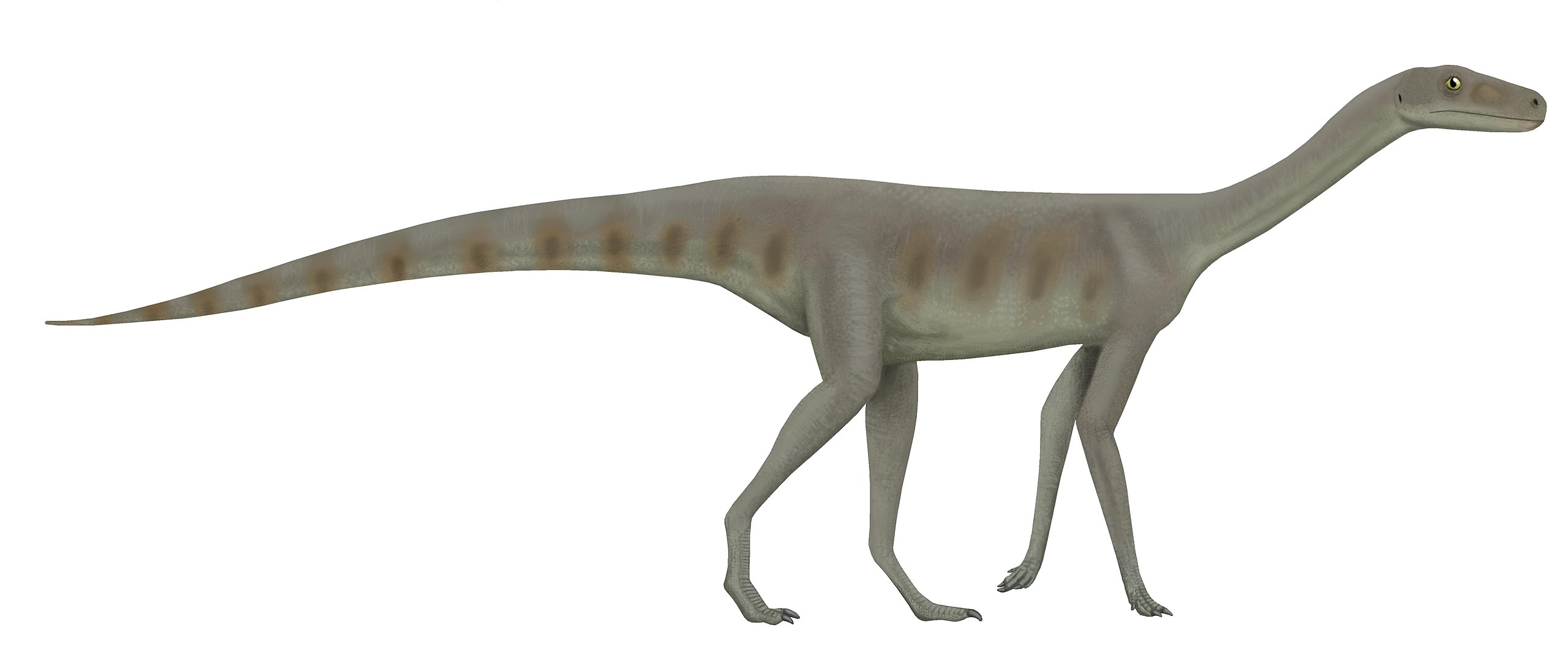
Eoraptor

Eoraptor, meaning “dawn thief,” lived approximately 231 million years ago in present-day Argentina. It was a small dinosaur, standing just over half a meter tall, but its agile frame made it swift. This dinosaur had a mixed diet, featuring both plants and small animals, making it one of the first omnivorous dinosaurs. Eoraptor’s fossils indicate it had both primitive and advanced skeletal features, hinting at its transitional place in dinosaur evolution. It lived during the Late Triassic period and inhabited river valleys and forested areas. Eoraptor’s nimble build helped it avoid larger predators of its time.
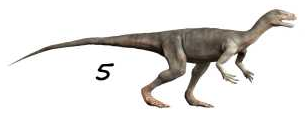
Staurikosaurus
Staurikosaurus, one of the earliest dinosaurs, existed around 225 million years ago in Brazil. Its name means “Southern Cross lizard,” inspired by its discovery in South America. This small dinosaur measured about 2 meters long, with a lightweight, agile frame. Staurikosaurus was a carnivore, feeding on small animals and insects in its environment. It lived during the Late Triassic period, thriving in dry, warm climates. Fossils reveal it had a strong tail that helped with balance and speed. As a predator, it likely relied on quick movements to catch prey.
