Smartphones have transformed the way we live, work, and connect, evolving into powerful tools that redefine technology with every innovation. Over the years, certain devices have stood out, setting new standards and pushing boundaries in design, performance, and functionality. From introducing revolutionary operating systems to changing how we interact with our phones, these game-changing devices have shaped the industry and our daily lives. This article explores iconic smartphones that left an indelible mark on technology, highlighting the unique features and breakthroughs they brought to the market.
Apple iPhone (2007)

In 2007, Apple unveiled the original iPhone, a device that revolutionized the smartphone industry by integrating a phone, iPod, and internet communicator into a single, sleek package. Its capacitive touchscreen eliminated the need for physical keyboards, introducing multi-touch gestures that made navigation intuitive and user-friendly. Its operating system, iOS, provided a robust platform for developers, leading to the creation of the App Store in 2008, which transformed how users accessed and utilized mobile applications. This device set a new standard for mobile design and functionality, influencing countless subsequent models across the industry. Its success also propelled Apple to become one of the world’s most valuable companies. Its introduction marked a significant shift from hardware-centric to software-centric mobile devices, emphasizing user experience and ecosystem integration. The original iPhone sold over 6 million units before being succeeded by the iPhone 3G in 2008.
HTC Dream / T-Mobile G1 (2008)
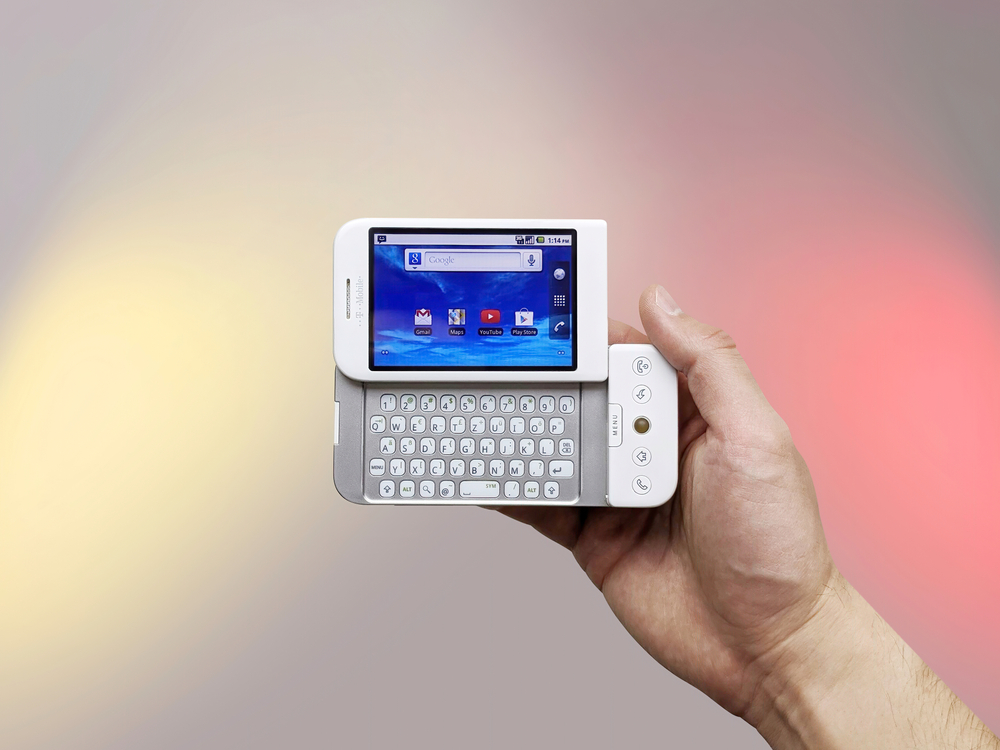

Released in 2008, the HTC Dream, also known as the T-Mobile G1, was the first smartphone to run Google’s Android operating system. This device featured a slide-out physical keyboard combined with a touchscreen interface, catering to users transitioning from traditional phones. The open-source nature of Android encouraged a diverse range of applications and customization options, fostering a competitive ecosystem that challenged existing platforms. Its integration of Google services like Gmail and Maps showcased the potential of cloud-based mobile experiences. Its launch marked the beginning of Android’s rise to become one of the dominant mobile operating systems globally. Its hardware included a 3.2-inch display and a 3.2-megapixel camera, features that were competitive at the time. It laid the foundation for the vast array of Android smartphones available today.
Motorola Droid (2009)

