Insects are some of the most vital organisms in ecosystems around the world. Though small, they impact everything from pollination to decomposing organic matter. Some insects help control pests, while others aid in the cycle of nutrients. Understanding the role they play in maintaining ecological balance is crucial. Let’s take a closer look at several fascinating insects that contribute significantly to our environment.
Honeybee
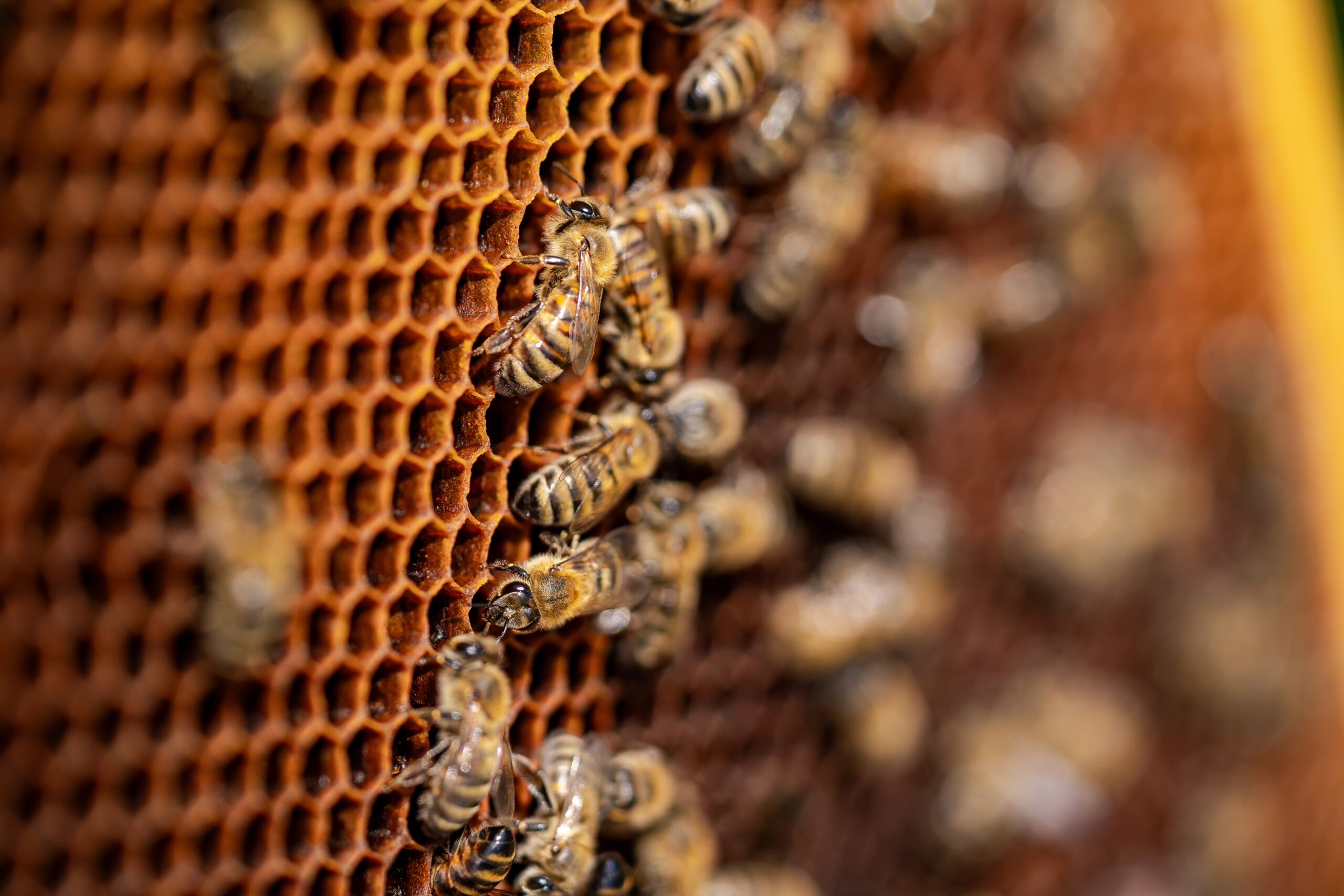

Honeybees are known for their essential role in pollination. They travel from flower to flower, transferring pollen and ensuring plant reproduction. These busy insects are also vital for producing honey and beeswax. Honeybees help pollinate many crops, including fruits and vegetables. Without them, food supplies would be at risk.
Monarch Butterfly
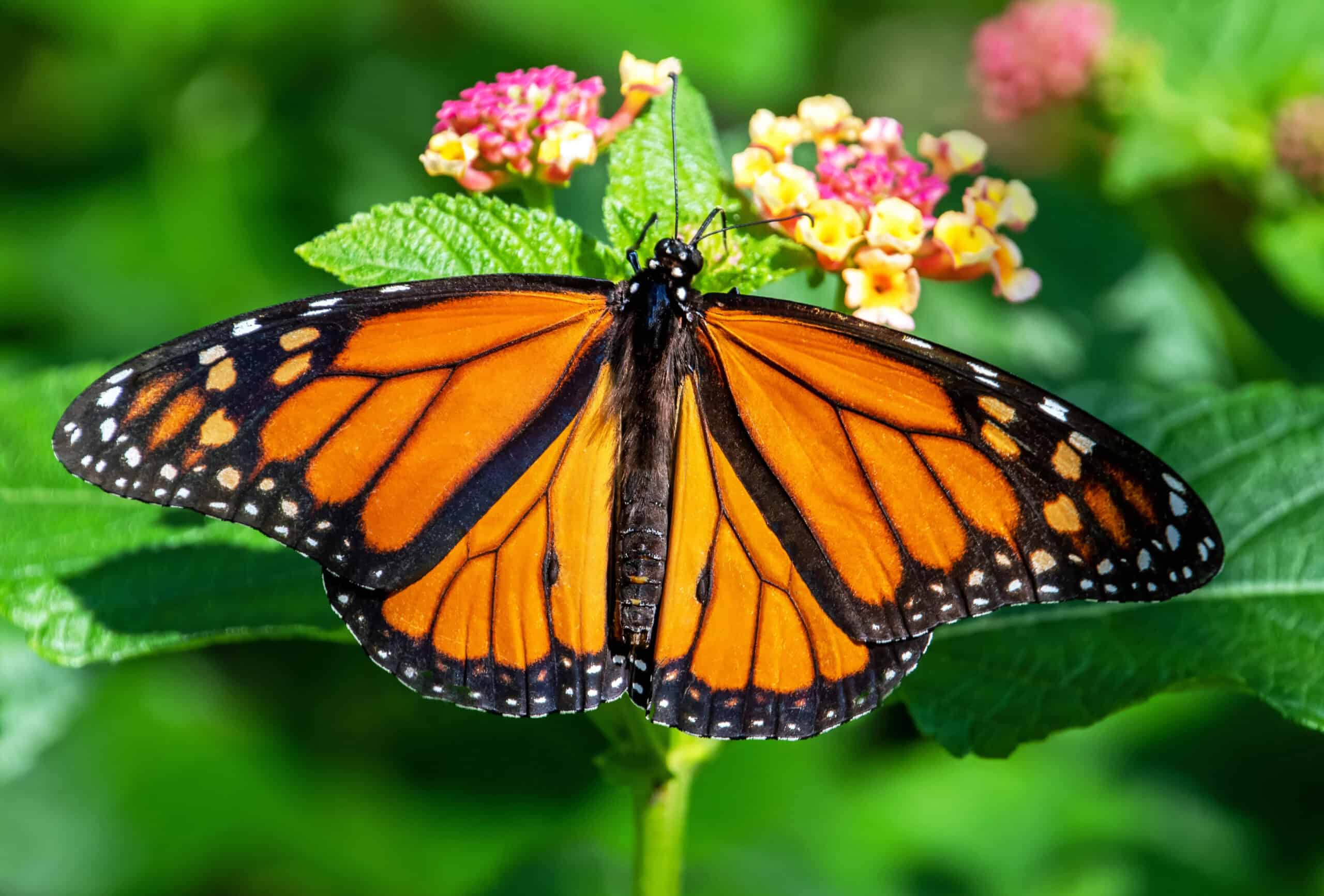

Monarch butterflies are well-known for their striking appearance and long migration. They travel thousands of miles between their breeding grounds and wintering sites. Monarchs play a key role in pollination, especially for milkweed plants. Their vibrant wings make them effective in spreading pollen. Their life cycle also highlights the importance of conservation efforts for pollinators.
Ladybug
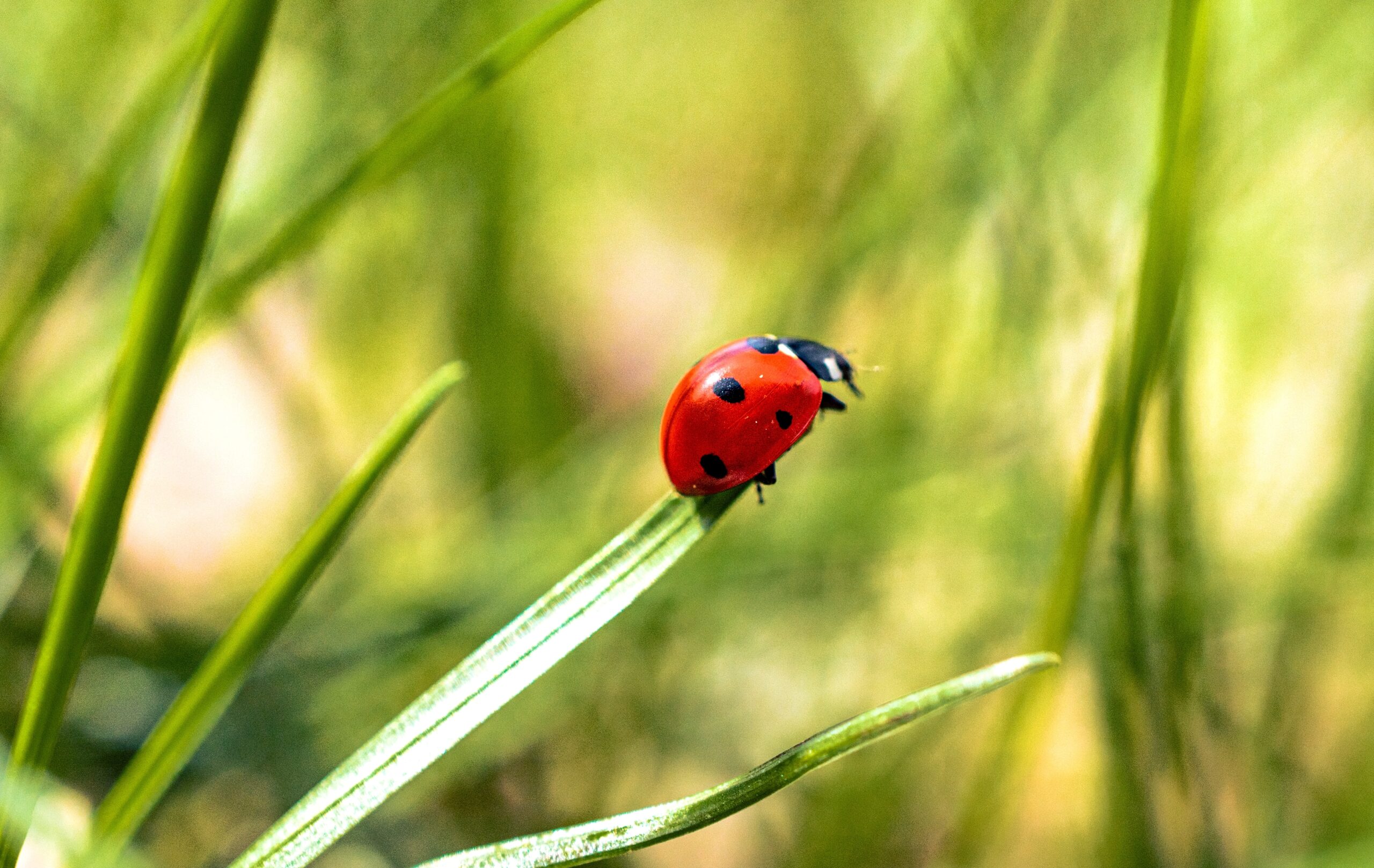