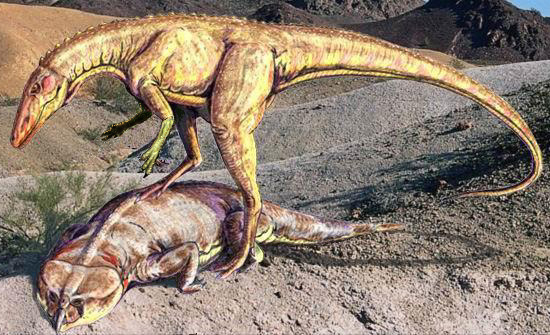
Guaibasaurus
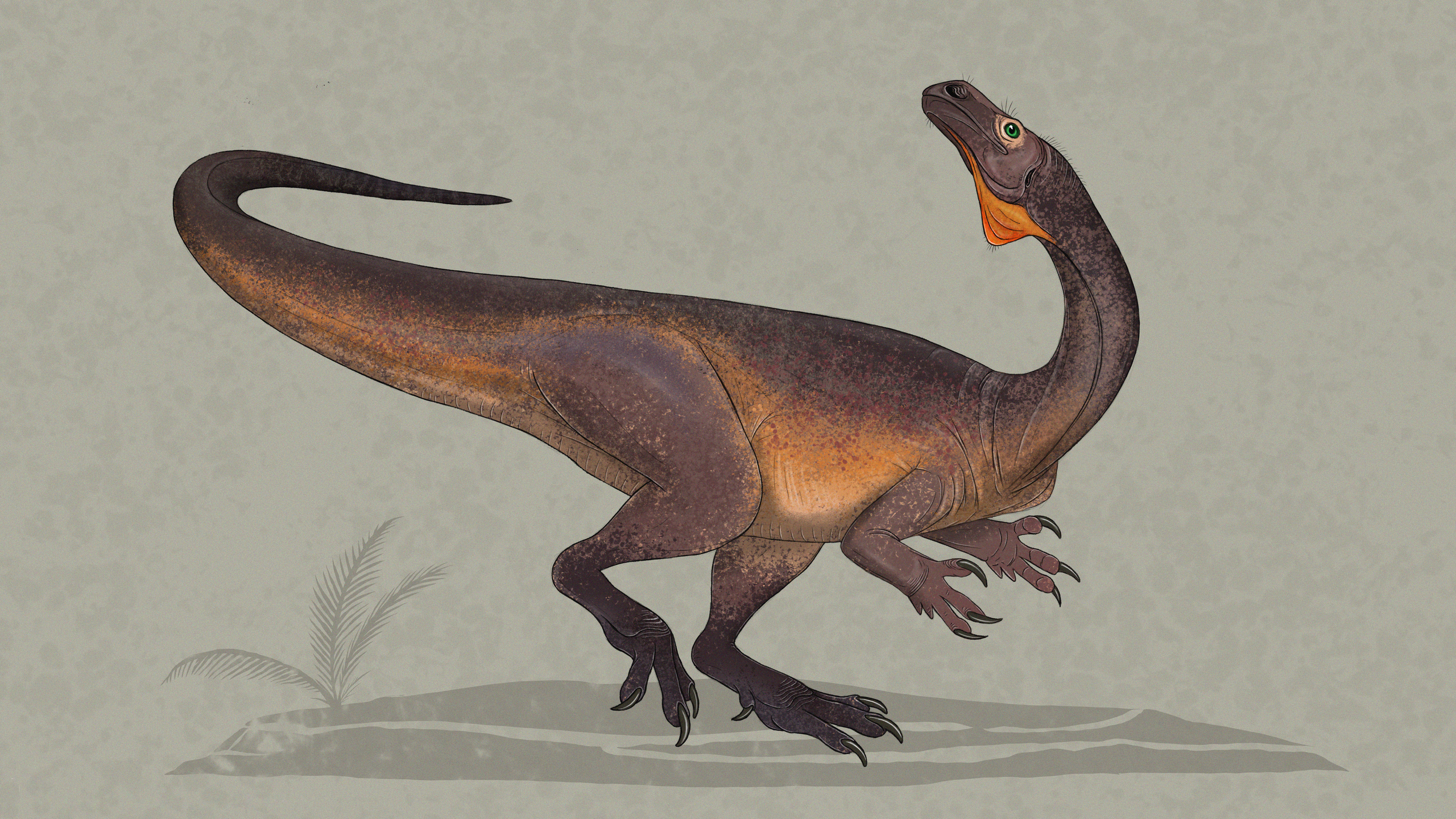
Guaibasaurus lived around 225 million years ago in what is now southern Brazil. Its fossils were found near the Guaíba River, hence its name. This early dinosaur was about 2 meters long and likely moved on two legs. It’s believed to have been omnivorous, consuming a mix of plants and small animals. Guaibasaurus inhabited forests and river valleys during the Late Triassic period. Its lightweight body made it agile, ideal for navigating through dense vegetation. This dinosaur shows early adaptations common to both herbivorous and carnivorous dinosaurs.