Motorola’s Droid, released in 2009, was pivotal in popularizing Android in the U.S. market. It featured a large capacitive touchscreen and a slide-out QWERTY keyboard, appealing to both touchscreen enthusiasts and those preferring physical keys. It was among the first to run Android 2.0, introducing features like turn-by-turn navigation via Google Maps, which was a significant advancement at the time. Its robust hardware and extensive app support provided a compelling alternative to the iPhone, contributing to the rapid adoption of Android devices. Its marketing campaign emphasized its capabilities over competitors, highlighting features such as multitasking and customizable home screens. Its success helped establish Motorola as a key player in the smartphone market during that period. Its influence extended beyond its hardware, as it played a role in shaping the Android ecosystem’s growth.
Samsung Galaxy S (2010)
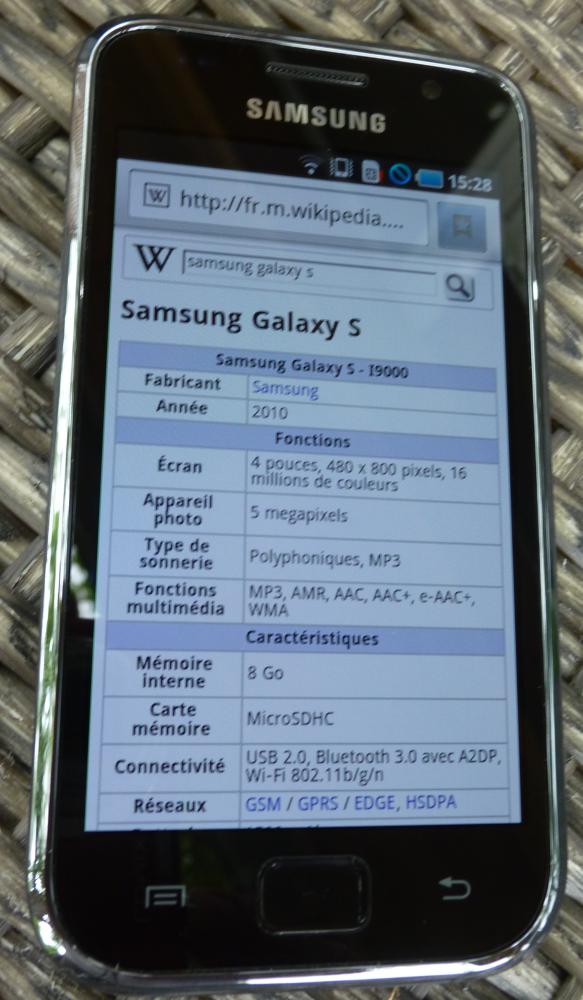
The Samsung Galaxy S, launched in 2010, marked Samsung’s significant entry into the high-end smartphone market. It featured a Super AMOLED display, offering vibrant colors and deep blacks, setting a new standard for screen quality. Running Android, it provided users with extensive customization options and access to a growing app ecosystem. Its success led to the development of the Galaxy S series, which has become one of the best-selling smartphone lines globally. Its design emphasized slimness and lightweight construction, appealing to a broad audience. Samsung’s focus on hardware innovation, such as integrating high-quality cameras and powerful processors, began with this model. Its impact is evident in Samsung’s continued dominance in the smartphone industry.
Nokia N95 (2007)
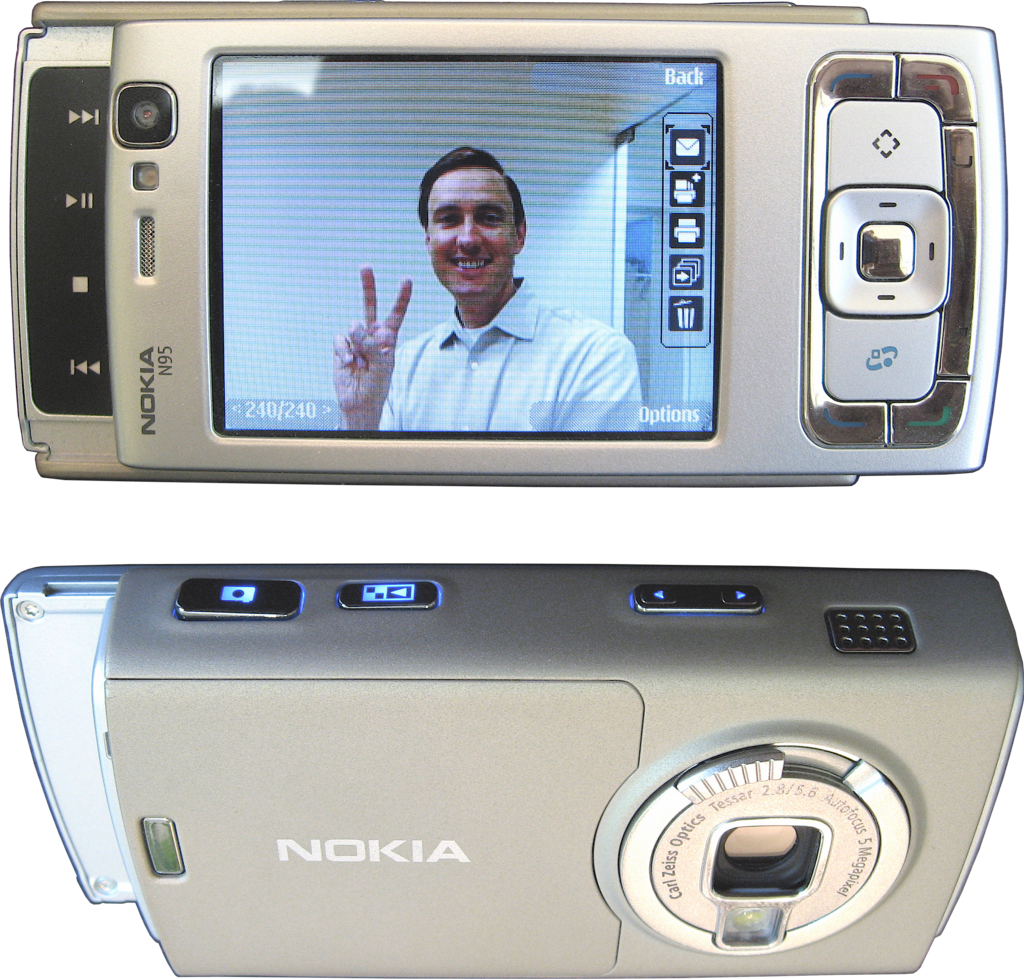