Ladybugs are natural predators that help control pest populations. They feed on aphids and other harmful insects. Gardeners often welcome ladybugs for their ability to reduce the need for pesticides. Their colorful shells also make them easy to spot. Ladybugs help maintain a healthy balance in ecosystems by keeping plant-eating pests in check.
Praying Mantis
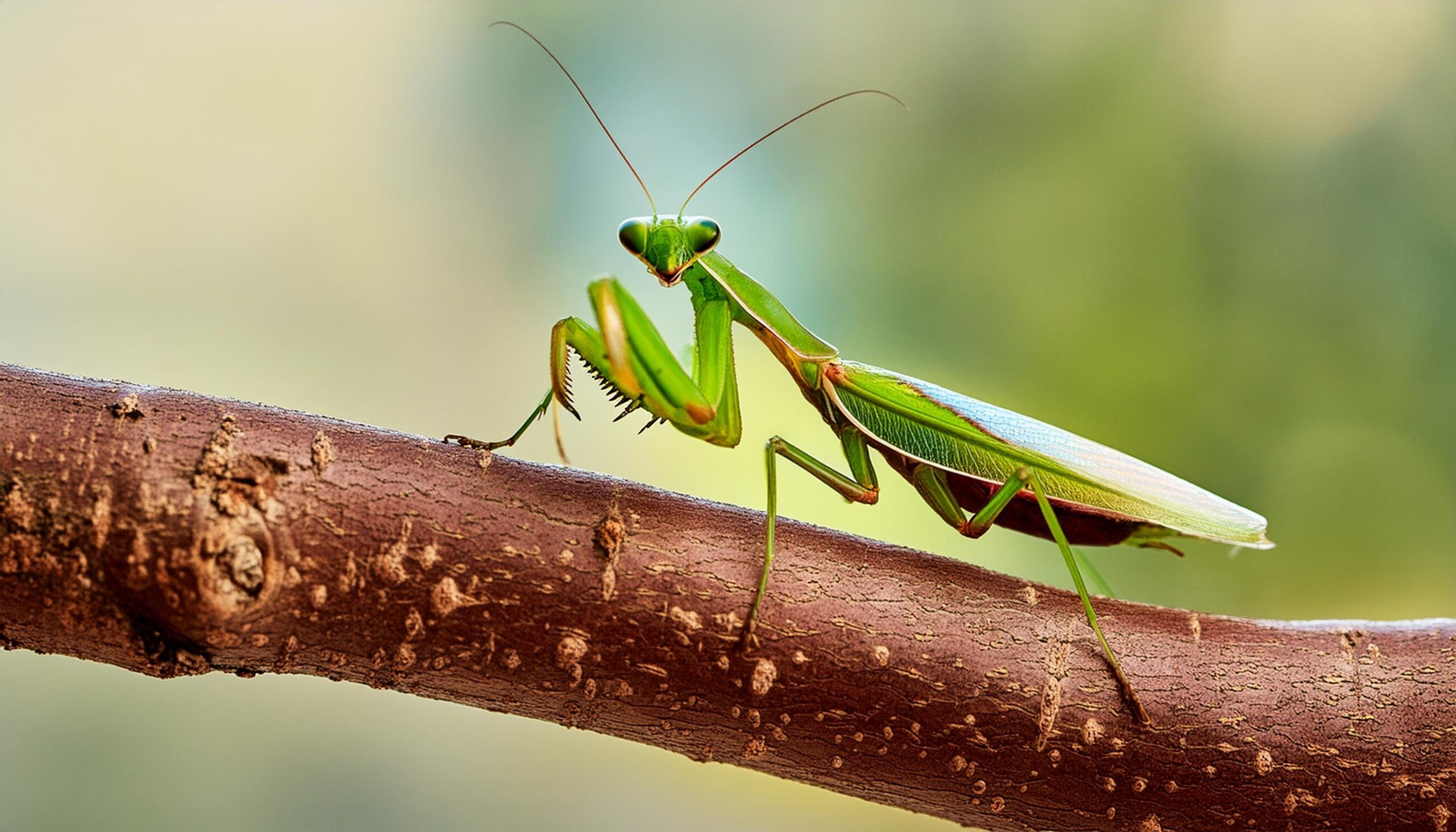

Praying mantises are expert hunters in the insect world. They feed on a variety of insects, including those that damage crops. Their quick reflexes and camouflaged bodies make them effective predators. These insects help control pest populations naturally. Praying mantises play a crucial role in maintaining the balance between prey and predator in their habitats.
Dragonfly
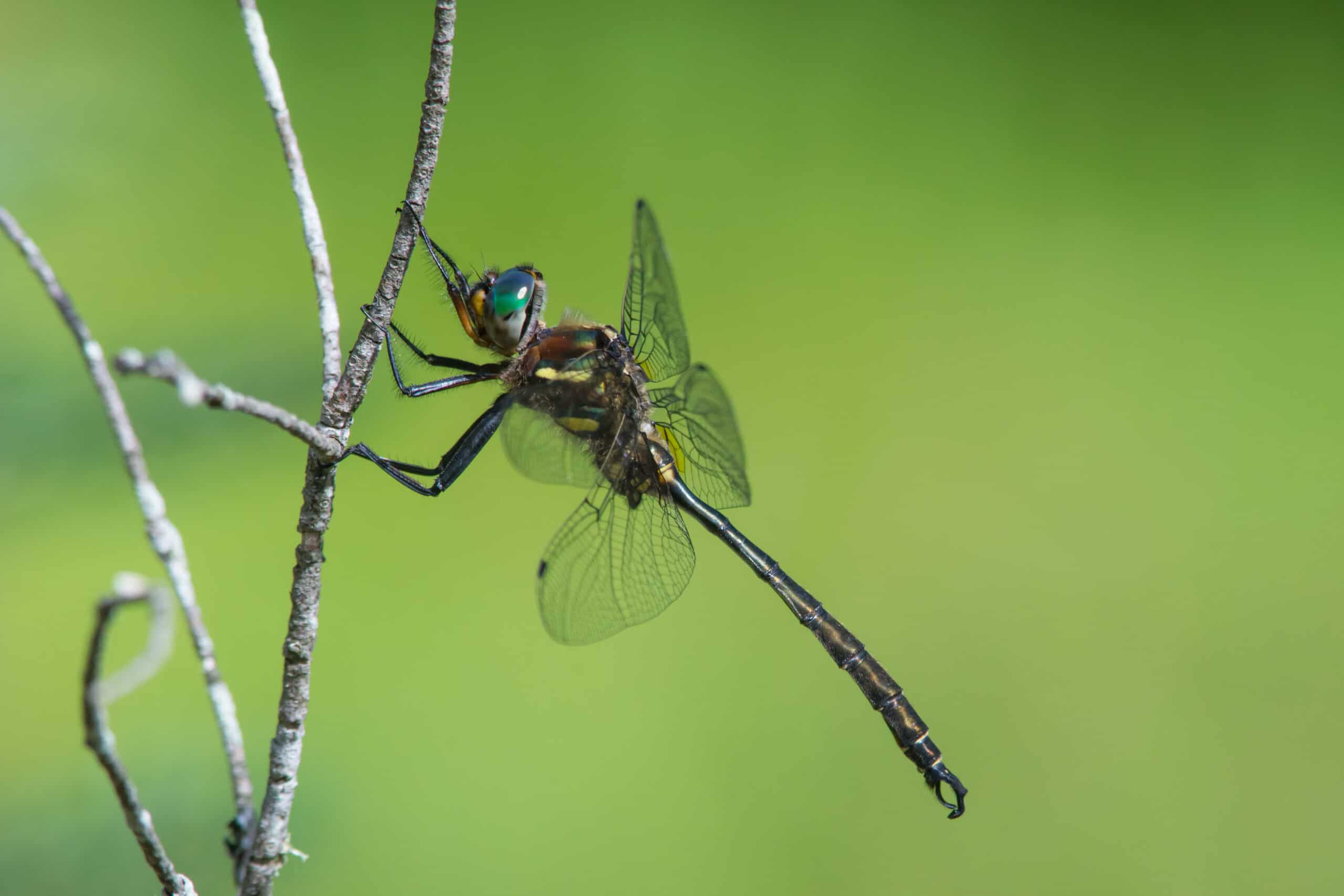