Saturnalia
Saturnalia, discovered in Brazil, dates back about 225 million years. Its name refers to the Roman festival of Saturn, symbolizing the “beginning.” This dinosaur was small, only about 1.5 meters long, with a slender, bipedal build. Fossils suggest Saturnalia may have been an herbivore or omnivore, feeding on ferns and small plants. It lived during the Late Triassic period in warm, lush forests. Saturnalia’s skeletal structure includes traits found in both early dinosaurs and their close relatives. This combination of features shows its unique position in dinosaur evolution.
Buriolestes
Buriolestes lived approximately 230 million years ago in present-day Brazil. This dinosaur was relatively small, measuring about 1.5 meters in length. Buriolestes is believed to have been a carnivore, with sharp teeth adapted for catching small prey. It lived during the Late Triassic period, inhabiting forested areas filled with small animals. The discovery of its fossils sheds light on the early stages of sauropodomorph evolution. Buriolestes’ agility and lightweight body suggest it was a quick, efficient hunter. This dinosaur provides crucial insight into early meat-eating dinosaurs.
Panphagia
Panphagia, discovered in Argentina, lived about 228 million years ago. Its name, meaning “eats everything,” refers to its likely omnivorous diet. This small dinosaur was about 1.5 meters long and had a mix of sharp and flat teeth. Panphagia roamed during the Late Triassic period, inhabiting forested environments rich in vegetation. Its fossils show it had a lightweight frame and slender limbs, aiding its mobility. Panphagia’s unique tooth structure indicates it ate both plants and small animals. This dinosaur is one of the earliest known ancestors of the massive sauropods that appeared later.
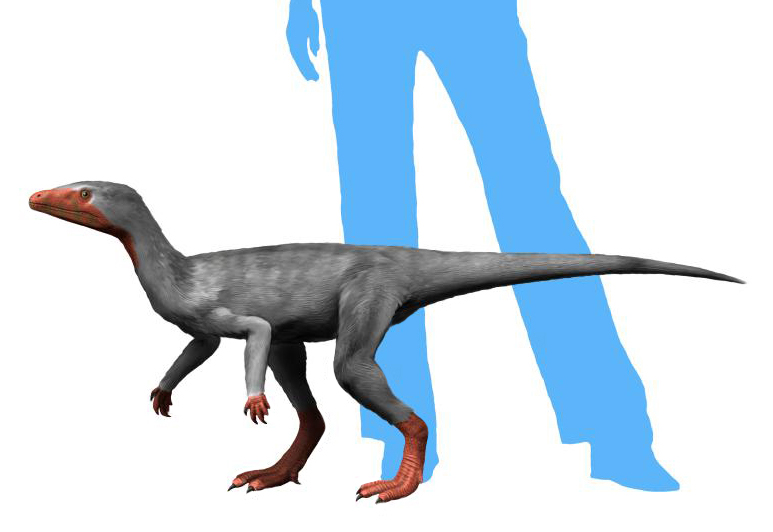
Asilisaurus

Asilisaurus lived around 245 million years ago, making it one of the earliest known dinosaur relatives. Discovered in Tanzania, this small creature was about 1-3 meters long. Asilisaurus was likely herbivorous, with teeth suited for a plant-based diet. It inhabited a time called the Middle Triassic period, well before most true dinosaurs evolved. Its body structure is a mix of primitive and advanced features, showing its early place in dinosaur ancestry. Asilisaurus had long limbs that helped it move quickly through forested areas. This dinosaur relative provides insight into the early evolution of dinosaurs and their close relatives.