Released in 2007, the Nokia N95 was a feature-rich smartphone that combined multimedia capabilities with robust hardware. It featured a 5-megapixel camera with Carl Zeiss optics, GPS navigation, and a dual-slider design that revealed media playback controls or a numeric keypad. It ran on the Symbian operating system, offering multitasking and a range of applications for productivity and entertainment. Its ability to connect to 3G networks provided faster internet access, enhancing the mobile browsing experience. Its success demonstrated the demand for smartphones that could serve as all-in-one devices for communication, media consumption, and navigation. Its design and functionality influenced future smartphone developments, particularly in integrating high-quality cameras and GPS features. It remains a notable example of Nokia’s innovation during its peak years in the mobile industry.
BlackBerry Curve 8300 Series (2007)
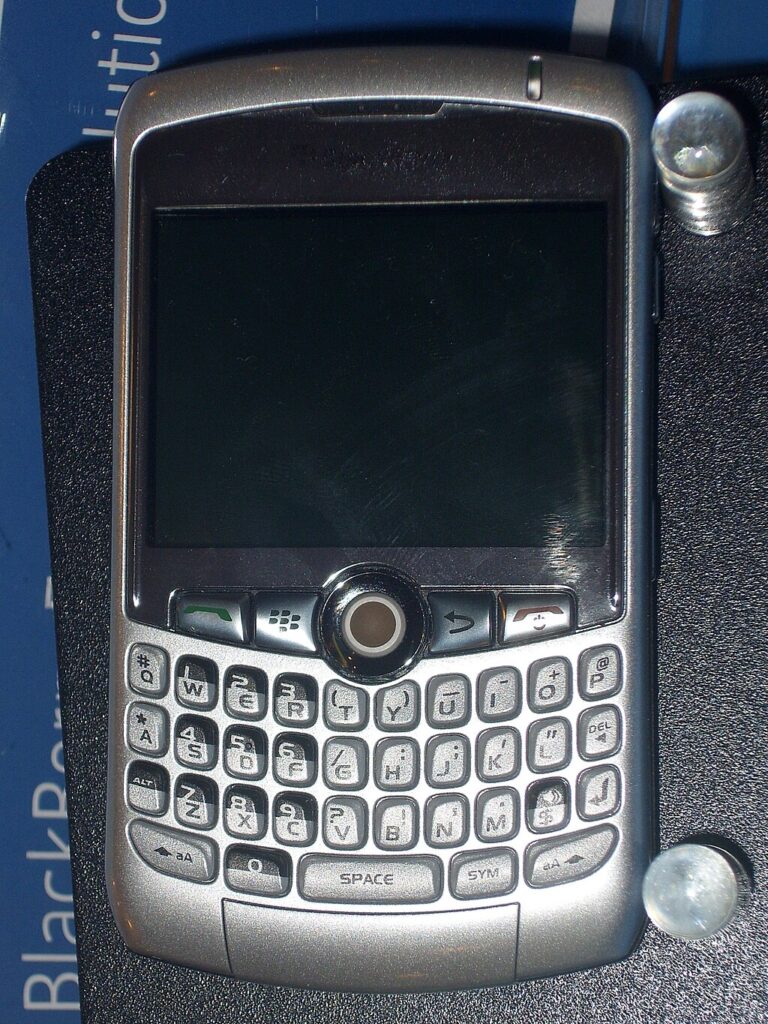