Dragonflies are both beautiful and beneficial insects. Their ability to eat mosquitoes and other small pests is invaluable. They spend part of their lives in water, contributing to aquatic ecosystems. Dragonflies are also indicators of healthy environments, as they thrive in clean water. Their impressive speed and agility make them effective hunters.
Bumblebee
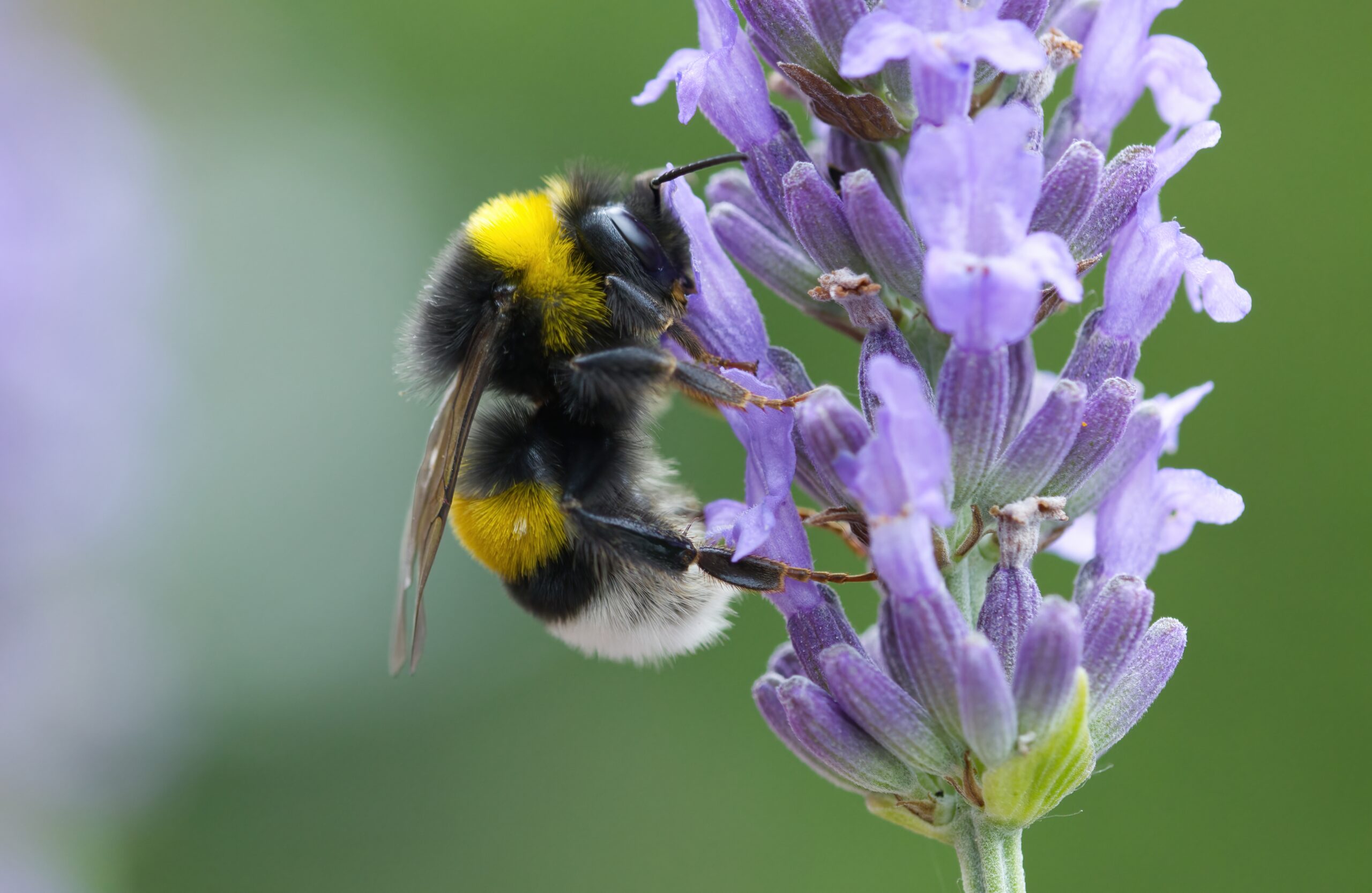

Bumblebees are essential for pollination, particularly for crops like tomatoes. Their large bodies allow them to carry more pollen. They vibrate flowers, which helps release pollen more efficiently. Bumblebees are known for their resilience in colder temperatures. Their work ensures the survival of various plants and crops in many regions.
Ant
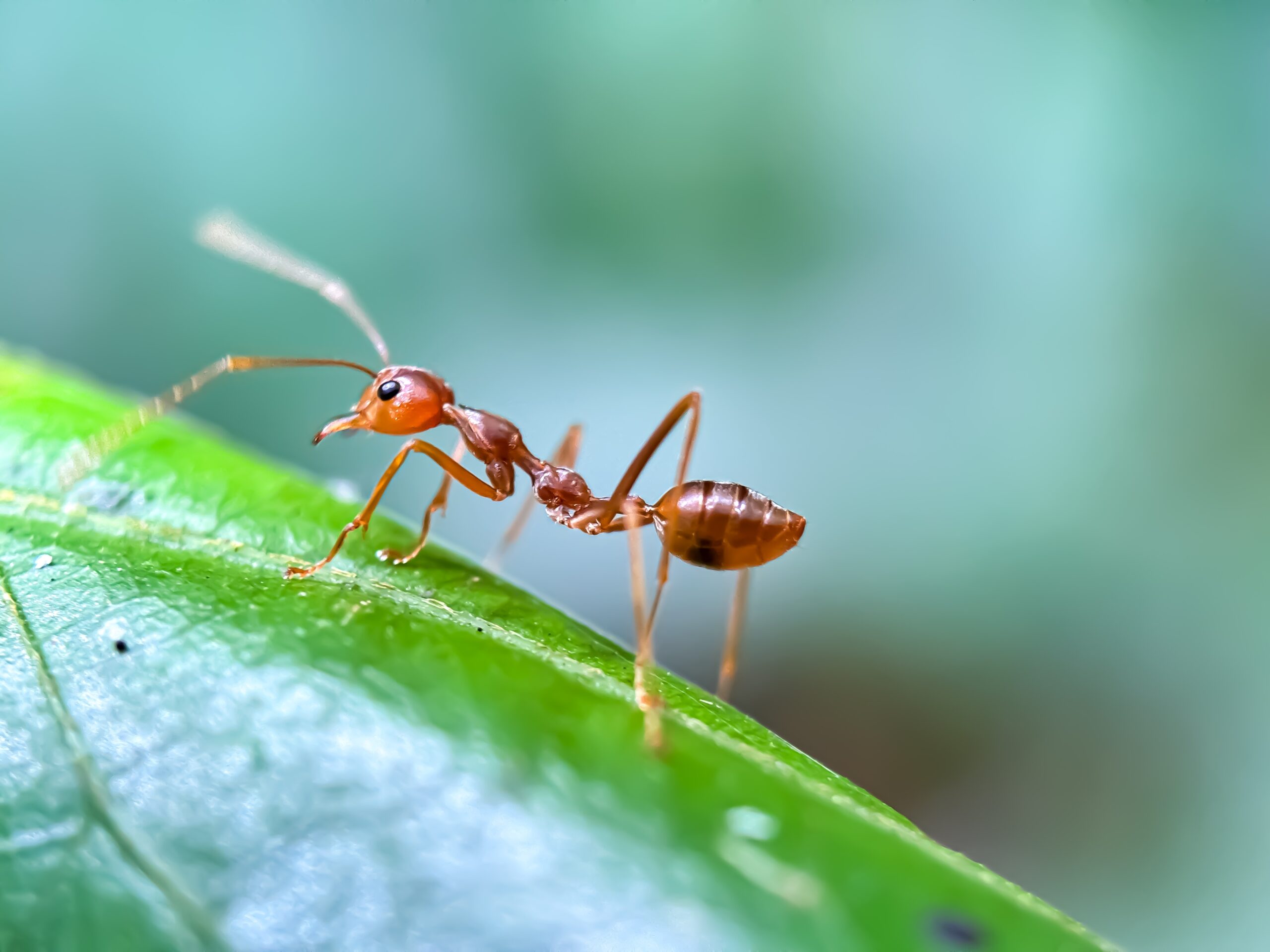

Ants are key players in nutrient recycling and soil aeration. They help decompose organic material by breaking it down and carrying it underground. Ants also play a role in seed dispersal, aiding plant growth. Some species of ants control pest populations by preying on harmful insects. Their colonies create complex networks that benefit the ecosystem.
Dung Beetle
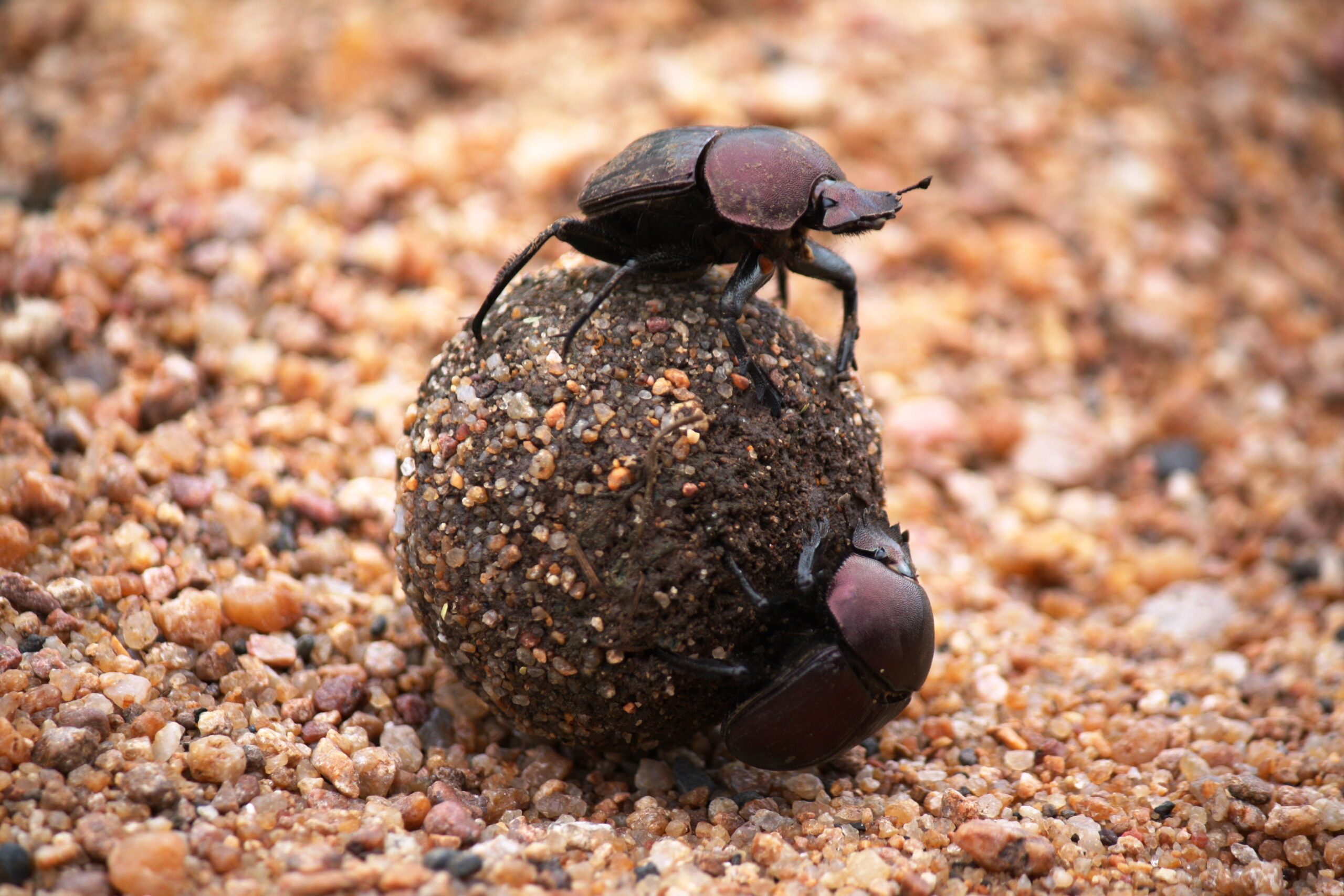