Coelophysis
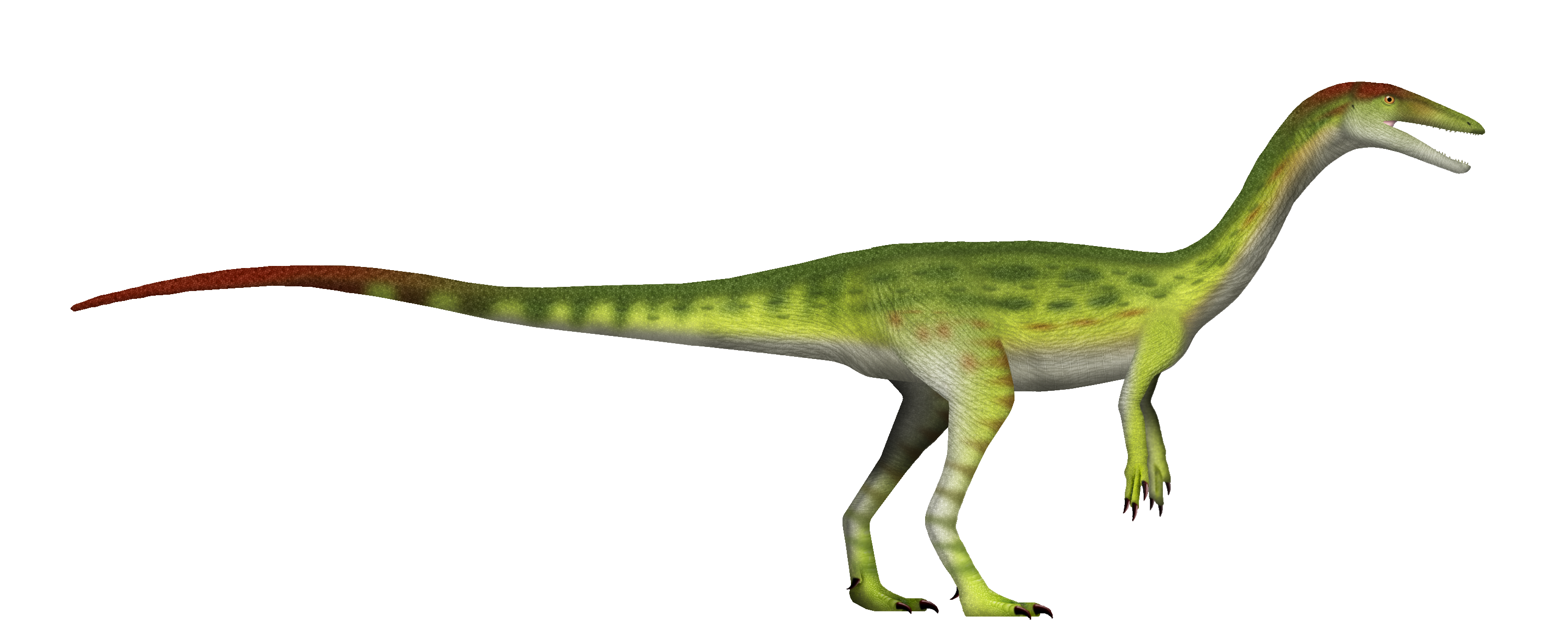

Coelophysis, one of the oldest true dinosaurs, roamed North America around 225 million years ago. This small, agile dinosaur measured about 2-3 meters in length. It was a carnivore, feeding on small animals and possibly insects. Coelophysis lived during the Late Triassic period in arid, scrubby landscapes. Fossils reveal it had hollow bones, making it lightweight and highly mobile. It hunted in packs, which may have given it an advantage over larger predators. Coelophysis is one of the earliest examples of successful dinosaur predators.
Lagerpeton

Lagerpeton, one of the oldest dinosaur relatives, lived around 237 million years ago in Argentina. It was a small creature, about 70 centimeters long, and had a slim, agile body. Lagerpeton was likely insectivorous, with features suited for catching small prey. It lived during the Middle Triassic period, in dry and open environments. Fossil evidence suggests it was a quick runner, using long legs to navigate its surroundings. Lagerpeton’s skeletal structure shows an early form of limb structure seen in later dinosaurs. This dinosaur relative helps fill gaps in our understanding of early dinosaur evolution.