The BlackBerry Curve 8300 series, introduced in 2007, was instrumental in bringing BlackBerry’s email-centric smartphones to a broader consumer market. It featured a full QWERTY keyboard, a 2-megapixel camera, and multimedia capabilities, appealing to both business users and general consumers. Its integration of push email services made it a popular choice for professionals needing real-time communication. Its user-friendly interface and robust security features set it apart from competitors at the time. The success of the Curve series helped solidify BlackBerry’s position in the smartphone market during the late 2000s. However, the rise of touchscreen smartphones eventually led to a decline in BlackBerry’s market share. The Curve 8300 series remains a significant part of BlackBerry’s legacy in mobile communication.
Palm Pre (2009)
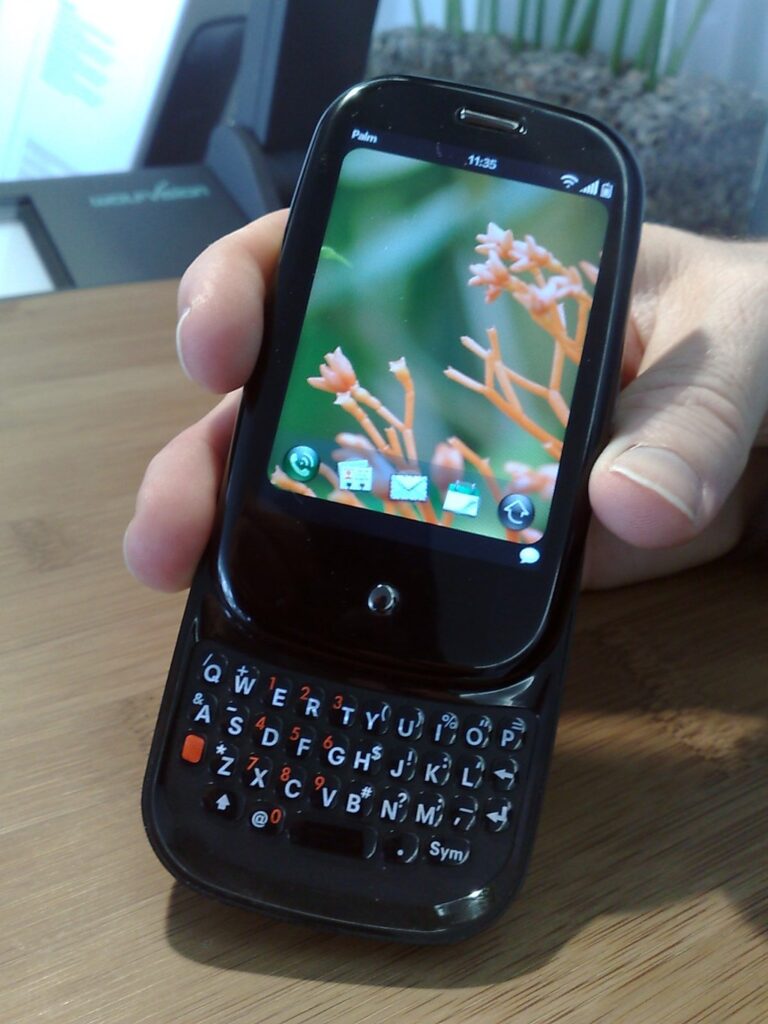