Dung beetles are nature’s recyclers, breaking down animal waste. They collect dung and bury it underground, which helps fertilize the soil. Dung beetles reduce the spread of diseases by removing waste from the environment. They also play a role in nutrient cycling, improving soil health. These beetles contribute to the overall cleanliness and balance of ecosystems.
Termite
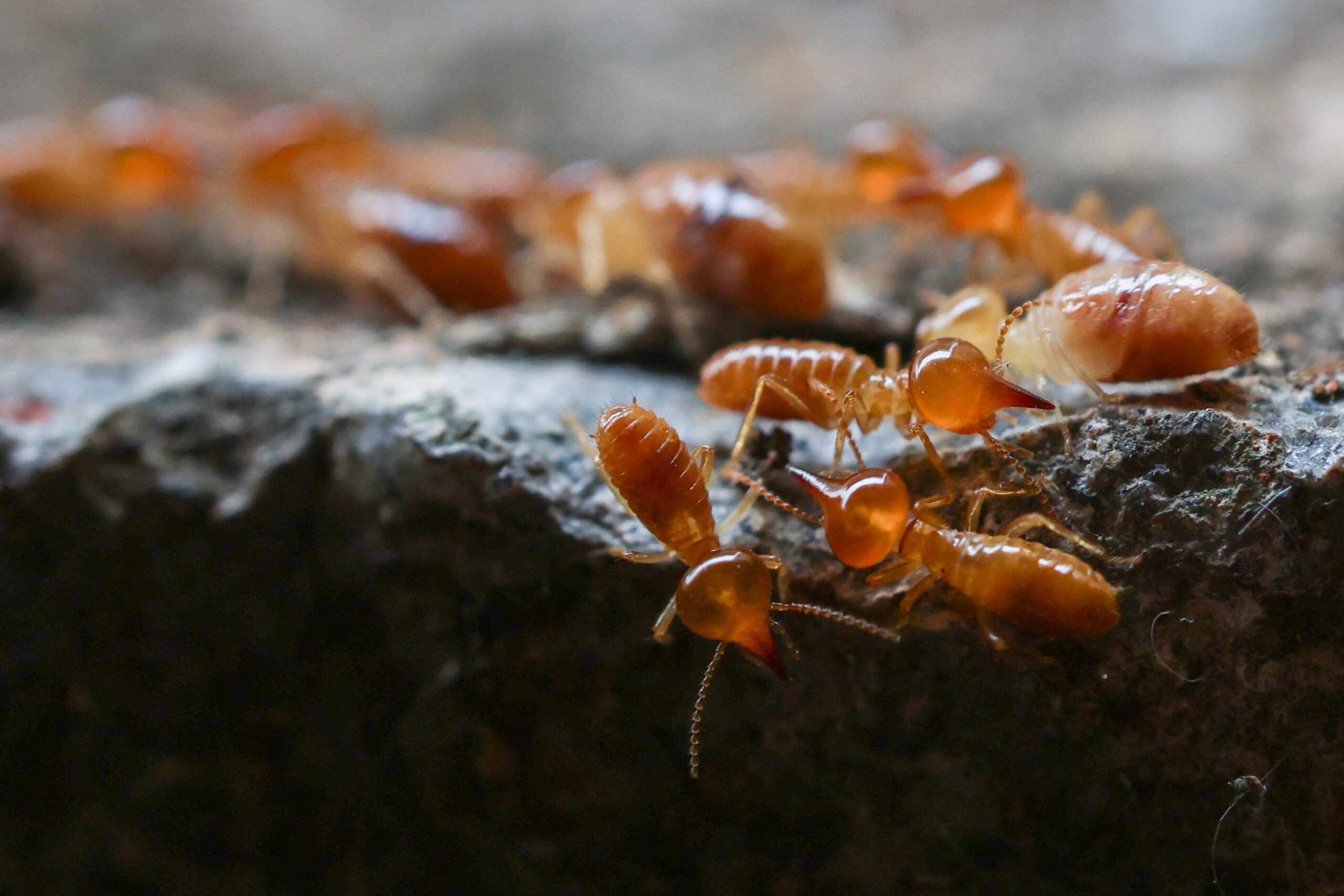

Termites play a critical role in decomposing dead wood and plant material. They help break down tough cellulose, returning nutrients to the soil. While often seen as pests, termites are essential for recycling organic material. Their colonies work together to create large underground systems. Termites improve soil structure, benefiting plant life and other organisms.
Firefly
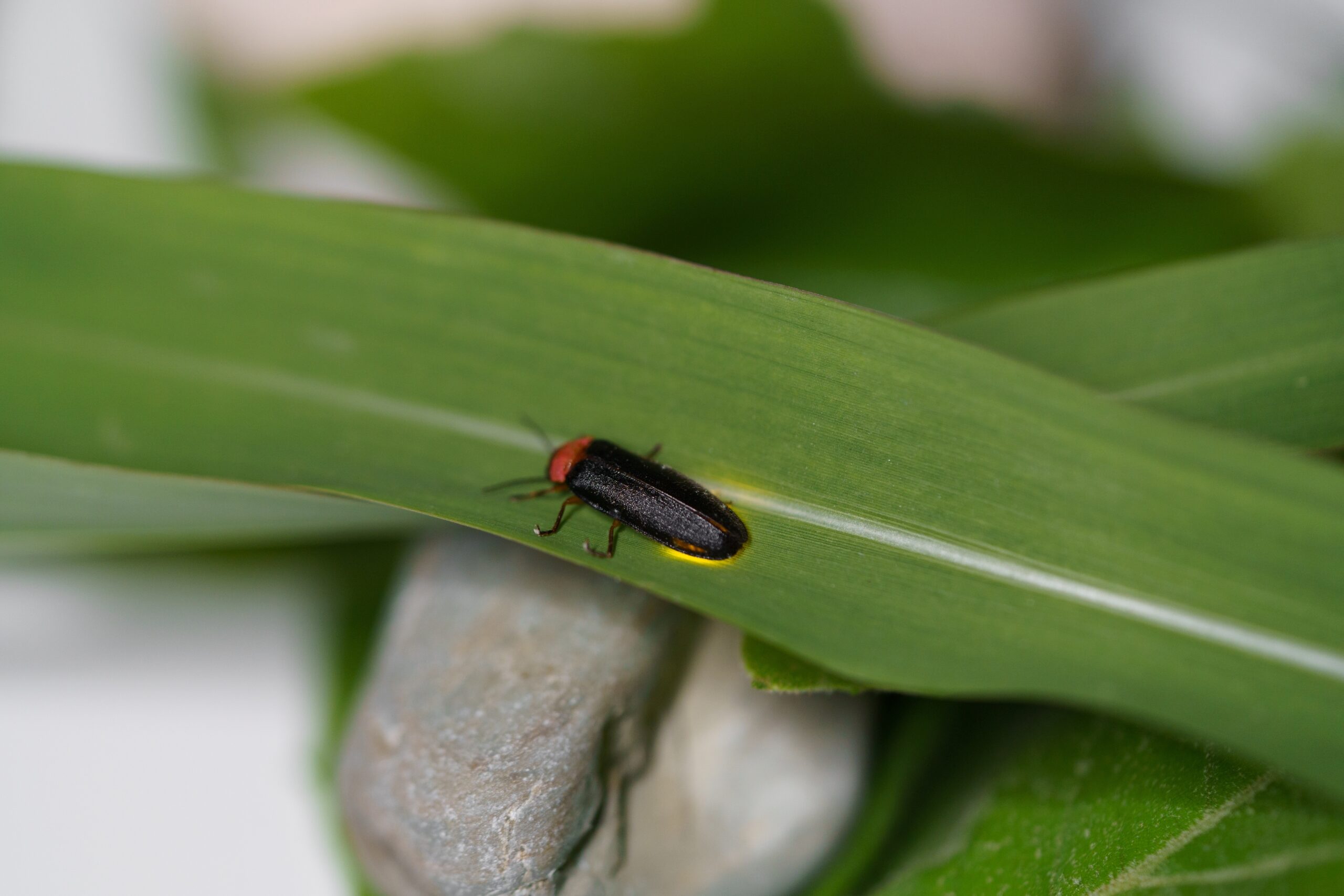

Fireflies, known for their glowing abdomens, play an important role in ecosystems. Their larvae feed on small insects, slugs, and snails, controlling pest populations. Fireflies also contribute to nutrient cycling by decomposing organic matter. Their bioluminescent glow helps them attract mates and is a sign of healthy habitats. Fireflies are indicators of a balanced and thriving ecosystem.
Aphid
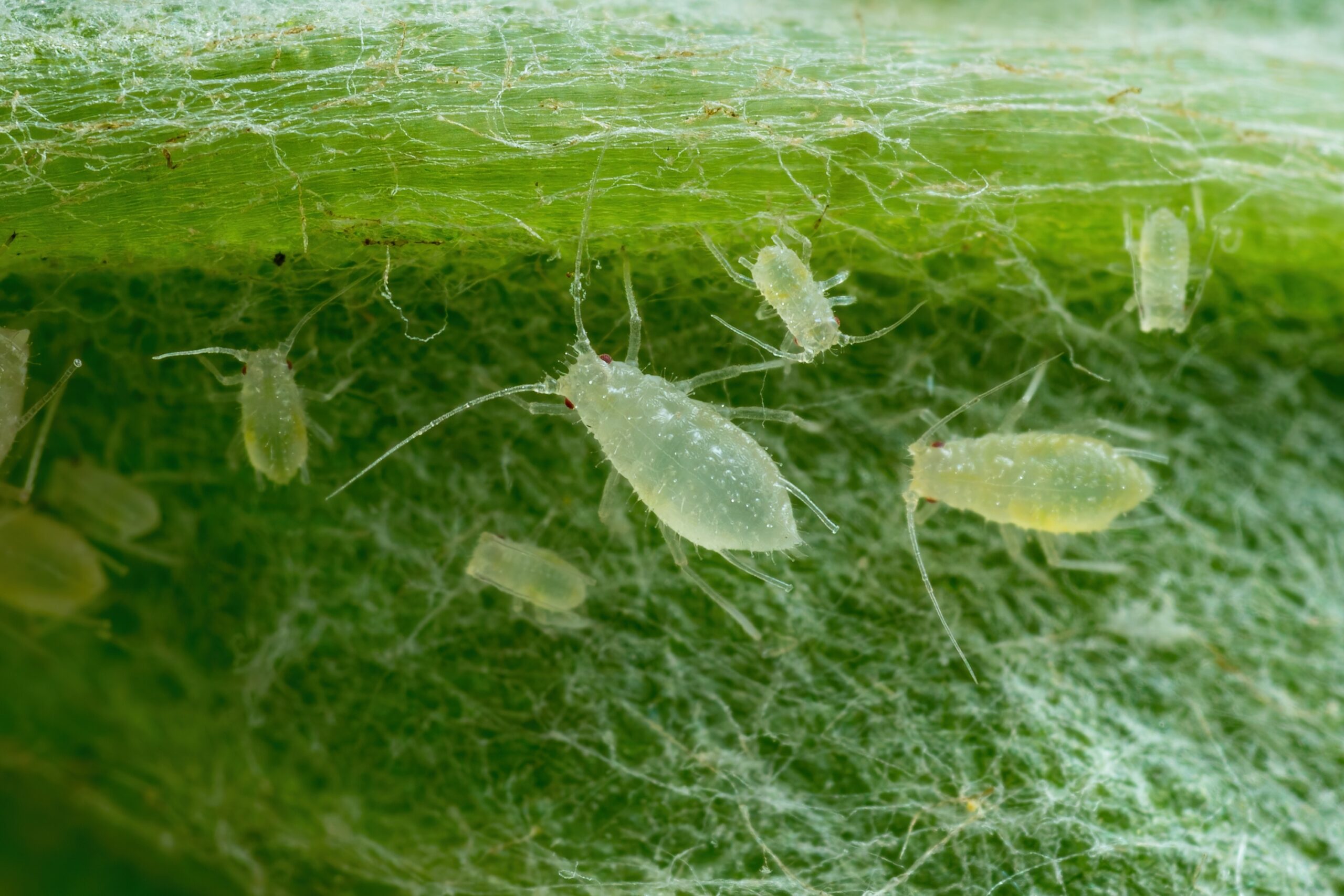