Pisanosaurus
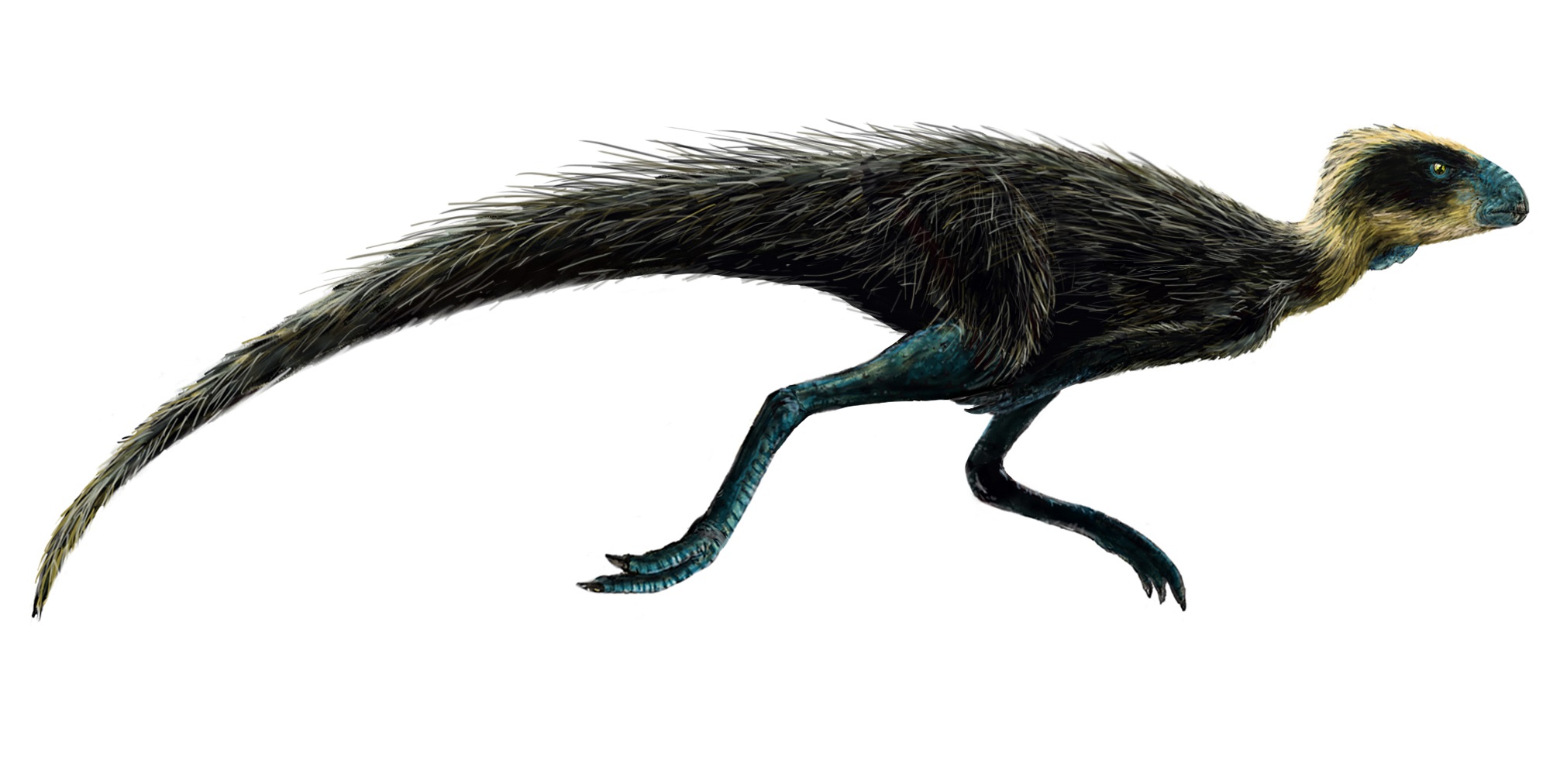

Pisanosaurus is one of the earliest known herbivorous dinosaurs, dating back around 228 million years. Found in Argentina, it was a small dinosaur, about 1 meter in length. Pisanosaurus had teeth adapted for a plant-based diet, making it a pioneer among herbivorous dinosaurs. It lived during the Late Triassic period in forested regions with abundant vegetation. Its lightweight body and bipedal stance allowed it to move quickly. Fossils suggest it may have lived in small herds for protection. Pisanosaurus is considered one of the earliest members of the Ornithischia group.