The Palm Pre, launched in 2009, introduced the webOS operating system, which featured a card-based multitasking interface that allowed users to manage multiple applications seamlessly. Its design included a 3.1-inch touchscreen and a slide-out QWERTY keyboard, catering to users who preferred physical keys. Its gesture-based navigation and Synergy feature, which integrated information from various sources into unified views, were ahead of their time. Despite its innovative features, it struggled to gain significant market share due to limited app support and intense competition. However, webOS’s design principles influenced future mobile operating systems, particularly in multitasking and gesture navigation.
LG Nexus 5 (2013)
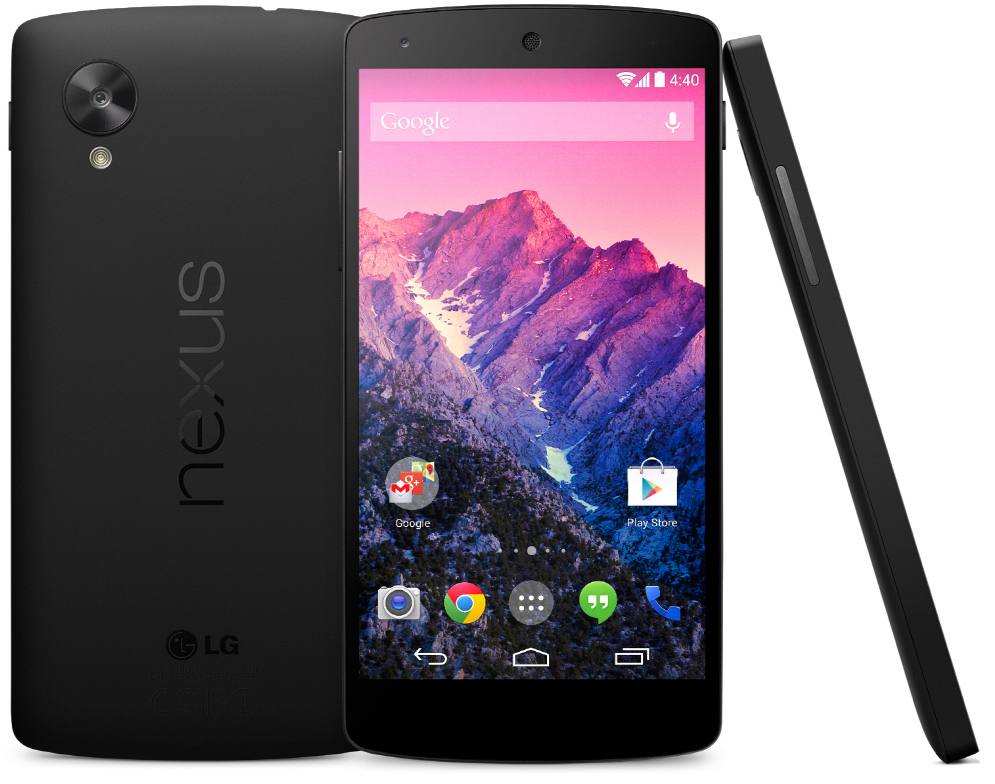