Aphids may be small, but they have a big impact on ecosystems. These tiny insects feed on plant sap, often causing damage to crops. However, they are also a vital food source for many predators like ladybugs and lacewings. Their presence helps support the natural balance between predators and prey. Aphids also assist in nutrient cycling by releasing honeydew, which nourishes fungi and bacteria.
Cicada
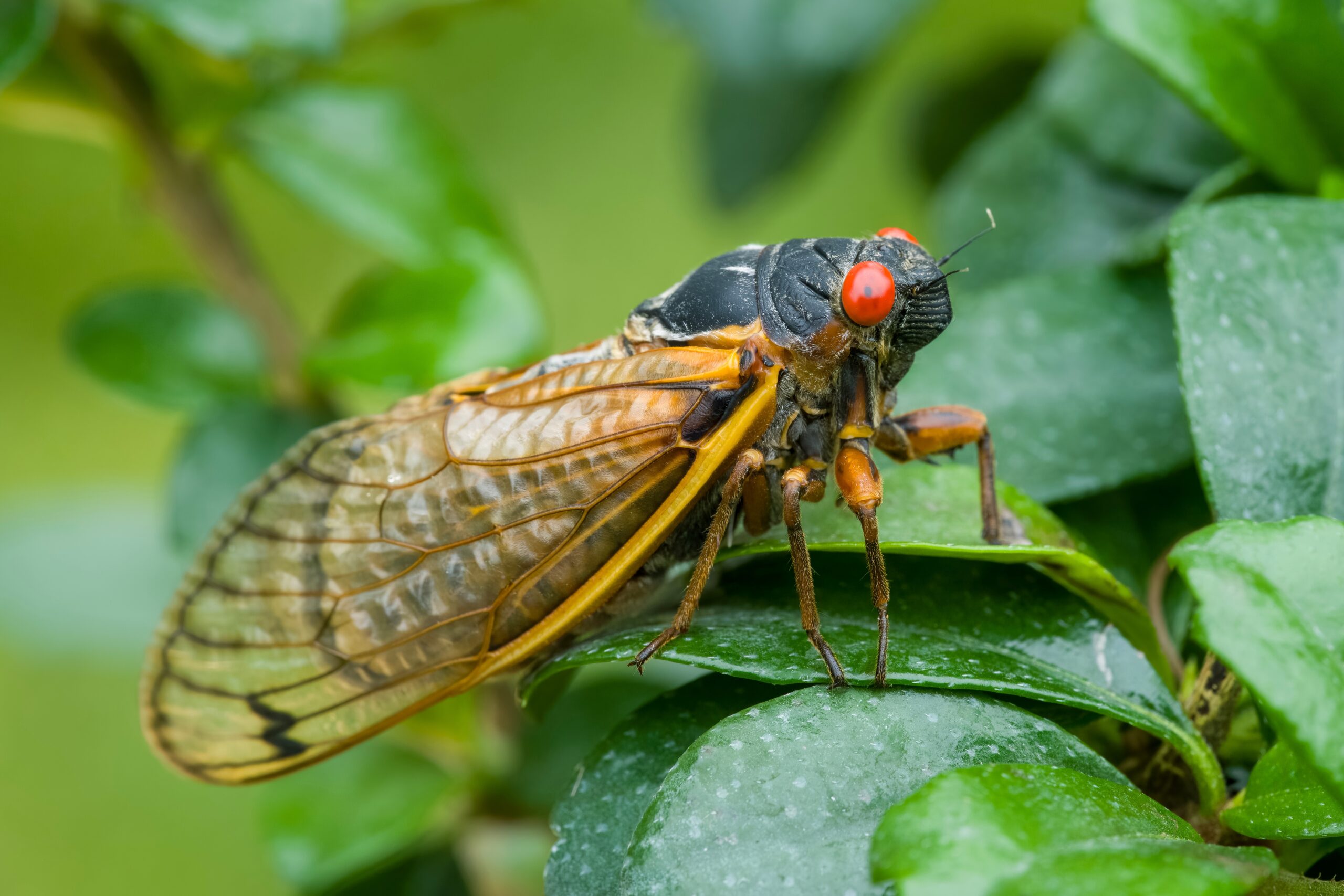

Cicadas are famous for their loud, buzzing calls during the summer months. They spend most of their lives underground, feeding on tree roots before emerging in large numbers to reproduce. Cicadas play an important role in aerating the soil through their burrowing activities. After they die, their bodies decompose, enriching the soil with nutrients. Their large numbers provide a feast for predators like birds and mammals.
Grasshopper
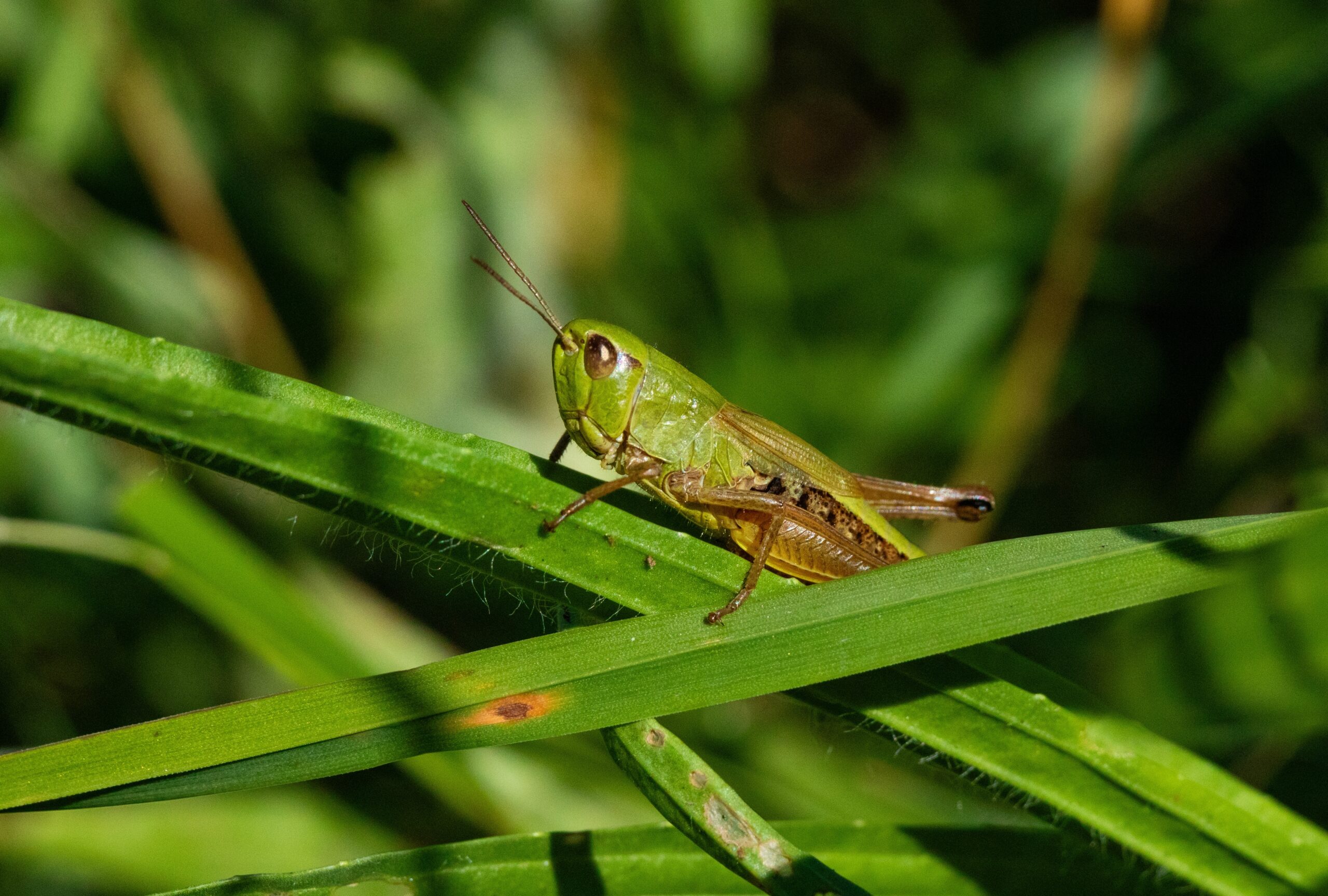