Procompsognathus
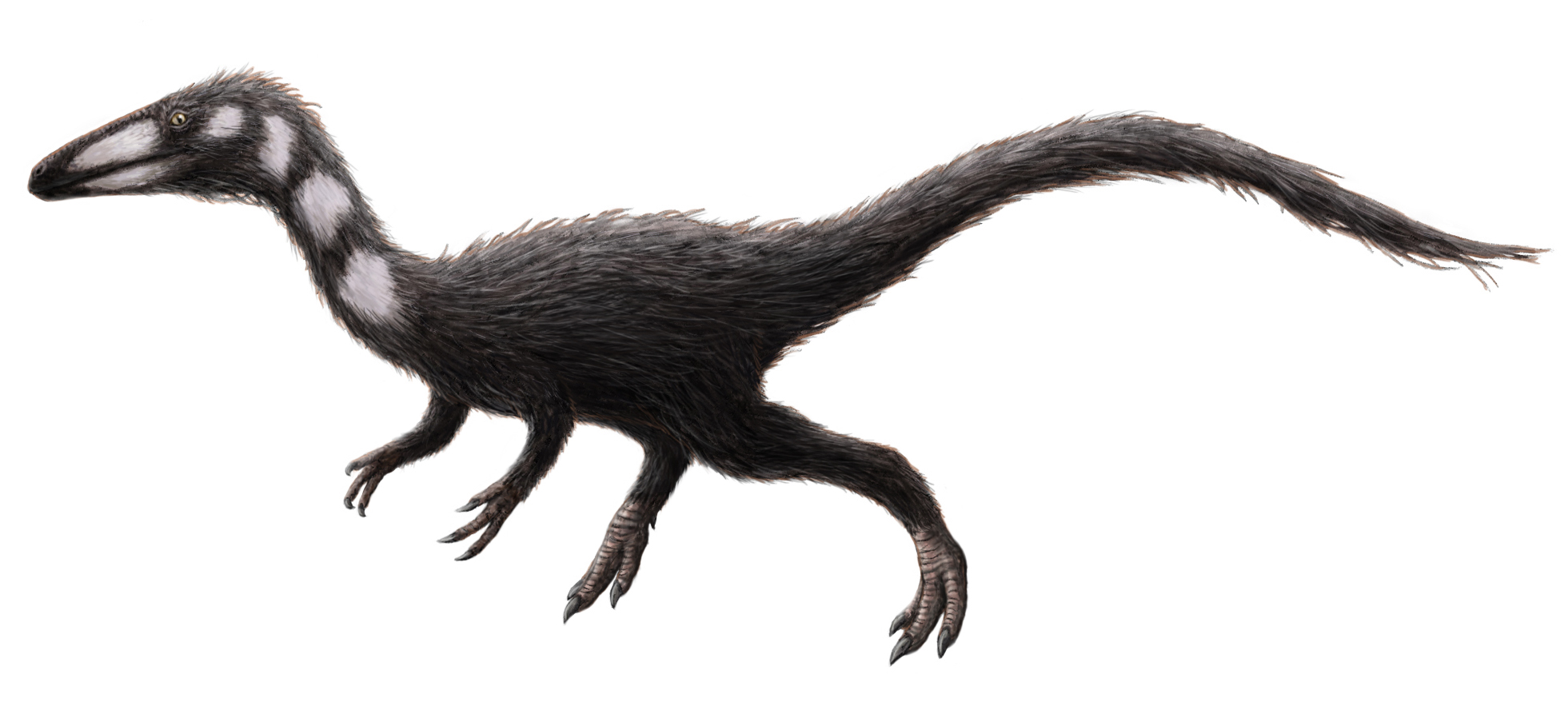

Procompsognathus lived around 210 million years ago in what is now Germany. This small dinosaur measured about 1 meter in length and had a slender, agile build. It was a carnivore, likely feeding on small animals and insects. Procompsognathus thrived in the Late Triassic period, navigating a mix of forests and open plains. Its lightweight skeleton and long limbs made it a fast runner. Fossils show it had a sharp, pointed snout, ideal for catching quick-moving prey. Procompsognathus gives insight into the early evolution of small predatory dinosaurs.