The LG Nexus 5, launched in 2013 as part of Google’s Nexus program, was a smartphone that combined cutting-edge technology with an affordable price. It ran pure Android 4.4 KitKat, offering users a clean, bloatware-free experience with regular software updates directly from Google. Its 4.95-inch full HD display provided sharp visuals, making it ideal for media consumption. It was powered by a Snapdragon 800 processor and 2GB of RAM, delivering excellent performance for its time. One of its key innovations was its integration with Google’s ecosystem, featuring advanced Google Now functionality and seamless cloud synchronization. Despite being a high-performance device, its pricing disrupted the market by making premium features accessible to more users. It remains one of the most beloved smartphones among Android enthusiasts for its balance of affordability and quality.
Sony Xperia Z (2013)
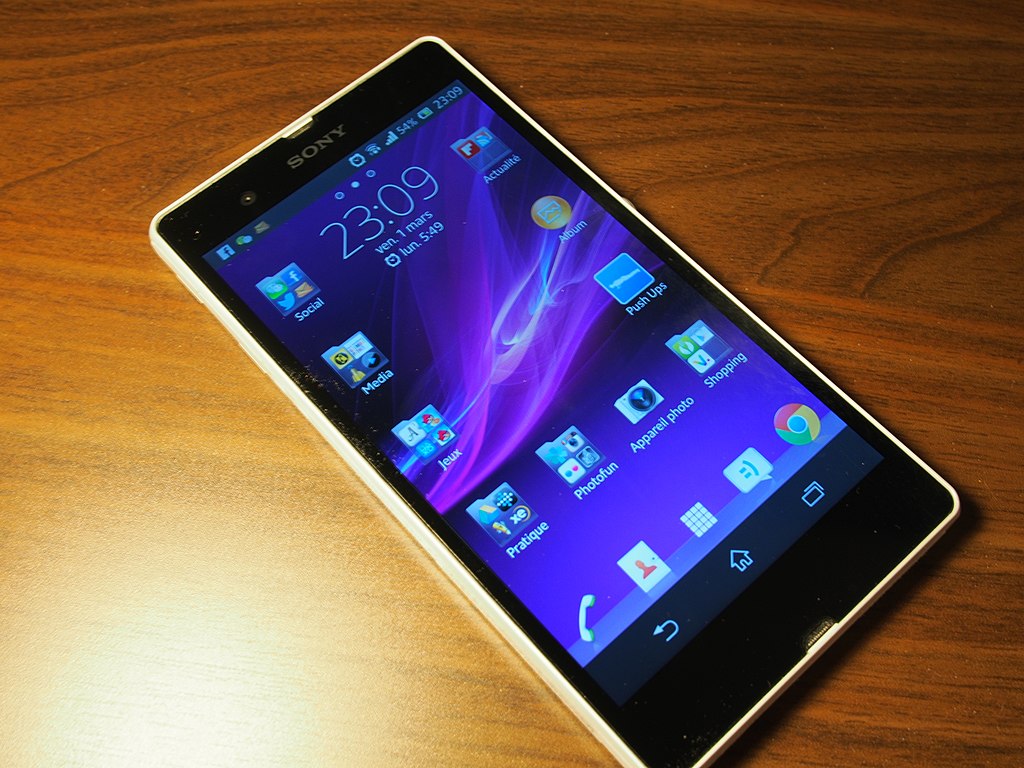