Grasshoppers are important herbivores in many ecosystems. They feed on grasses and other plants, helping to regulate plant growth. By consuming vegetation, grasshoppers promote biodiversity by preventing any single plant species from dominating. Their presence also supports a variety of predators, including birds and small mammals. Grasshoppers contribute to nutrient cycling through their waste, enriching the soil.
Silk Moth
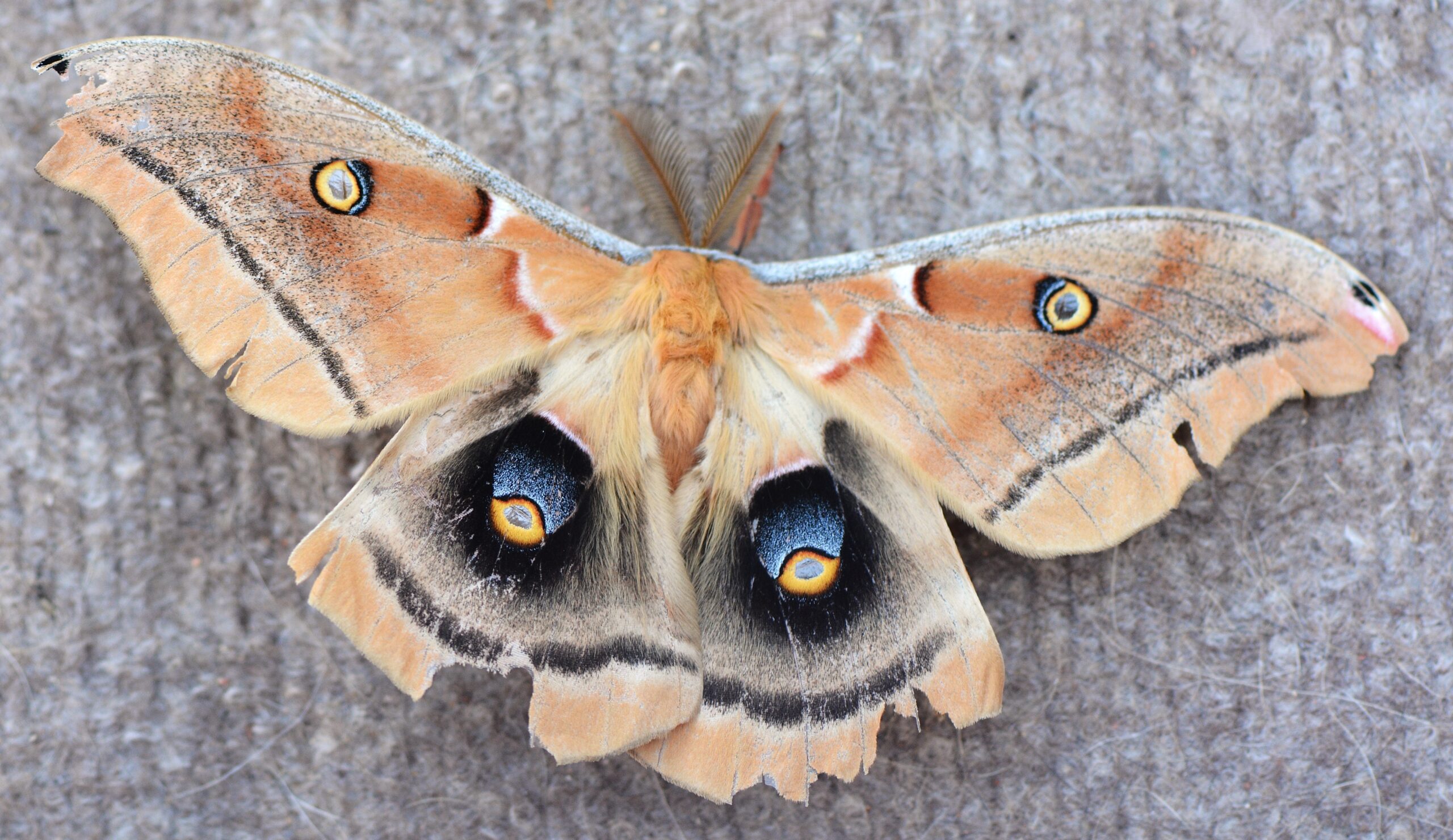

Silk moths are best known for producing silk, but their role in nature is just as significant. The larvae, or caterpillars, of silk moths feed on leaves, helping control plant growth. After pupating, they emerge as adult moths, contributing to pollination in certain species. Silk moths are also a food source for many predators, playing a role in maintaining balance in ecosystems.
Soldier Fly
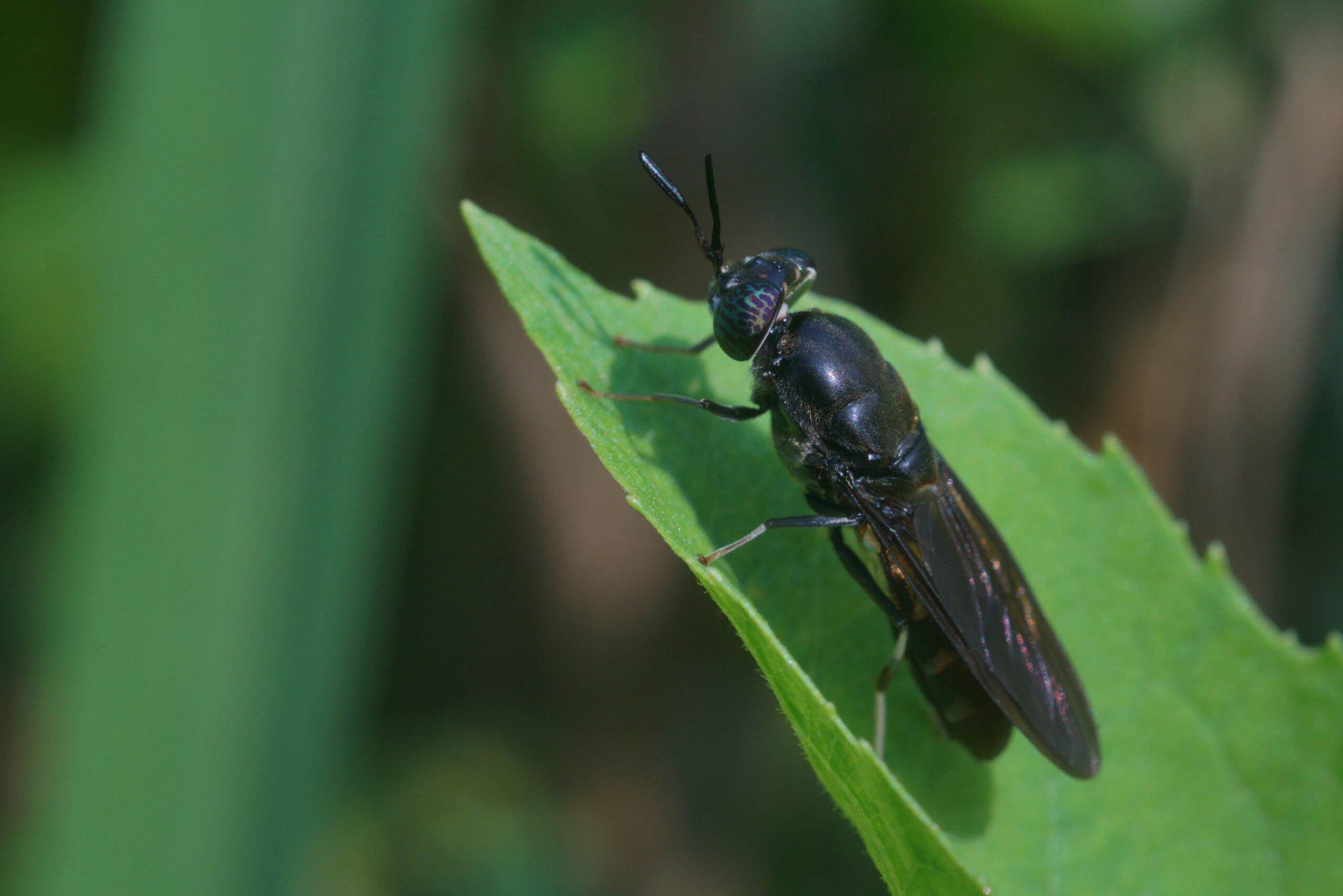

Soldier flies are crucial in recycling organic matter, particularly in composting systems. Their larvae feed on decaying plants and animals, helping to break down waste. Soldier flies improve soil health by turning organic matter into nutrient-rich compost. They also serve as food for many birds, reptiles, and other predators. Soldier flies help speed up the decomposition process in many ecosystems.
Lacewing
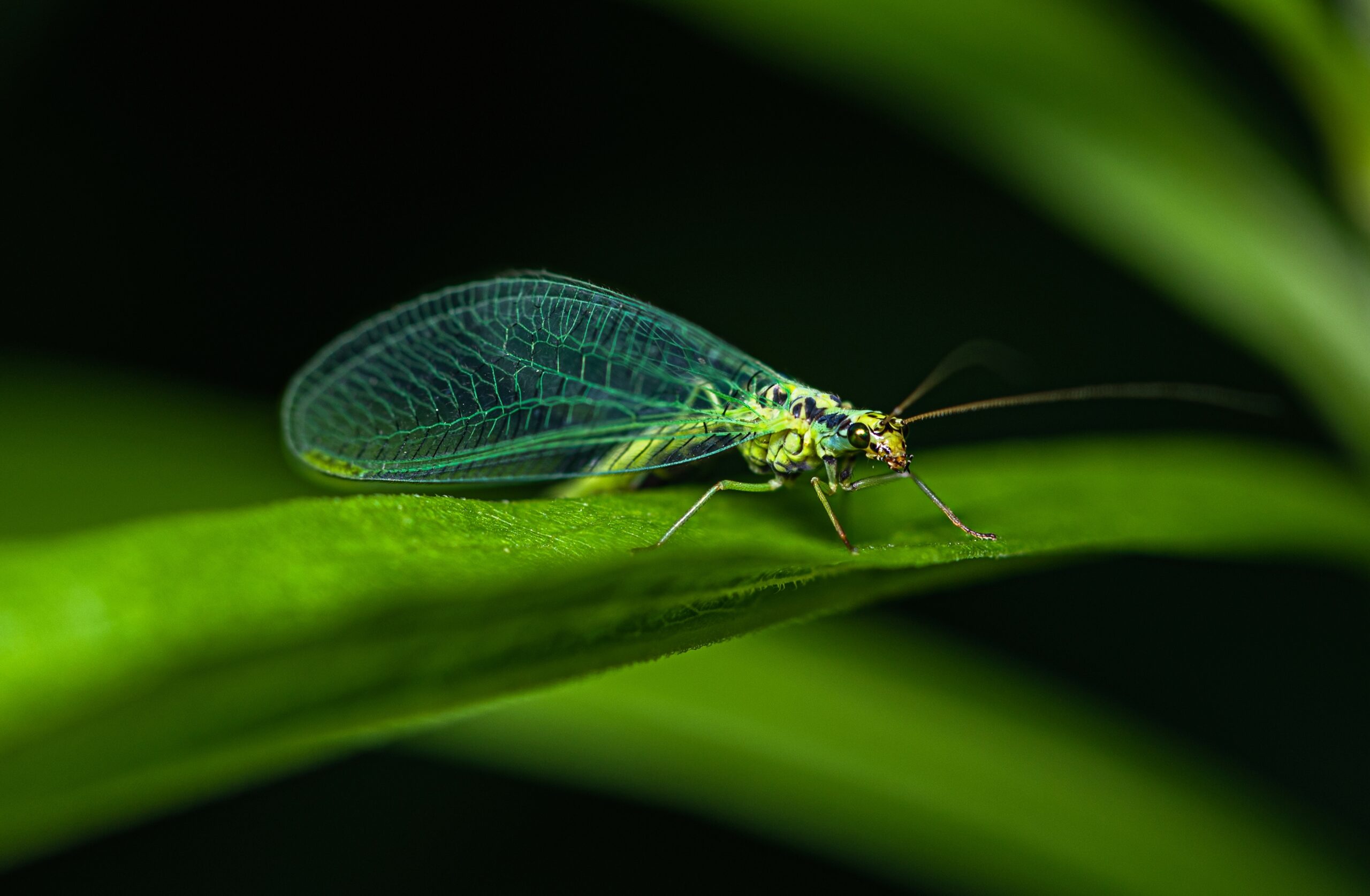