Marasuchus
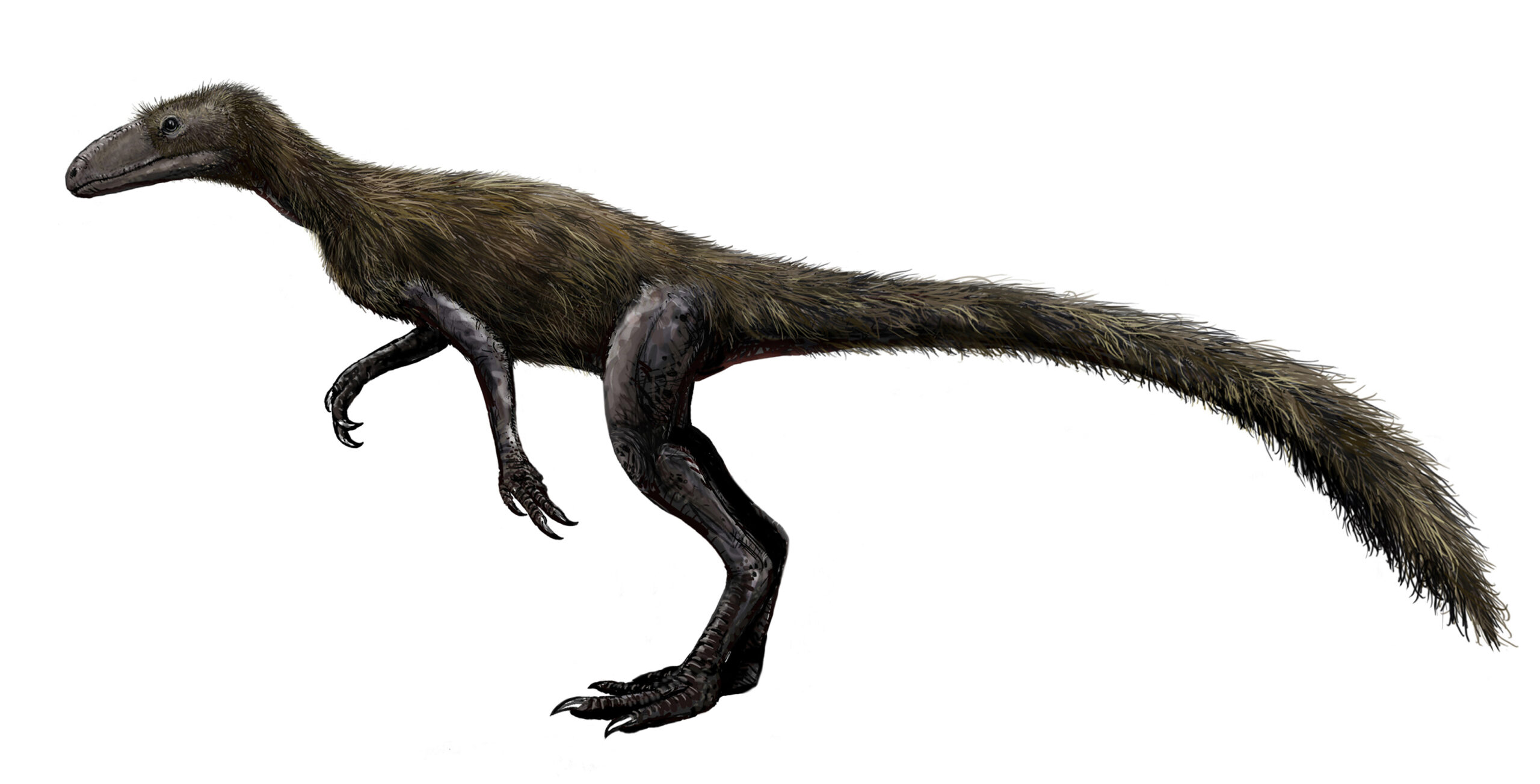

Marasuchus, one of the oldest dinosaur relatives, lived around 235 million years ago in Argentina. It was a small, agile creature, about 30 centimeters long, resembling early dinosaurs in structure. Marasuchus was likely insectivorous, feeding on small invertebrates and insects. It roamed during the Middle Triassic period in dry, open environments. Fossils show it had long hind limbs, allowing for efficient, bipedal movement. Its lightweight frame made it agile and quick on its feet. Marasuchus bridges the gap between earlier archosaurs and later dinosaurs.