Sony’s Xperia Z, introduced in 2013, was a trailblazer for water-resistant smartphones, bringing durability to the forefront without compromising on style. Featuring an IP55/57 rating, it could withstand immersion in water, a feature that was rare at the time. Its sleek glass-and-aluminum design set a new benchmark for premium aesthetics in smartphones. It boasted a 5-inch full HD display, showcasing Sony’s prowess in display technology. It also included a 13-megapixel camera with Exmor RS sensor, which excelled in low-light photography. Powered by a Snapdragon S4 Pro processor and 2GB of RAM, it delivered reliable performance for gaming and multitasking. It laid the foundation for the popular Xperia Z series and brought water resistance into mainstream mobile design. Sony’s emphasis on durability and style made the Xperia Z a standout device.
Huawei P9 (2016)
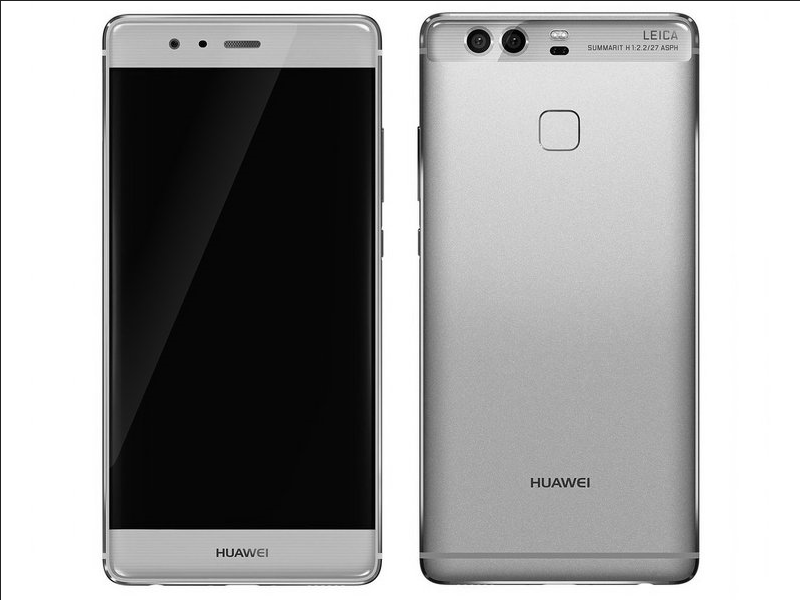

The Huawei P9, launched in 2016, redefined smartphone photography with its dual-camera system co-engineered with Leica. This innovative setup included a 12-megapixel RGB sensor and a 12-megapixel monochrome sensor, allowing users to capture stunning photos with rich detail and depth. Its 5.2-inch full HD display provided crisp visuals, while the Kirin 955 processor ensured smooth performance. Its camera introduced advanced features like wide aperture mode and professional-grade manual controls, appealing to photography enthusiasts. It was also one of the first devices to highlight the potential of AI in photography, enhancing image quality through intelligent processing. Its sleek aluminum design and focus on camera innovation helped Huawei gain significant recognition in the global smartphone market. Its success demonstrated the growing importance of camera technology as a defining feature in smartphones.
OnePlus One (2014)

The OnePlus One, launched in 2014, earned the nickname “flagship killer” for offering top-tier specifications at a fraction of the price of competitors. Running CyanogenMod, a customizable Android-based operating system, it catered to enthusiasts who valued flexibility and control. Its 5.5-inch full HD display, Snapdragon 801 processor, and 3GB of RAM provided flagship-level performance. Its premium design and powerful hardware made it an appealing alternative to higher-priced devices from established brands. Its direct-to-consumer sales model and invite-only purchase system generated significant buzz and exclusivity around the brand. It marked the beginning of OnePlus’s rise as a major player in the smartphone industry. It also set the tone for future devices by emphasizing performance and affordability without compromising on quality.
This article originally appeared on Rarest.org.
More from Rarest.org
10 Endangered Cultural Practices Preserved by Indigenous Tribes

Indigenous tribes around the world hold a wealth of cultural practices that have endured for generations. Many of these traditions are at risk due to modernization, environmental changes, and external pressures. However, tribes continue to preserve these practices, ensuring that their heritage remains alive. Read More.
17 Brilliantly Colored Frogs and Amphibians That Stand Out in Nature

Nature is full of vibrant colors, but few creatures display them as boldly as frogs and amphibians. These animals often use their bright hues for protection, signaling danger to predators or blending into their colorful environments. Read More.
10 Beautifully Preserved Ancient Cities Buried Beneath the Earth

Ancient cities hold mysteries of civilizations long gone, hidden beneath the earth for centuries. These cities, once bustling with life, are now beautifully preserved time capsules of history. Read More.