Lacewings are valuable predators in the insect world, especially as larvae. They feed on aphids, mites, and other harmful pests, making them natural pest controllers in gardens and crops. Adult lacewings contribute to pollination as they feed on nectar and pollen. Lacewings play a key role in keeping pest populations in check, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Their presence supports healthy plant growth and biodiversity.
Stink Bug
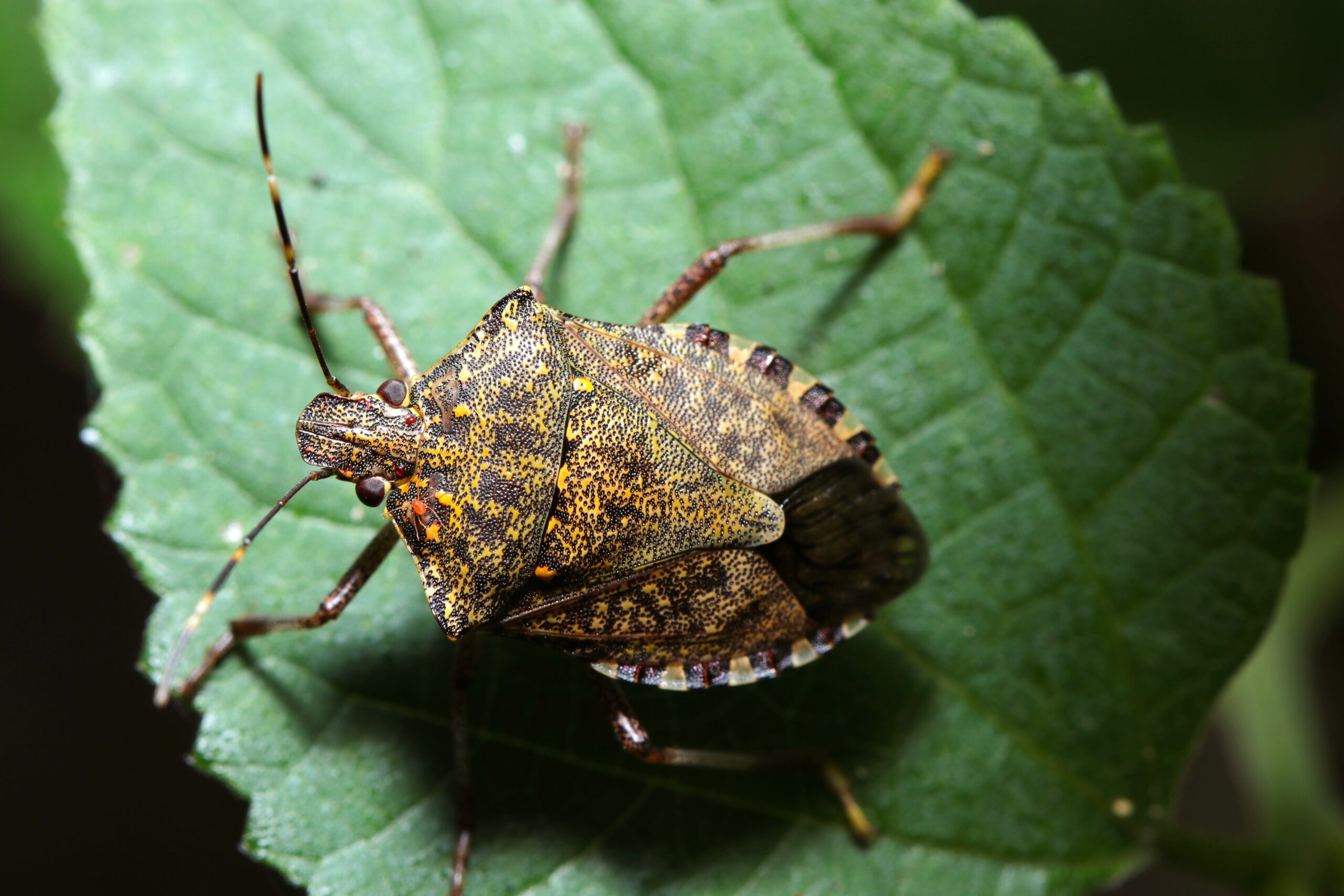

Stink bugs are often seen as pests, but they also have beneficial roles in ecosystems. Some species of stink bugs are predators that feed on harmful insects, helping control pest populations. They are also a food source for birds, spiders, and other predators. Stink bugs contribute to nutrient cycling by feeding on plant material and releasing it back into the soil. Their ability to adapt to various environments makes them a resilient part of many ecosystems.
Mosquito
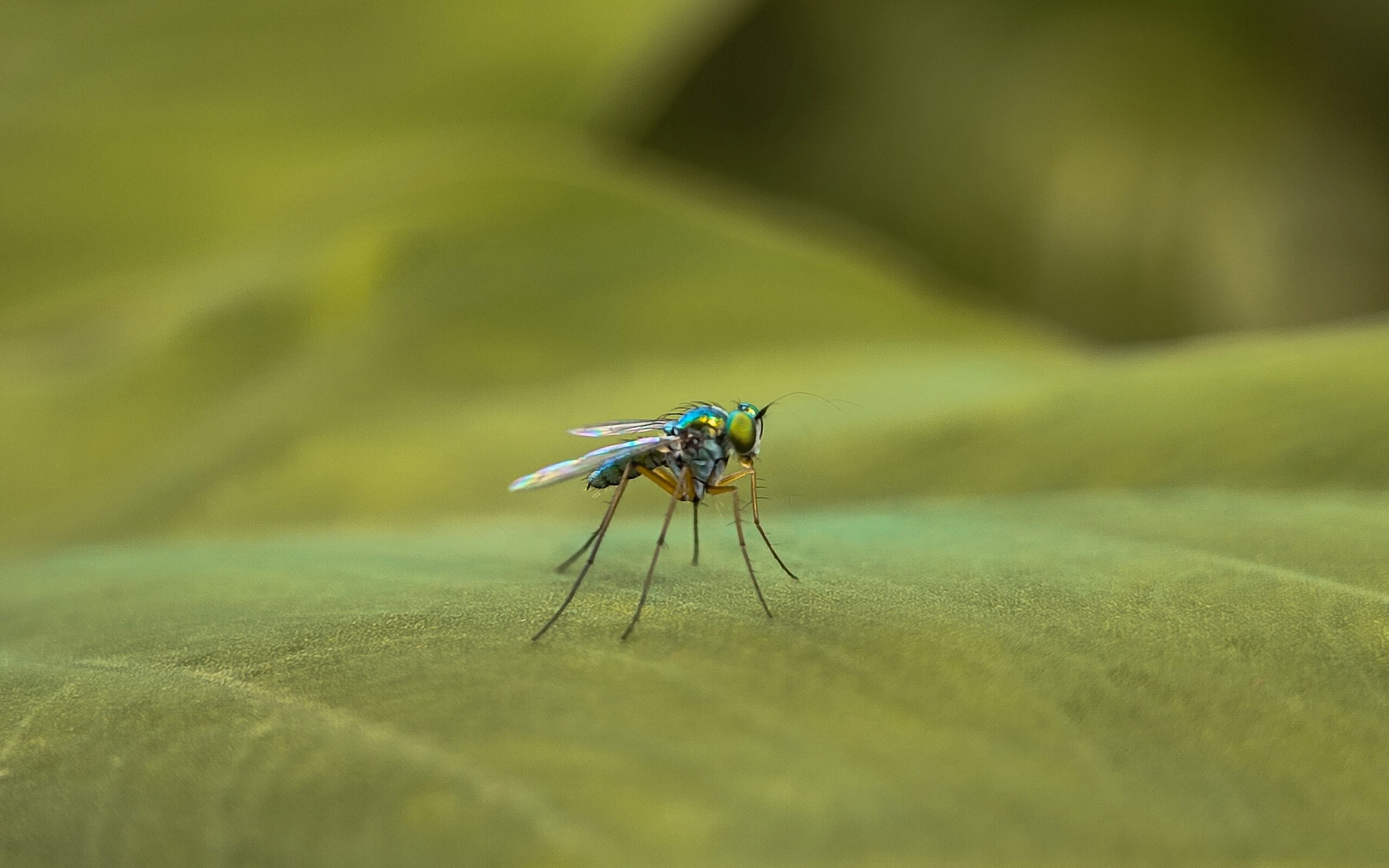

Mosquitoes are often seen as pests, but they play an important role in ecosystems. Male mosquitoes feed on nectar, aiding in pollination for many plant species. Mosquito larvae also help filter water by feeding on organic matter in aquatic habitats. They provide a key food source for fish, birds, and amphibians. Although mosquitoes are known for spreading diseases, their ecological contributions are significant.
Hoverfly
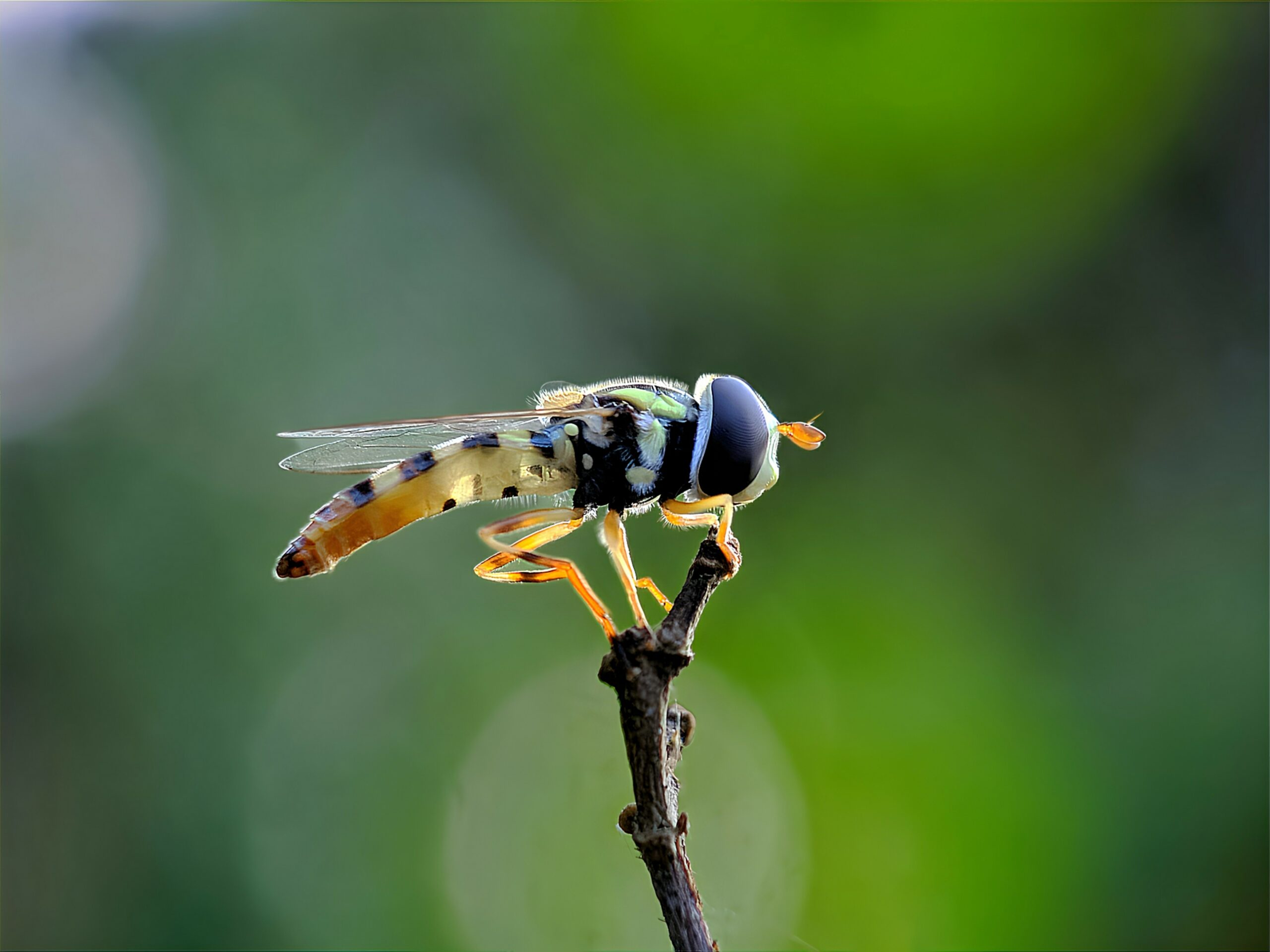