Euparkeria
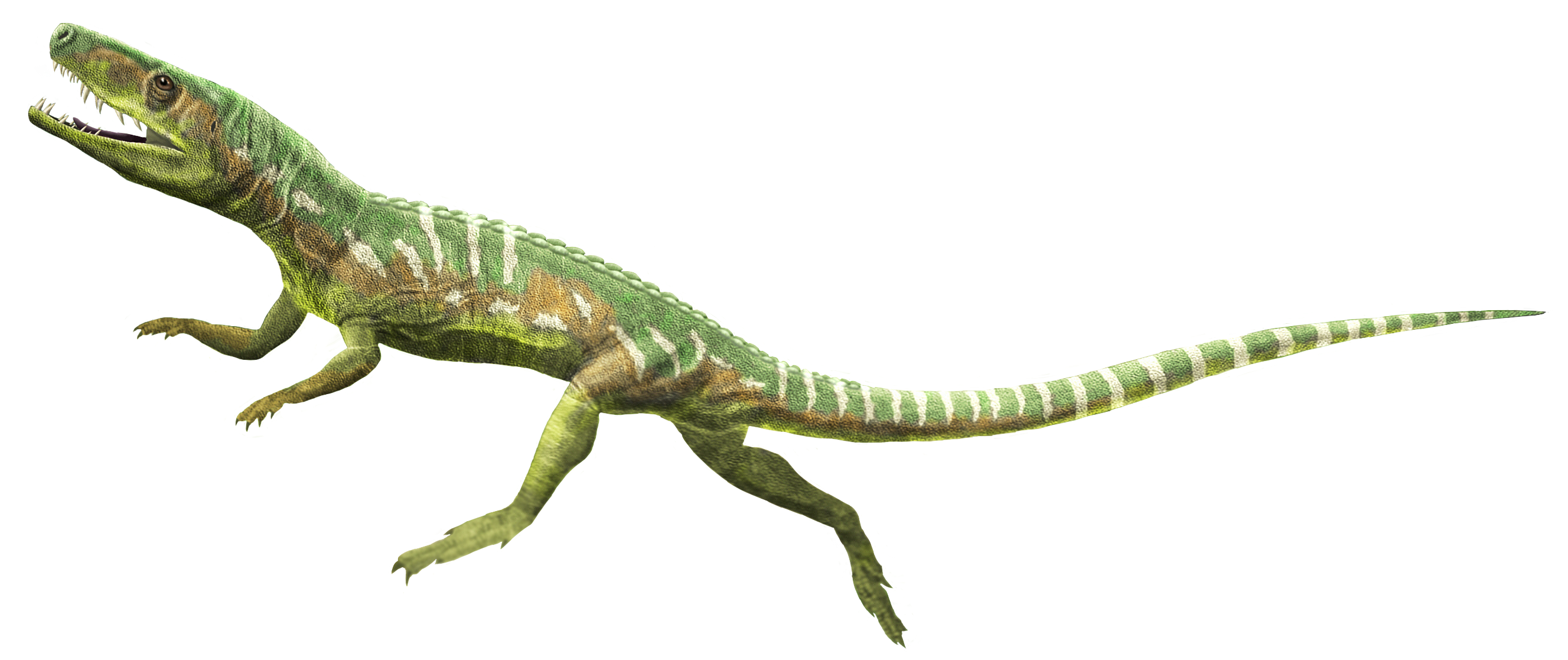

Euparkeria is an ancient dinosaur relative that lived around 245 million years ago in South Africa. It was a small, agile creature, about 50 centimeters long, with a lean, lightweight build. Euparkeria was likely an insectivore, preying on insects and small animals. It lived during the Middle Triassic period in warm, forested habitats. Fossils reveal it could shift between walking on two legs and four, an early adaptation for mobility. Euparkeria had sharp teeth and claws, aiding its predatory behavior. Its unique traits suggest it was an early link in the evolution of later dinosaurs.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More from Rarest.org
10 Largest Lakes in the United States

The United States is home to some of the largest and most iconic lakes in the world, each with its own unique ecosystem, recreational opportunities, and geographical significance. Read More.
10 Oldest Buildings in America

America is home to some of the oldest buildings that still stand strong today. These structures offer a glimpse into the country’s deep history. Read More.
10 Largest Eagles in the World

Eagles are among the most powerful birds of prey, known for their impressive size and sharp hunting skills. Read More.