Hoverflies are remarkable for their role in both pollination and pest control. Their appearance resembles bees, making them effective pollinators for flowers and crops. As larvae, they feed on aphids and other pests, reducing the need for chemical pesticides. Hoverflies help maintain healthy plant populations by transferring pollen between flowers. Their dual role makes them a valuable part of many ecosystems.
Earwig
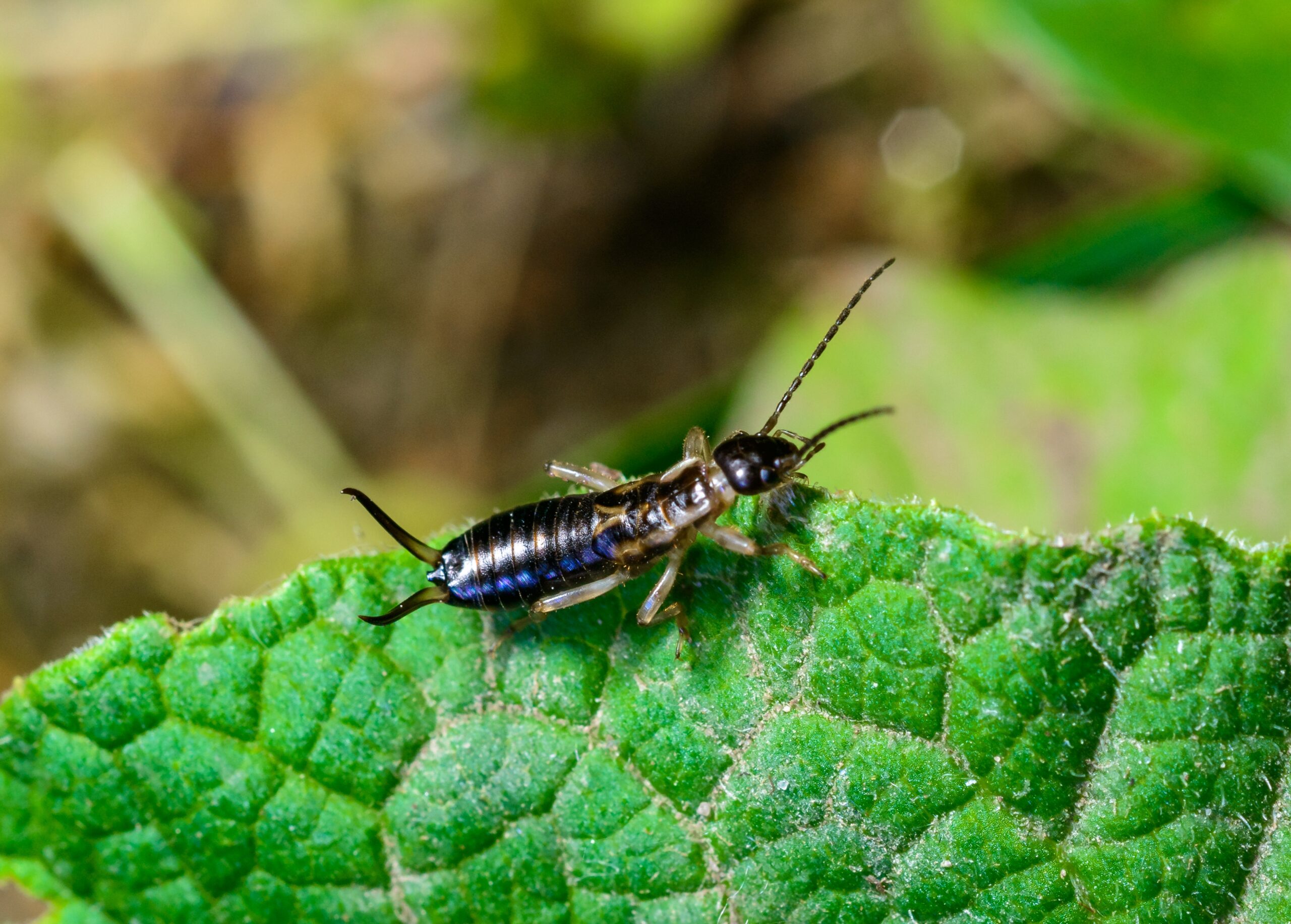

Earwigs are small insects with long, flat bodies and pincers at the end of their abdomen. They thrive in moist environments and are commonly found in gardens and under logs. Earwigs feed on decaying plant material, helping to break down organic matter. Their diet also includes other insects, making them useful in pest control. Despite their intimidating appearance, earwigs play a beneficial role in maintaining healthy ecosystems.
Hornet
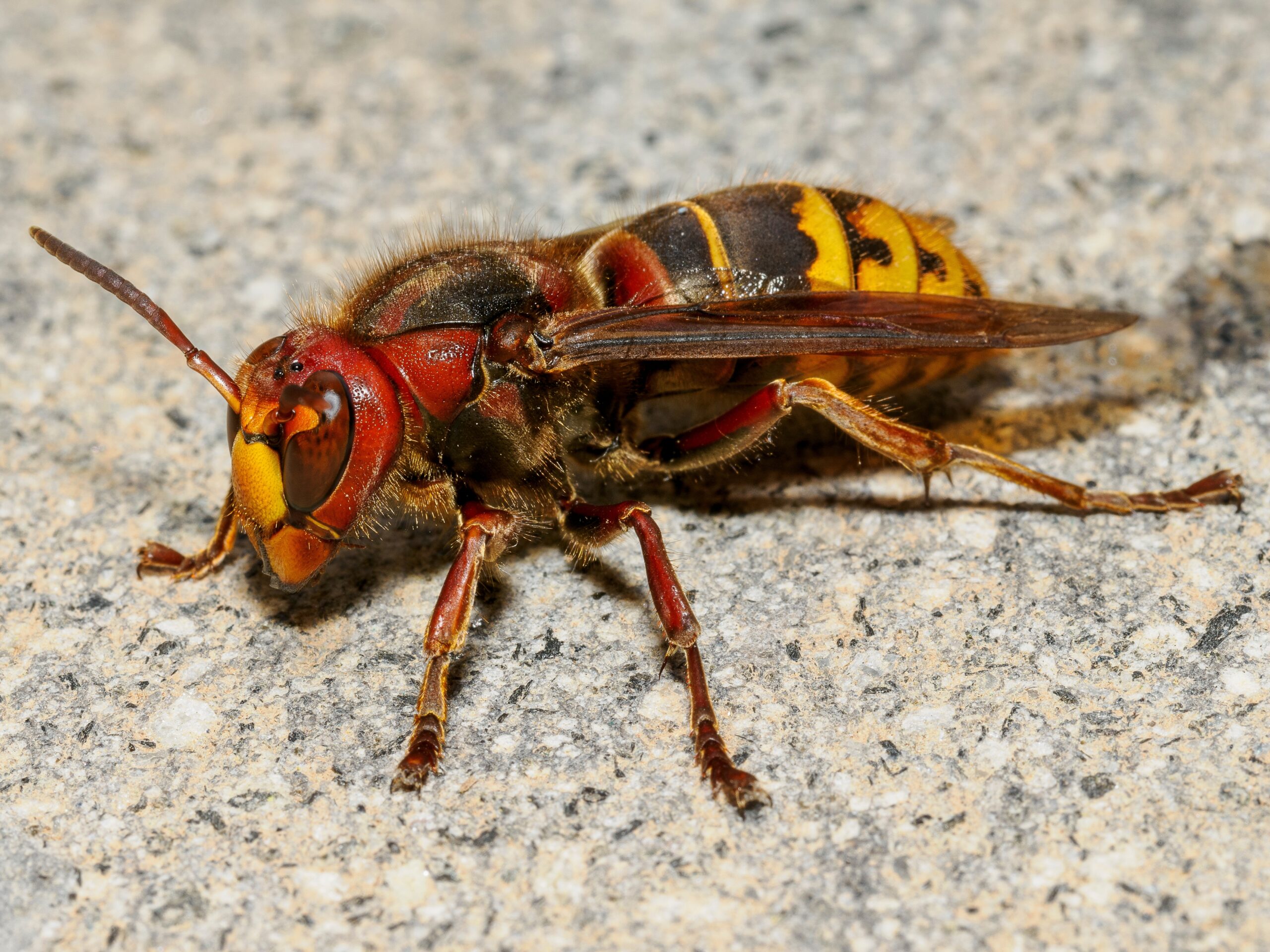

Hornets are large, social wasps known for their aggressive behavior. They build paper-like nests, often high in trees or on structures. Hornets prey on other insects, acting as natural pest controllers. Their strong mandibles allow them to catch and kill a variety of bugs, reducing populations of harmful pests. While they can be dangerous to humans, hornets contribute significantly to maintaining the balance of insect populations in their habitats.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More from Rarest.org
19 Fog-Covered Forests with an Air of Mystery

Fog-shrouded forests have a way of transforming even the most ordinary landscapes into places of mystery and enchantment. Read More.
1962 Jefferson Nickel Value Guide
The 1962 Jefferson nickel is made of 75% copper and 25% nickel. Although, there was a time when nickel was made of 56% copper, 35% silver, and 9% manganese. Read More.
1958 Lincoln Penny Value Guide

The 1958 Lincoln penny comprises 95% copper and 5% tin and zinc. The same composition is used for pennies struck from 1909 to 1942 and 1944 to 1982. Read More.
